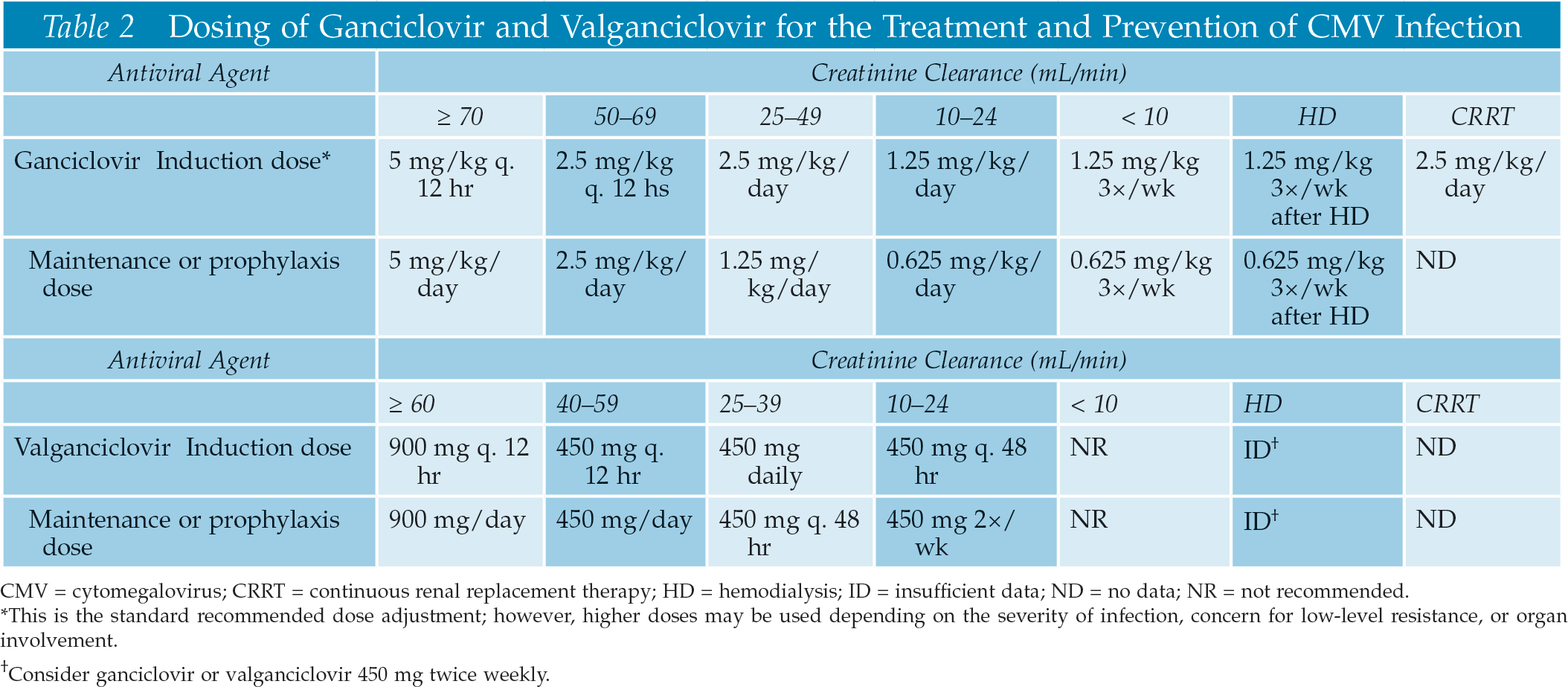
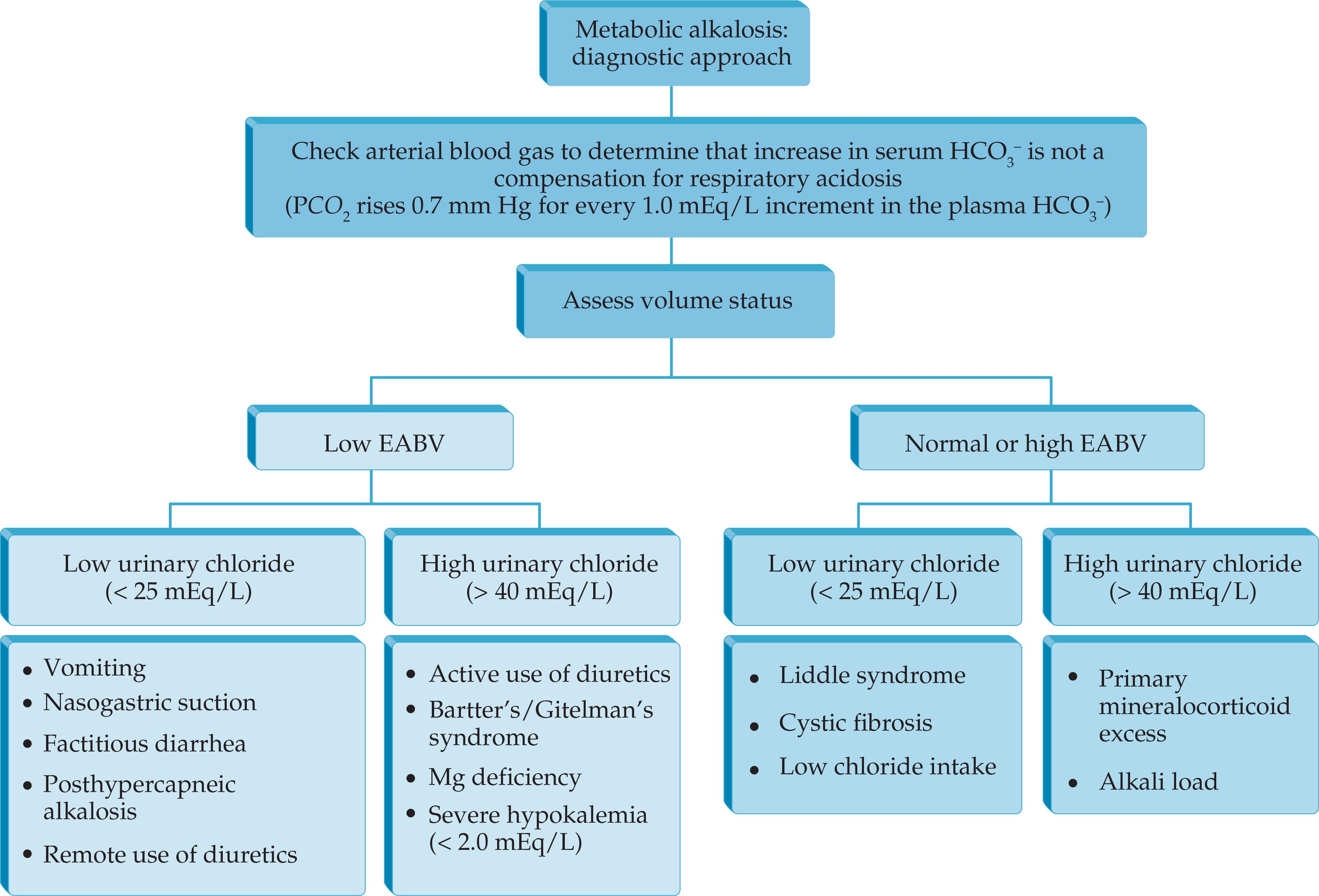
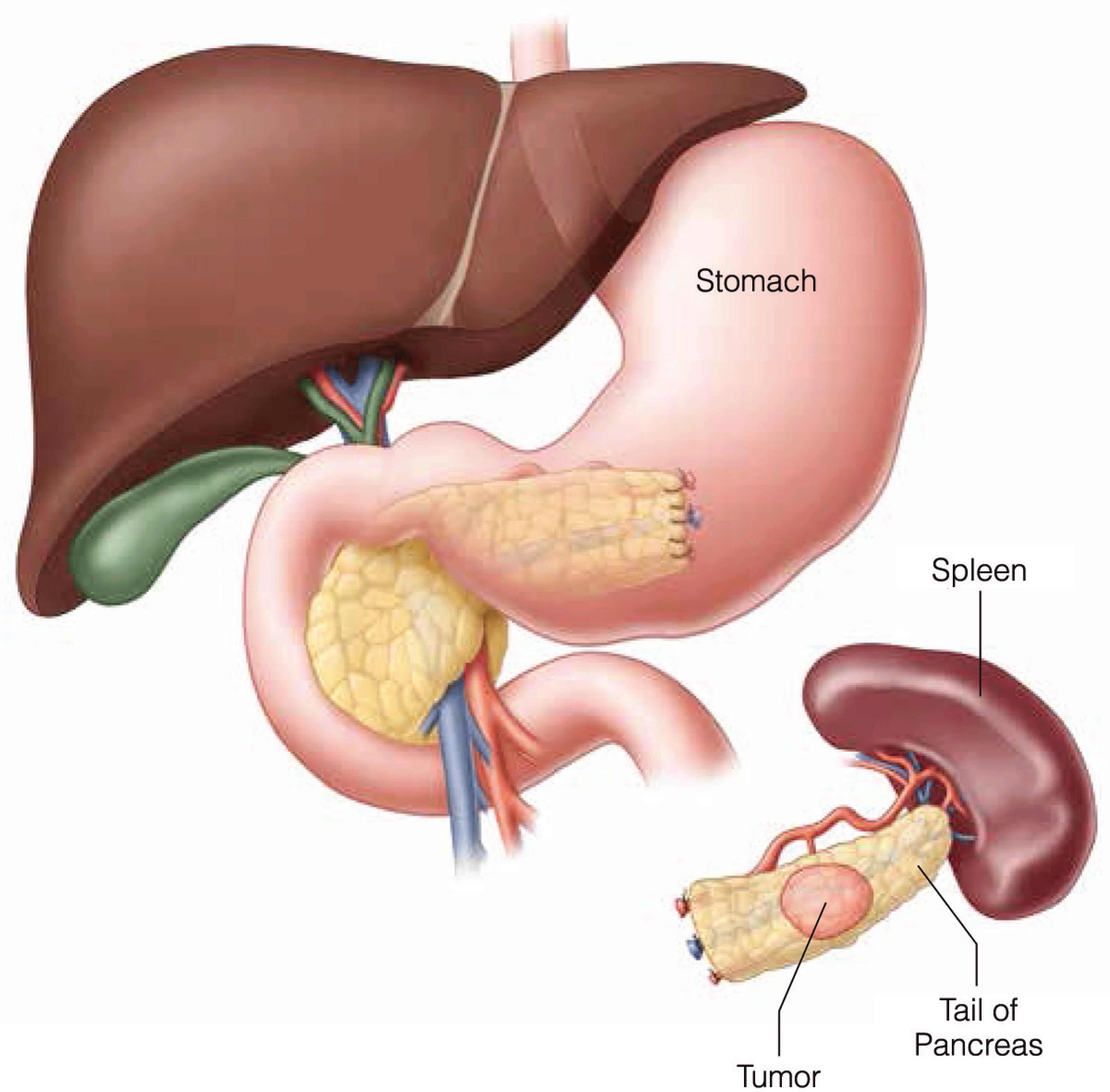
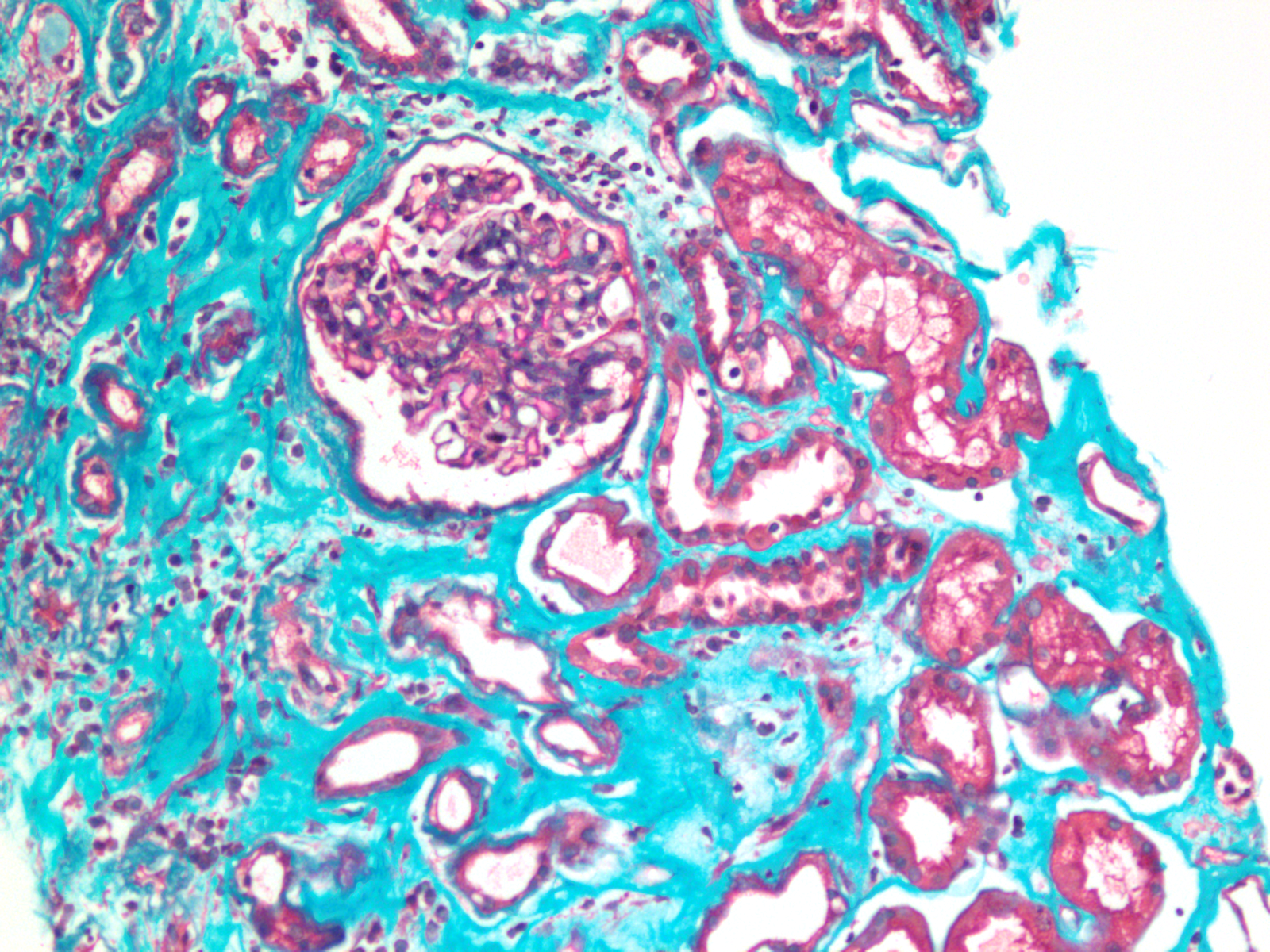
The Immunocompromised Surgical Patient and Opportunistic Infections
- Solid-organ transplant recipients may not present with classic signs and symptoms of infections due to their immunosuppressive state
- Due to overlapping radiologic and clinical features of various opportunistic infections, a tissue biopsy should be obtained, if feasible, to establish diagnosis.
- Mycobacterium chimaera,associated with heater cooler devices used during cardiac surgery, has recently emerged as an important pathogen in post cardiac surgery patients.
- Rapamycins cause delayed wound healing and should be avoided in the immediate postoperative period.
- Isavuconazole is as efficacious as voriconazole in the treatment of invasive aspergillosis.


.png)







