- Recognition of inherited genetic predisposition for breast cancer, need for genetic counseling and genetic cancer screening
- Appreciation that breast-conserving therapy is feasible and oncologically safe in men
- Highlighting the recent inclusion of men with breast cancer in prospective national and international clinical trials
- Recognition of unique biomarker characteristics of breast cancer in men and the impact on systemic therapeutic approaches
Latest Updates
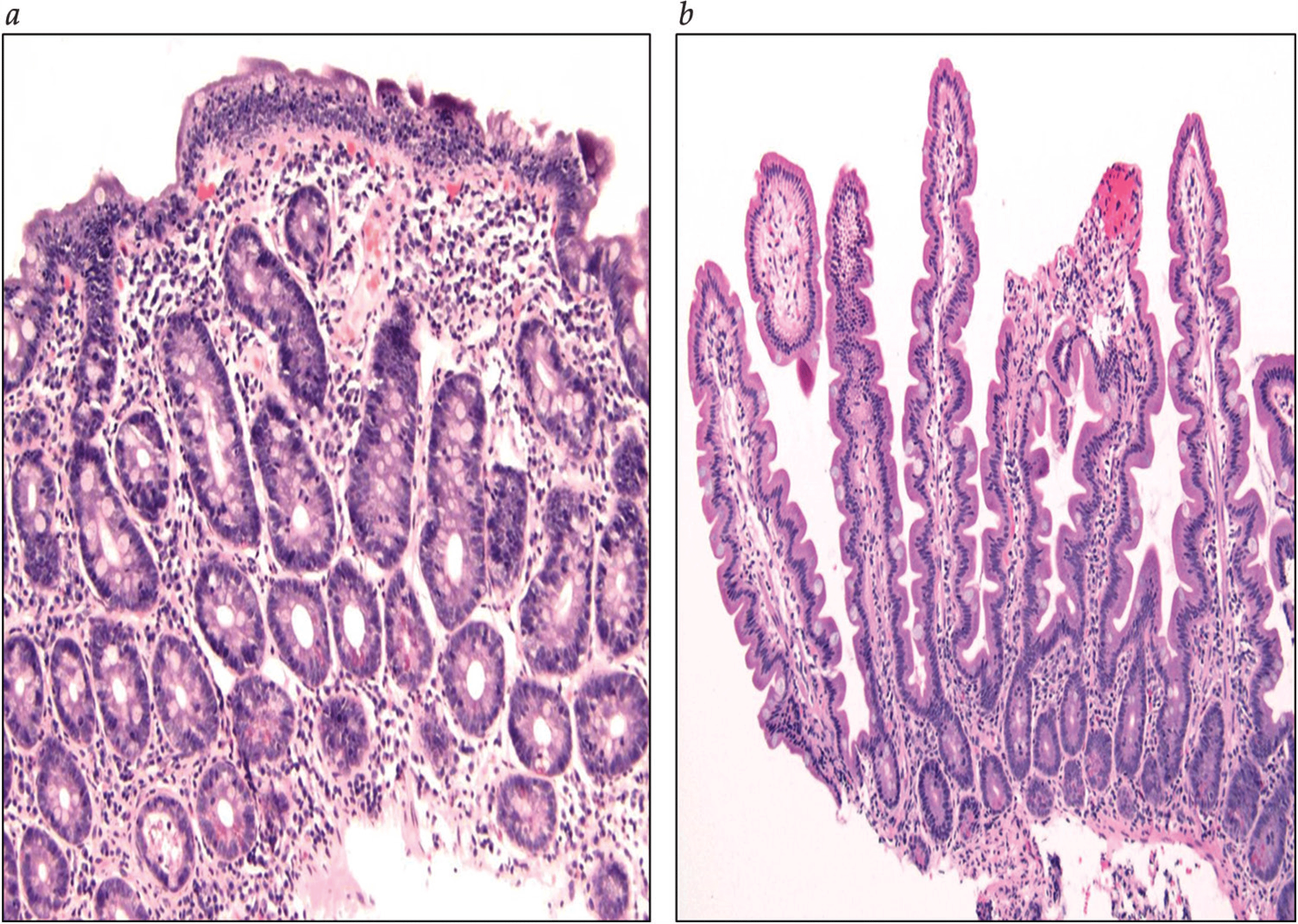
Nutritional Management of Celiac Disease
- Glutenases: Clinical trials using glutenases versus placebo have demonstrated worsening of histologic findings in the placebo group compared with glutenases on consumption of up to 2 g of gluten.
