- Merkel cell polyomavirus (MCV) is a nonenveloped circular dsDNA virus belonging to the Polyomaviridae family discovered in 2008 and found in approximately 80% of Merkel cell carcinomas (MCCs) in the United States. The integration of viral DNA into the cell genome prior to clonal expansion suggests that the virus may be oncogenic.
- Sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) at the time of wide local excision has been recognized as an important staging tool and should generally be offered to all medically fit patients with clinically localized MCC.
- Adjuvant radiation to the primary tumor site is generally recommended for MCC at least 1 cm in size as reduced rates of local recurrence have been shown in multiple studies.
- Radiation therapy to the regional lymph node basin may be considered after negative SLNB in patients at high risk for recurrence (i.e., immunosuppressed) or for false negative SLNB (i.e., head and neck tumors).
- Radiation therapy to the regional lymph node basin may also be considered in patients following lymphadenectomy with multiple involved or matted nodes.
- Immunotherapy such as monoclonal antibodies specific to PD1 and PD1 ligand show promise for MCC. PD1 ligand is expressed on MCC tumor cells and peritumoral immune cells that confer immunologic evasion. Avelumab and pembrolizumab are being investigated for the treatment of MCC.
- Checkpoint inhibitors targeting CTLA-4 such as ipilimumab and tremelimumab combined with poly-ICLC, a Toll-like receptor–3 ligand, are under investigation.
- Intratumoral injection of IL-12 plasmid vaccine followed by electroporation is currently under clinical trial for MCC.
Latest Updates
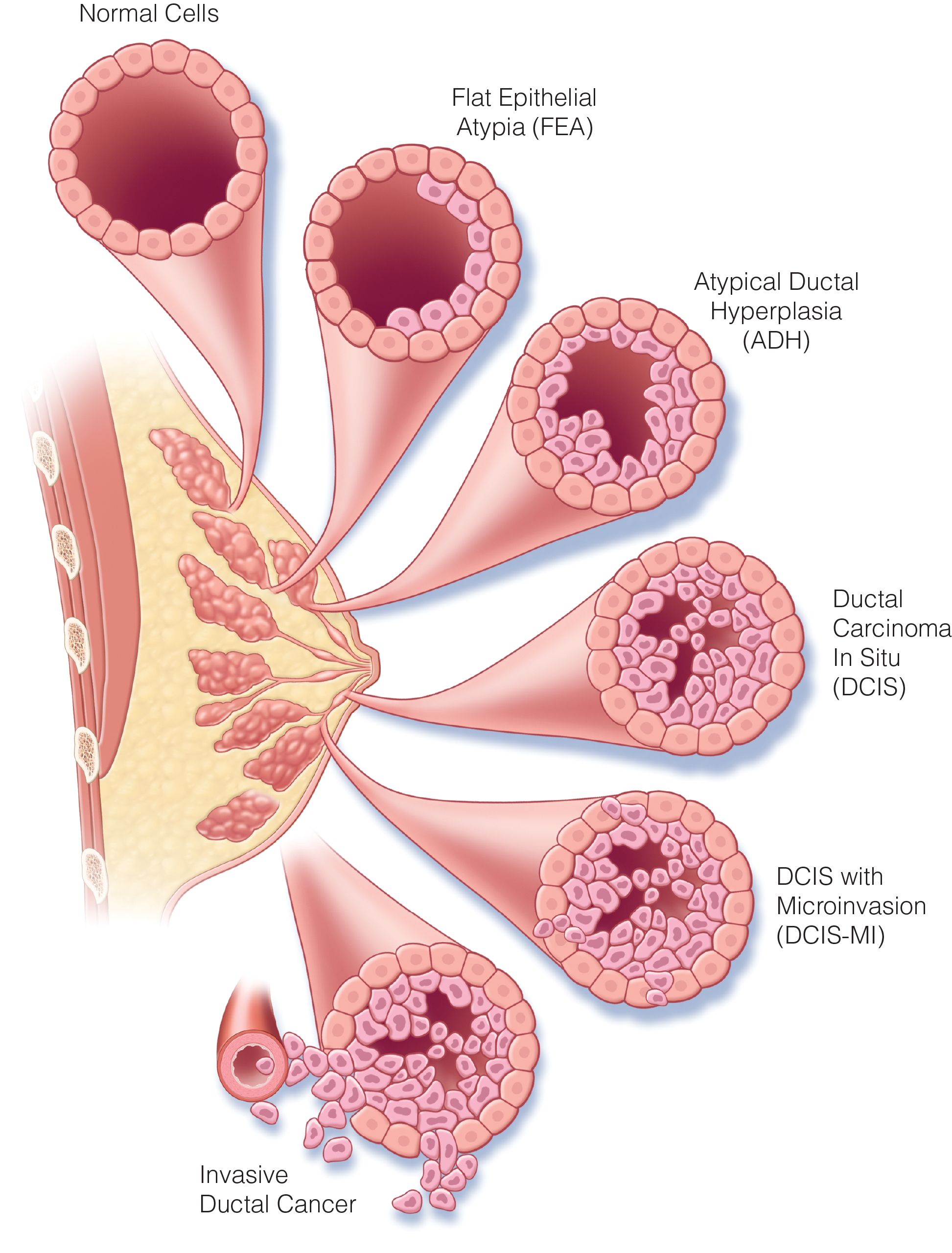
Ductal Carcinoma in Situ (DCIS)
- Four prospective RCTs examined the role of RT after breast-conserving surgery (BCS) in ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and found that RT was associated with a circa 50% reduction in local recurrence but no difference in breast cancer–specific mortality or overall survival.
- In two RCTs, use of adjuvant tamoxifen reduced the risk of local recurrence circa 30% and halved the risk of contralateral breast cancer but did not impact breast cancer–specific mortality or overall survival.
