- Early recognition of shock is difficult but essential for preservation of cellular and organ function and survival. The earliest clinical signs are nonspecific, with the initial inflammatory response including tachycardia, fevers, or cool or clammy skin.
- The approach to shock ultimately requires understanding and correcting its etiology (eg, antibiotics and source control for sepsis, thrombectomy after massive pulmonary embolus, hemorrhage control after trauma, and so forth). However, until these are diagnosed and addressed directly, clinicians ultimately have three approaches in their armamentarium: volume expansion, vasopressors, and cardioactive agents.
- The PAC was introduced in 1970. Its use increased over the next 3 decades and eventually was considered the standard of care for most critically ill patients. However, the use of PACs declined rapidly after the results of the randomized, controlled trial published in the New England Journal of Medicine revealing no benefit in high-risk surgical patients.
Latest Updates
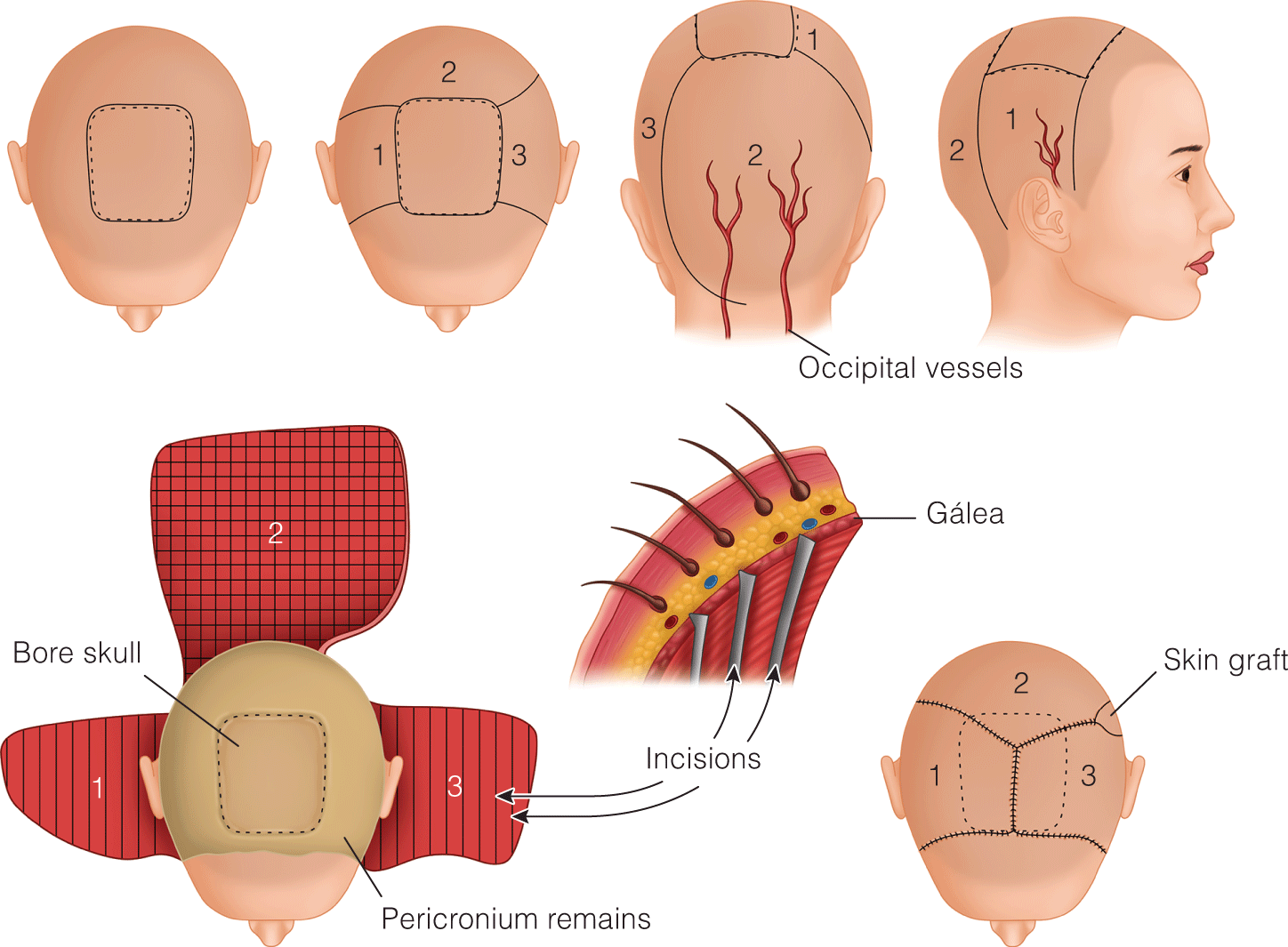
Lip, Cheek, & Scalp Reconstruction
- Indocyanine green based fluorescent imaging to assess vascular perfusion
- Allograft dermal skin regeneration: Acellular dermal regeneration templates
- Microvascular techniques for larger, deeper defects with skin and color matching

Allergic Response
- Radiofrequency ablation as a treatment modality has revolutionized therapy for many SVTs; acts as a first-line alternative to drug therapy in some circumstances, with a high acute success rate and relatively low complication rate.
- Cryoablation therapy emerging as an alternative in ablative therapies. Investigation of this modality for SVTs is ongoing.
- Detailed drug regimens optimized for acute and chronic management of specific SVTs; detailed in the 2015 ACC/AHA/HRS practice guidelines.

Injection Sclerotherapy and Ablation
- Endovenous laser ablation (EVLA) has many similarities to radiofrequency ablation (RFA), with the primary differences related to the catheter and mechanism used to ablate the vein. EVLA uses a bare-tipped or jacket-tipped fiber to deliver laser energy to a target area.
- The thermal energy generates heat and steam bubbles within the lumen of the target vessel, destroying the endothelial lining of the vessel. This causes an inflammatory and constricting reaction that leads to fibrosis and occlusion of the treated vein.
- Of note, the incidence of severe postprocedure pain and bruising has been significantly decreased with the advent of the new-generation covered fibers and hemoglobin-targeted chromophore, such that these adverse events are now comparable to those seen with RFA.

Antisocial Personality Disorder and Its Clinical Management
- Follow-up studies have shown the continuity of antisocial behaviors from childhood through the adult years.
- Research has implicated brain regions that control judgment and impulse control.
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy may be helpful in mild cases.

Epidemiology and Molecular Biology of Colorectal Cancer
- Current data on the epidemiology of colorectal cancer in United States and globally
- Classification and detailed description of the three major molecular pathways for colorectal cancer carcinogenesis
- Modern classification of familial syndromes based on polyp type and description of newly discovered familial colorectal cancer syndromes

Epidemiology and Molecular Biology of Colorectal Cancer
- Current data on the epidemiology of colorectal cancer in United States and globally
- Classification and detailed description of the three major molecular pathways for colorectal cancer carcinogenesis
- Modern classification of familial syndromes based on polyp type and description of newly discovered familial colorectal cancer syndromes

- With heightened awareness of side effects associated with narcotics, there has been increased frequency of multimodal pain management for the management and reduction of postoperative pain, including intra-operative local anesthetic and postoperative nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents.
- Current and future research that focuses on patient reported outcomes, using validated measures such as BREAST-Q, will further allow the evaluation of patient satisfaction and continue to improve the counseling and management plastic surgeons can provide reduction mammaplasty patients.
- The use of acellular dermal matrix (ADM) “slings” as a soft tissue substitute can offer additional support for natural tissue and might offer beneficial results for larger, ptotic breasts.


.png)