- Tight junction regulators: Larazotide acetate demonstrated a reduction in gluten-induced immune reactivity and symptoms when celiac subjects were exposed to a 2.7 g gluten challenge when compared with placebo in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.
- IgY antibodies: Animal studies using mice fed with gastric-stabilized antigliadin IgY antibodies derived from the egg yolks of gluten-immunized chickens in addition to gluten showed a reduction in gluten absorption from the diet.
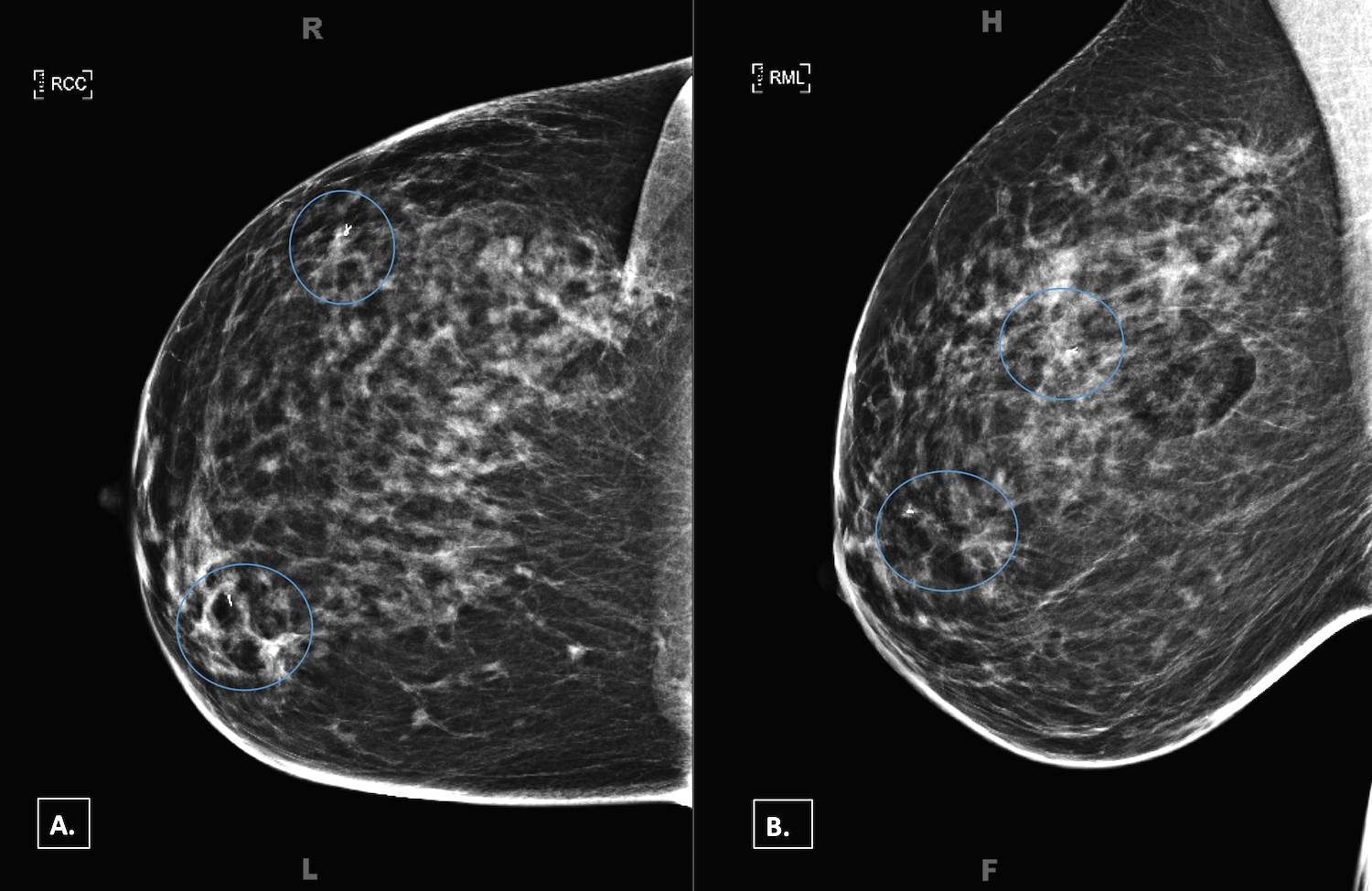
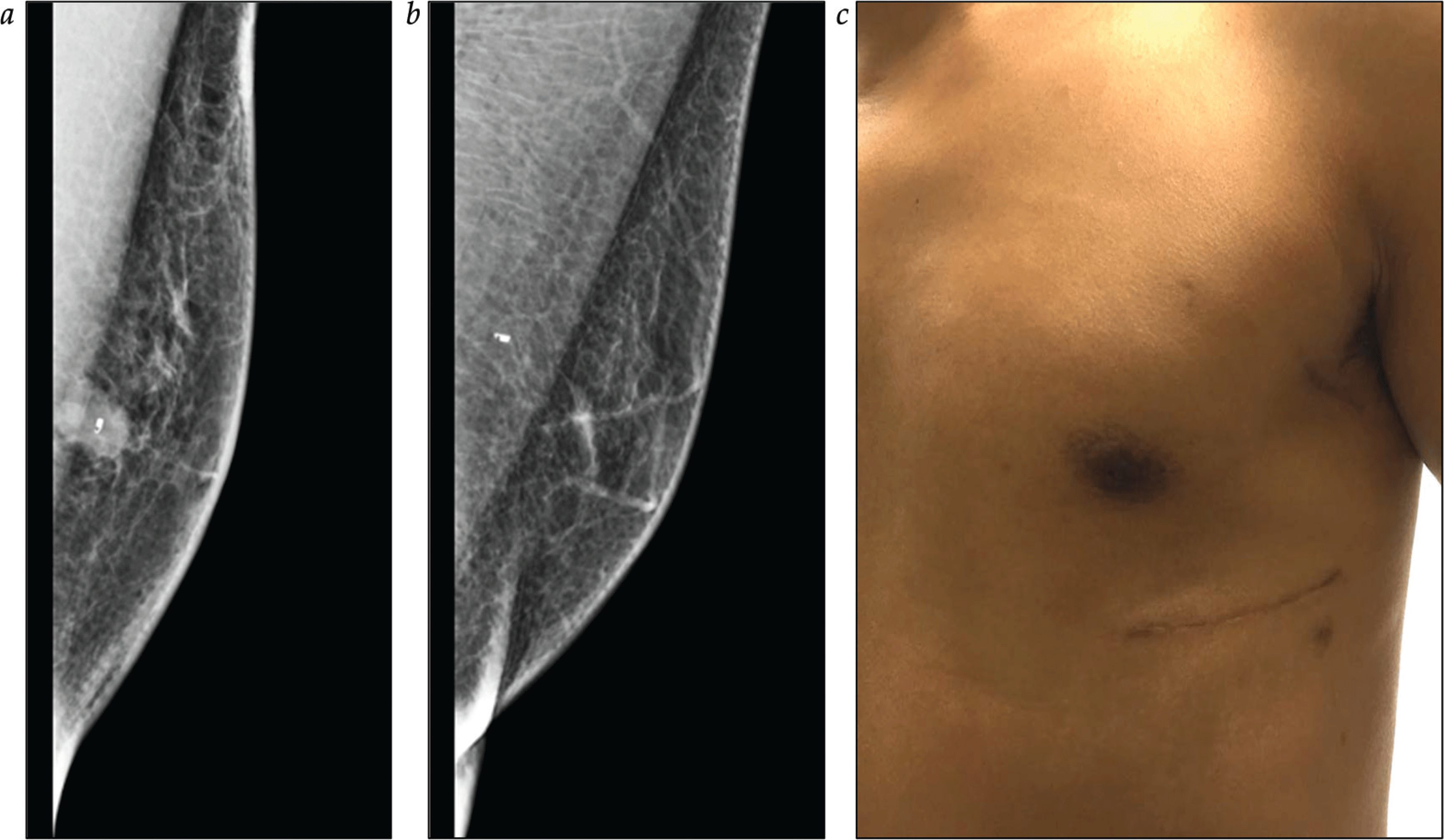
Estrogen Receptor–Positive, HER-2 Nonamplified Breast Cancer
- • Estrogen receptor (ER)-positive tumors represent 70% of all breast cancers and generally have a good prognosis but are heterogeneous, and biological behavior can be more closely predicted by luminal subtype.