- Two prospective studies of “low-risk” DCIS treated with BCS alone without RT proved that clinicopathologic characteristics can identify a subgroup at lower risk for recurrence than unselected series;10-year recurrence remained substantial at 12 to 16%.
- An RCT of RT in “low-risk” patients showed that even in this select subgroup, RT significantly reduced the 7-year recurrence rate.
- A study-level meta-analysis of 20 studies including almost 8,000 patients resulted in a consensus guideline that recommends 2 mm as an adequate margin in DCIS treated with breast-conserving surgery and RT.
- Accrual is ongoing into trials of active surveillance without surgery for “low-risk” DCIS. Surgery followed by consideration of adjuvant RT and endocrine therapy remains the standard of care; no subset of DCIS has been identified with minimal risk of progression to invasion without treatment.

Ductal Carcinoma in Situ (DCIS)
- Four prospective RCTs examined the role of RT after breast-conserving surgery (BCS) in ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and found that RT was associated with a circa 50% reduction in local recurrence but no difference in breast cancer–specific mortality or overall survival.
- In two RCTs, use of adjuvant tamoxifen reduced the risk of local recurrence circa 30% and halved the risk of contralateral breast cancer but did not impact breast cancer–specific mortality or overall survival.
- Two prospective studies of “low-risk” DCIS treated with BCS alone without RT proved that clinicopathologic characteristics can identify a subgroup at lower risk for recurrence than unselected series;10-year recurrence remained substantial at 12 to 16%.
- An RCT of RT in “low-risk” patients showed that even in this select subgroup, RT significantly reduced the 7-year recurrence rate.
- A study-level meta-analysis of 20 studies including almost 8,000 patients resulted in a consensus guideline that recommends 2 mm as an adequate margin in DCIS treated with breast-conserving surgery and RT.
- Accrual is ongoing into trials of active surveillance without surgery for “low-risk” DCIS. Surgery followed by consideration of adjuvant RT and endocrine therapy remains the standard of care; no subset of DCIS has been identified with minimal risk of progression to invasion without treatment.
