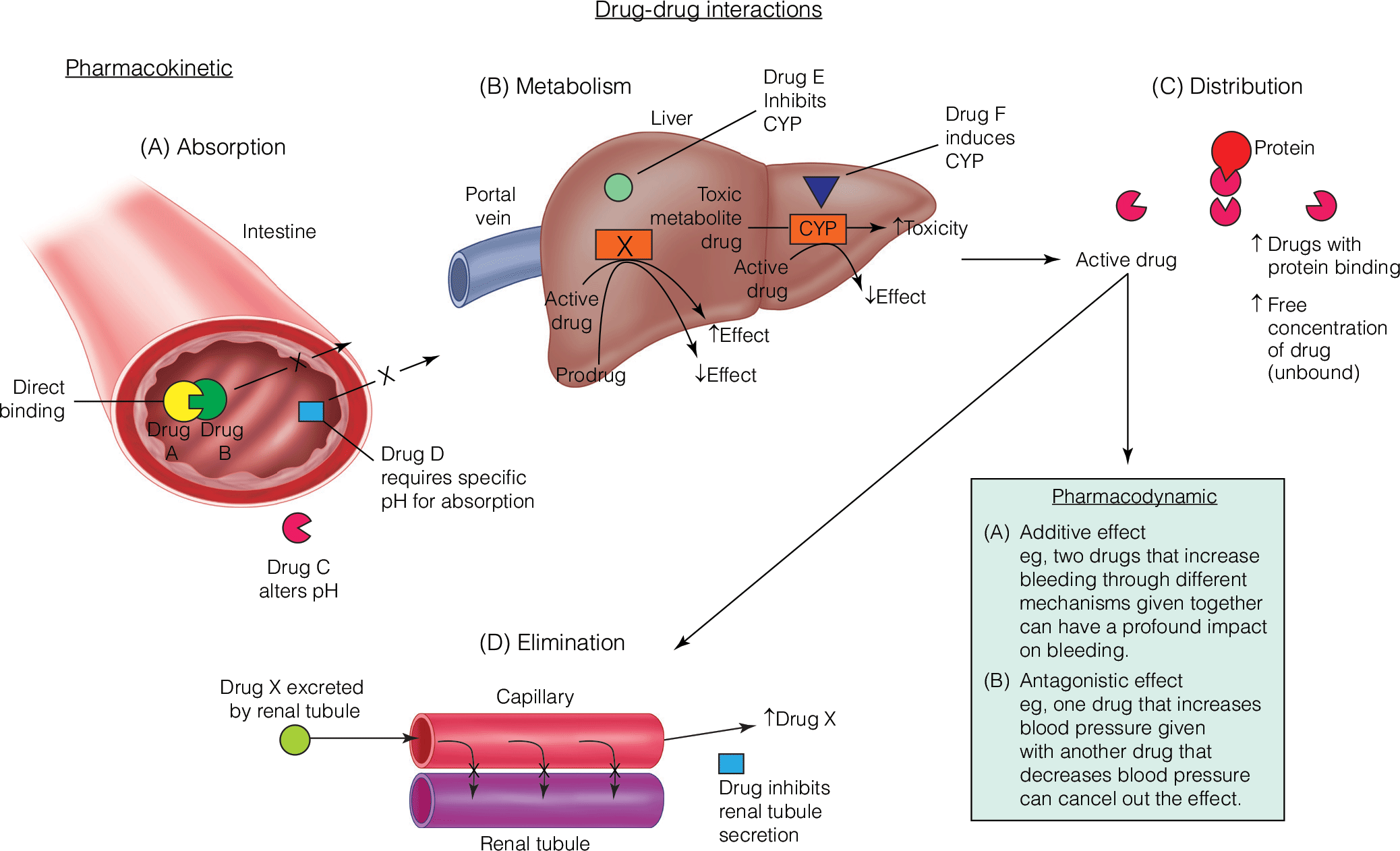
Management of Drug Interactions between Anti-infectives and Common Anesthetics
- Rocuronium-induced neuromuscular blockade is potentiated by a synergistic effect of gentamicin and clindamycin, which may delay recovery.
- Penicillins form a complex with sugammadex, which may interfere with the therapeutically intended sugammadex-rocuronium complex.
- Ondansetron can decrease the analgesic efficacy of acetaminophen at high doses.
- Anesthesiologists are positioned to manage interactions between anesthetic agents and antimicrobials in the operating room.



.png)