- • Endocrine therapy reduces locoregional and distant failure in ER-positive tumors, with tamoxifen being the drug of choice in premenopausal women and tamoxifen or an aromatase inhibitor alone or in sequence being used in postmenopausal women.
- • Although clinicopathologic features, such as patient risk factors, pathologic stage, and lymphovascular invasion, guide therapy selection, genomic profiling of the tumor provides insight into the risk of recurrence and is a commonly used tool to determine the need for adjuvant chemotherapy. Oncotype DX is the most broadly used molecular profiling tool.
- • Ovarian suppression, either reversibly or irreversibly, in addition to hormone therapy reduces the risk of recurrence in premenopausal women who are at high risk for recurrence indicated by the need for chemotherapy.
- • Neoadjuvant and adjuvant chemotherapy have equivalent long-term outcomes, but neoadjuvant therapy can be used to downstage a tumor to make it amenable to breast-conserving therapy or to evaluate tumor response to systemic therapy and provide prognostic information.
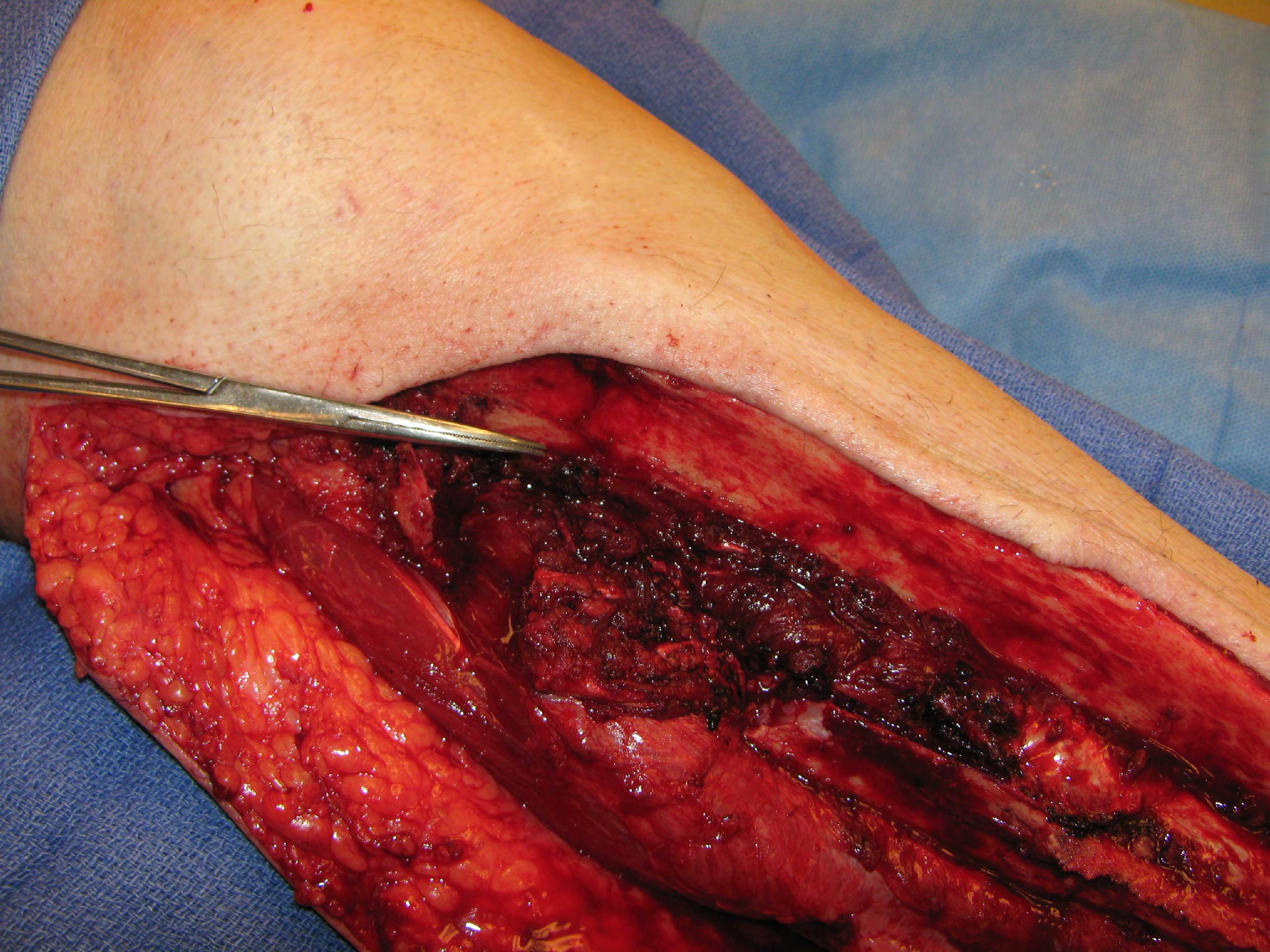
Principles in Reconstruction after Resection of Extremity and Truncal Sarcomas
- Resection and reconstruction of sarcoma defects require a multidisciplinary effort to achieve the oncologic and reconstructive result with the goal of negative margins and stable bony and soft tissue coverage with appropriate function.
- Although the reconstructive ladder still applies to postresection defects, advances in microsurgical techniques offer options that, although potentially more complex, provide a more stable long-term solution to complex reconstructive challenges.