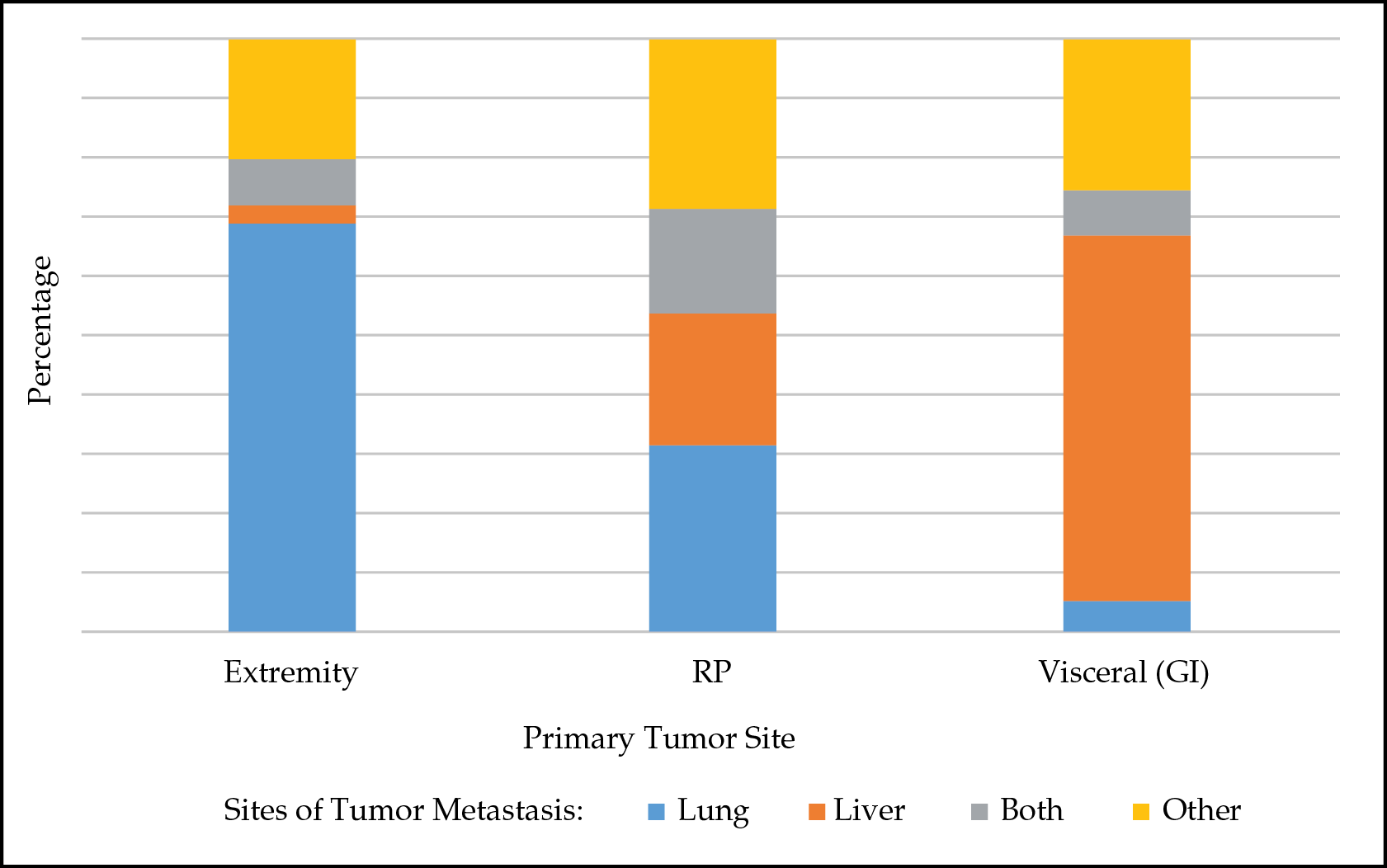
Management of Metastatic Sarcoma
- Advances in targeted therapies for the treatment of metastatic sarcoma, such as imatinib for the management of gastrointestinal stromal tumors.
