Initial Management of Life-Threatening Trauma
- Initial volume resuscitation should commence with 1 L isotonic crystalloid solution followed by blood products at 1:1:1 ratio (1 unit packed red blood cells to 1 unit fresh frozen plasma to 1 unit platelets) if the patient is not responsive to the initial fluid bolus.
- In patients with massive hemorrhage or evidence of fibrinolysis, tranexamic acid has demonstrated improved survival if administered within 3 hours of injury.
- Use of resuscitative endovascular balloon occlusion of the aorta may be an important adjunct in the control of life-threatening abdominal or pelvic hemorrhage.
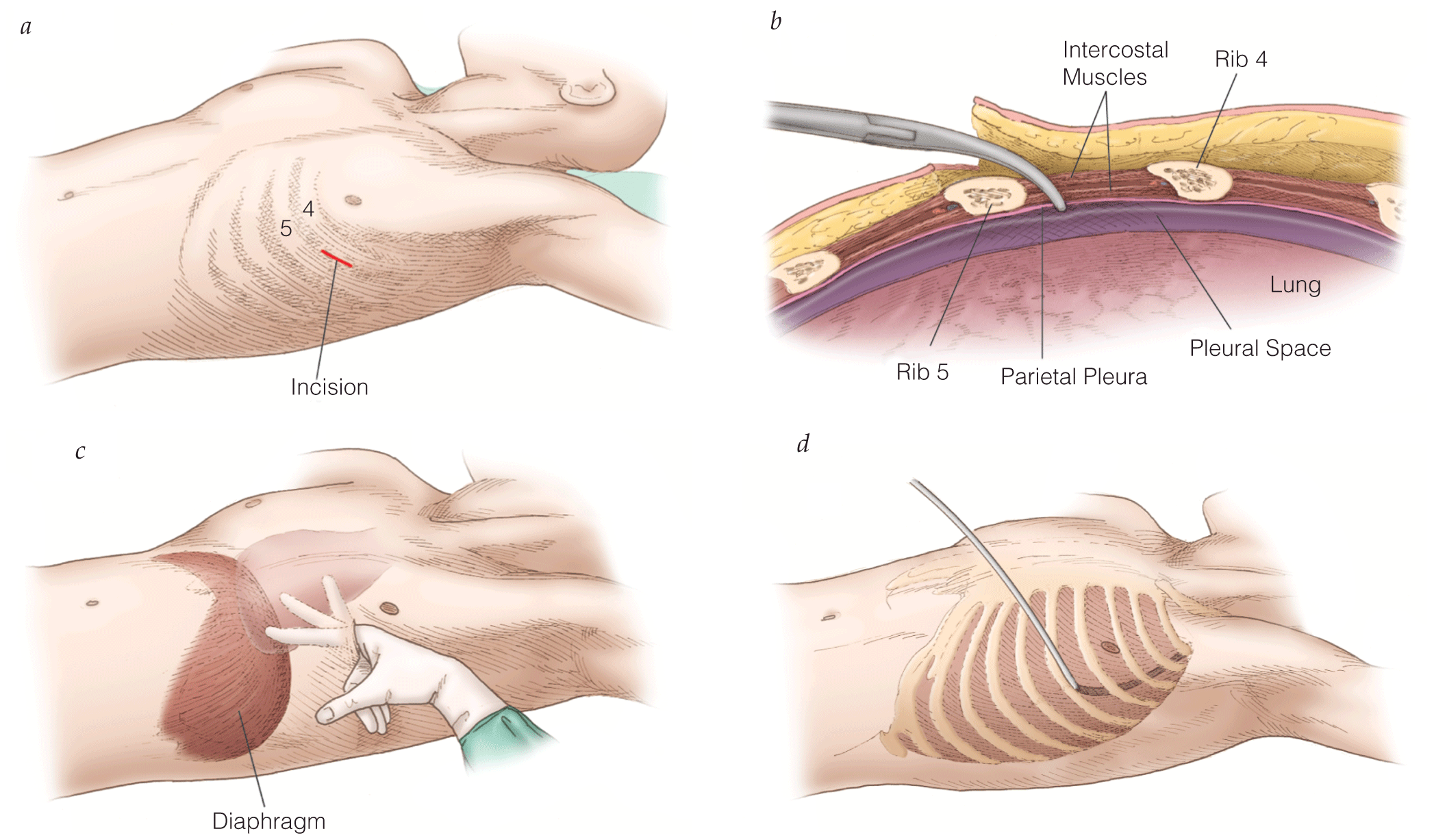
- In cases of external hemorrhage of an extremity, a tourniquet should be used to control bleeding.




.png)