- Advances in perforator techniques for reconstruction have afforded improved donor sites with less donor site morbidity as muscle units are not sacrificed.
- Limb salvage is now the standard of care following lower extremity sarcoma resection and reconstruction.

Estrogen Receptor–Positive, HER-2 Nonamplified Breast Cancer
- • Estrogen receptor (ER)-positive tumors represent 70% of all breast cancers and generally have a good prognosis but are heterogeneous, and biological behavior can be more closely predicted by luminal subtype.
- • Endocrine therapy reduces locoregional and distant failure in ER-positive tumors, with tamoxifen being the drug of choice in premenopausal women and tamoxifen or an aromatase inhibitor alone or in sequence being used in postmenopausal women.
- • Although clinicopathologic features, such as patient risk factors, pathologic stage, and lymphovascular invasion, guide therapy selection, genomic profiling of the tumor provides insight into the risk of recurrence and is a commonly used tool to determine the need for adjuvant chemotherapy. Oncotype DX is the most broadly used molecular profiling tool.
- • Ovarian suppression, either reversibly or irreversibly, in addition to hormone therapy reduces the risk of recurrence in premenopausal women who are at high risk for recurrence indicated by the need for chemotherapy.
- • Neoadjuvant and adjuvant chemotherapy have equivalent long-term outcomes, but neoadjuvant therapy can be used to downstage a tumor to make it amenable to breast-conserving therapy or to evaluate tumor response to systemic therapy and provide prognostic information.