- Advances in systemic management, including new combination regimens with traditional agents, as well as novel chemotherapeutic agents
- Advances in surgical management of sarcoma metastases. Ablation and radioembolization offer alternative methods for management of metastatic lesions in select candidates who are not candidates for surgical resection.

Management of Metastatic Sarcoma
- Advances in targeted therapies for the treatment of metastatic sarcoma, such as imatinib for the management of gastrointestinal stromal tumors.
- Advances in systemic management, including new combination regimens with traditional agents, as well as novel chemotherapeutic agents
- Advances in surgical management of sarcoma metastases. Ablation and radioembolization offer alternative methods for management of metastatic lesions in select candidates who are not candidates for surgical resection.
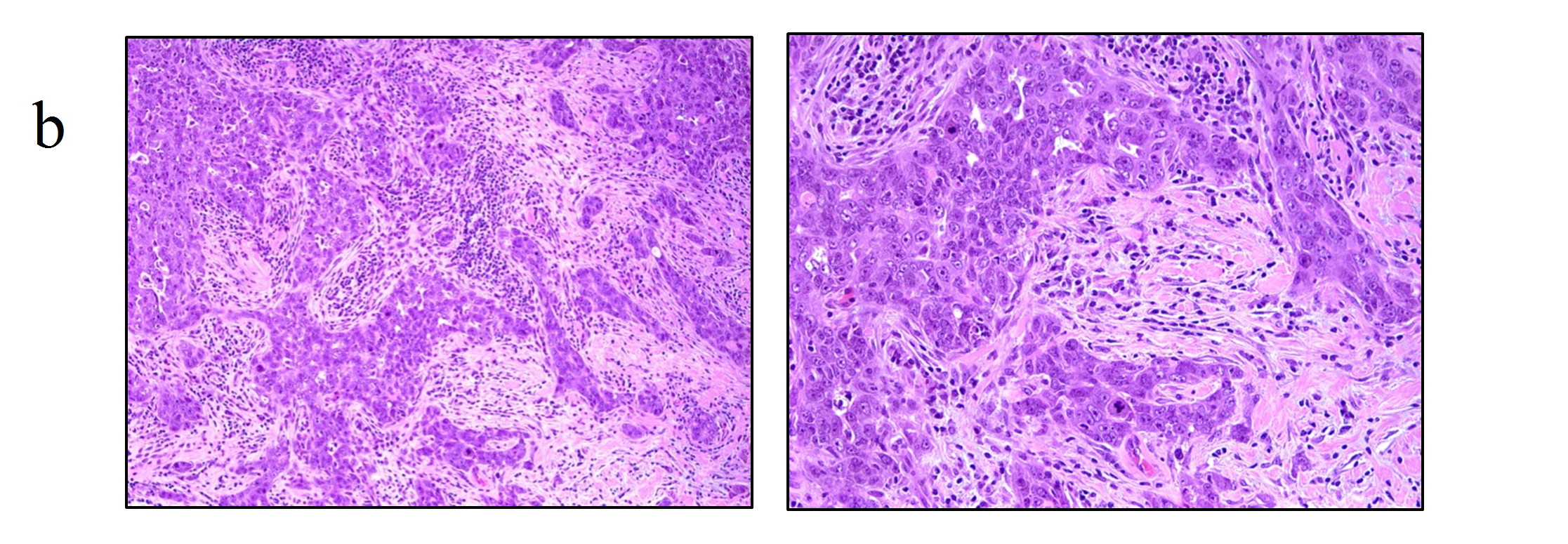
- Recognition of invasive lobular cancer as a biologically unique entity from invasive ductal cancer
- Identification of novel mutations more frequently identified in invasive lobular cancers in The Cancer Genome Analysis (TCGA) study
- Multimodality treatment approaches with an emphasis on tumor biology
- Consensus guidelines for negative margins at lumpectomy and applicability to lobular cancers
- Impact and utility of neoadjuvant chemotherapy and neoadjuvant endocrine therapy in lobular cancers
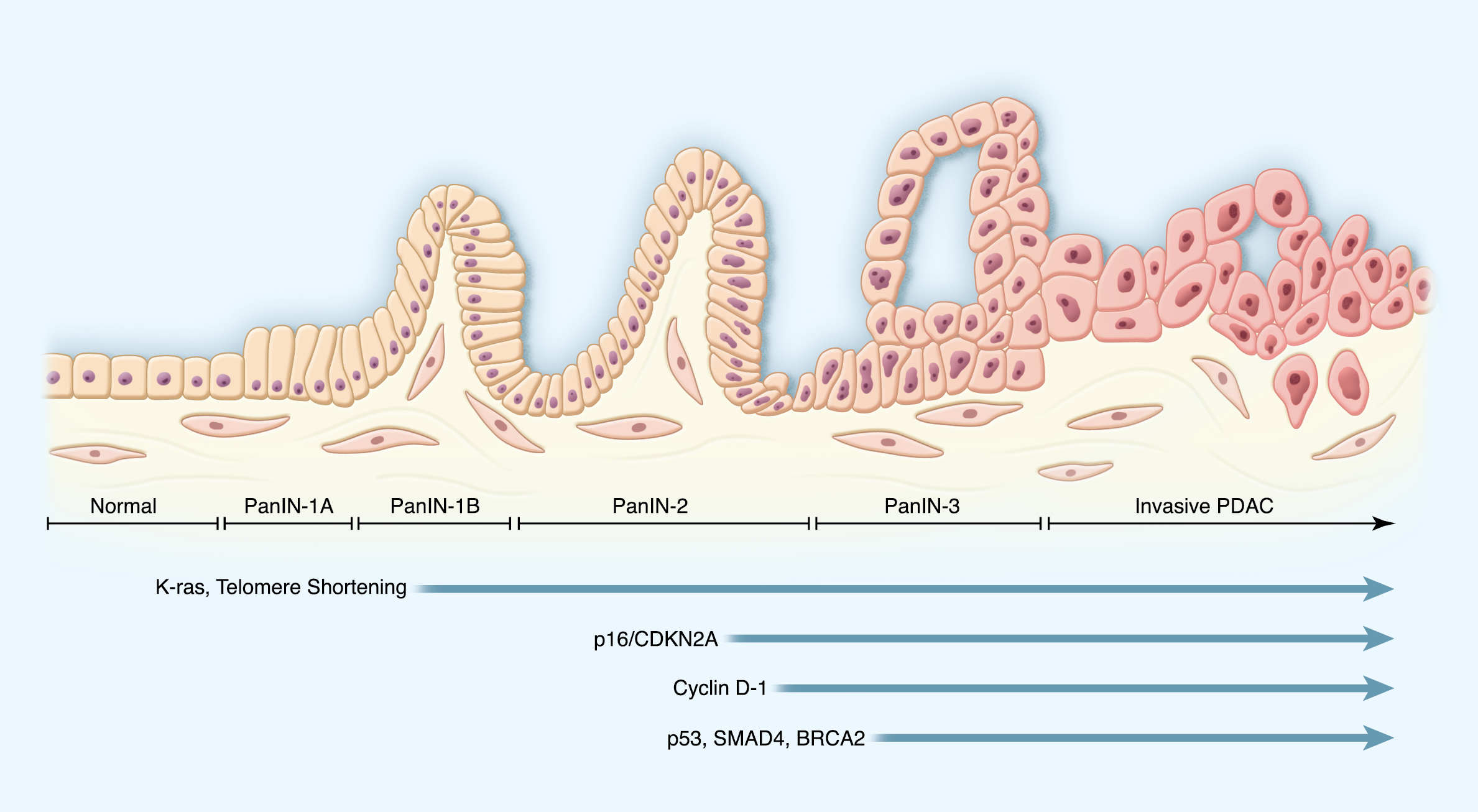
Understanding the Genetics of Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma
- Whole genome/exome sequencing
- RNA expression analysis
- Genome-wide association studies

Understanding the Genetics of Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma
- Whole genome/exome sequencing
- RNA expression analysis
- Genome-wide association studies


.png)