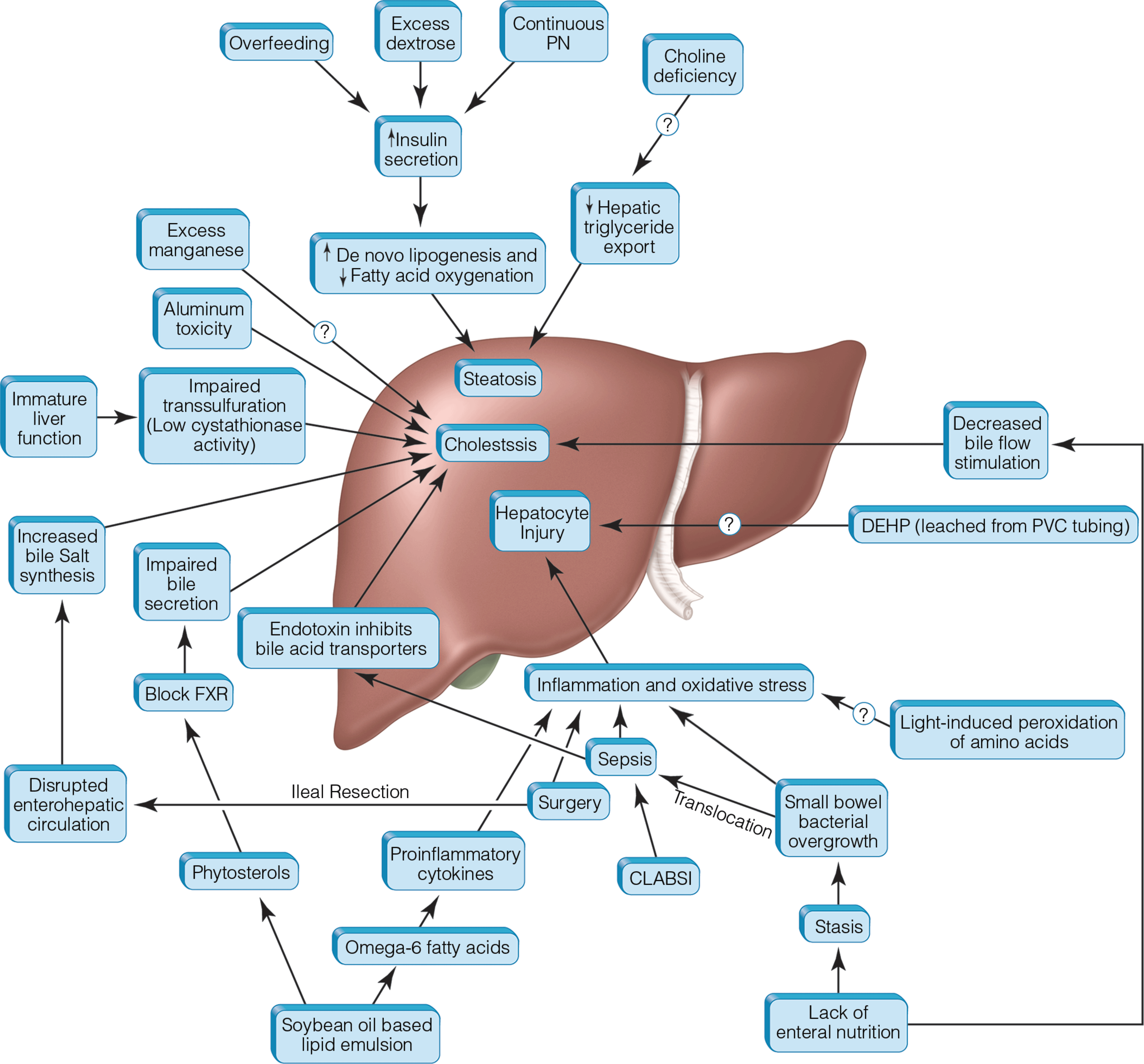
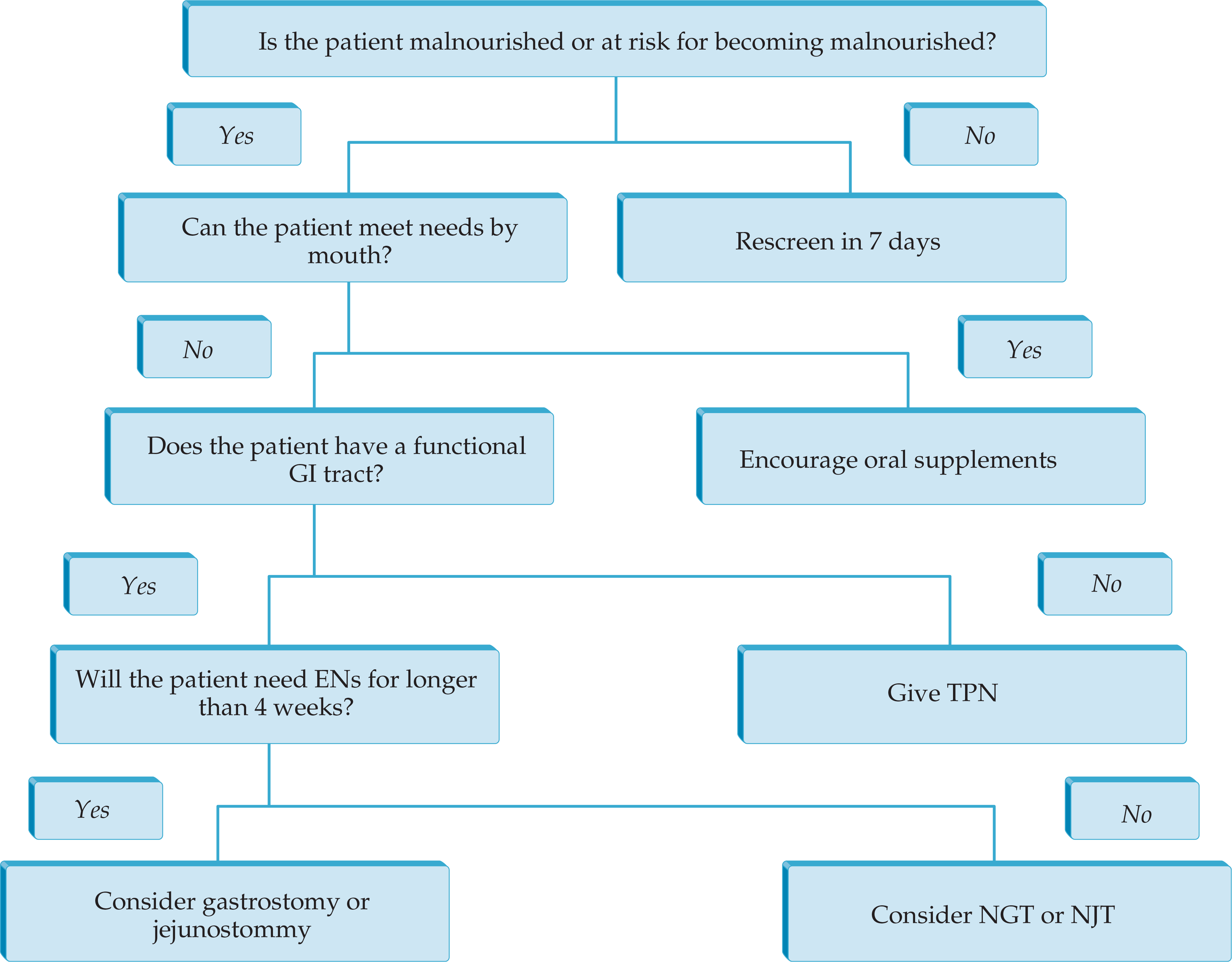
Parenteral Nutrition Associated Liver Toxicity: Prevention, Diagnosis, and Management
- Fish oil–based lipid emulsions may be efficacious in the treatment of parenteral nutrition–associated liver disease (PNALD).
- Lipid reduction (e.g., to 1 g/kg/day) does not decrease the incidence of PNALD but does slow its progression.
- Patients whose cholestasis reverses with fish oil therapy or achievement of enteral autonomy may have stable rather than progressive cirrhosis and should not be transplanted based on biopsy alone.

Principles in Reconstruction after Resection of Extremity and Truncal Sarcomas
- Resection and reconstruction of sarcoma defects require a multidisciplinary effort to achieve the oncologic and reconstructive result with the goal of negative margins and stable bony and soft tissue coverage with appropriate function.
- Although the reconstructive ladder still applies to postresection defects, advances in microsurgical techniques offer options that, although potentially more complex, provide a more stable long-term solution to complex reconstructive challenges.
- Advances in perforator techniques for reconstruction have afforded improved donor sites with less donor site morbidity as muscle units are not sacrificed.
- Limb salvage is now the standard of care following lower extremity sarcoma resection and reconstruction.


.png)







