- Review of emerging genetics and etiologic theories of bipolar disorders
- Correlation between recent neurobiologic findings and clinical manifestations of bipolar disorders
- Discussion of the role of endocrine and immune alterations in metabolic derangements associated with bipolar disorders
Latest Updates
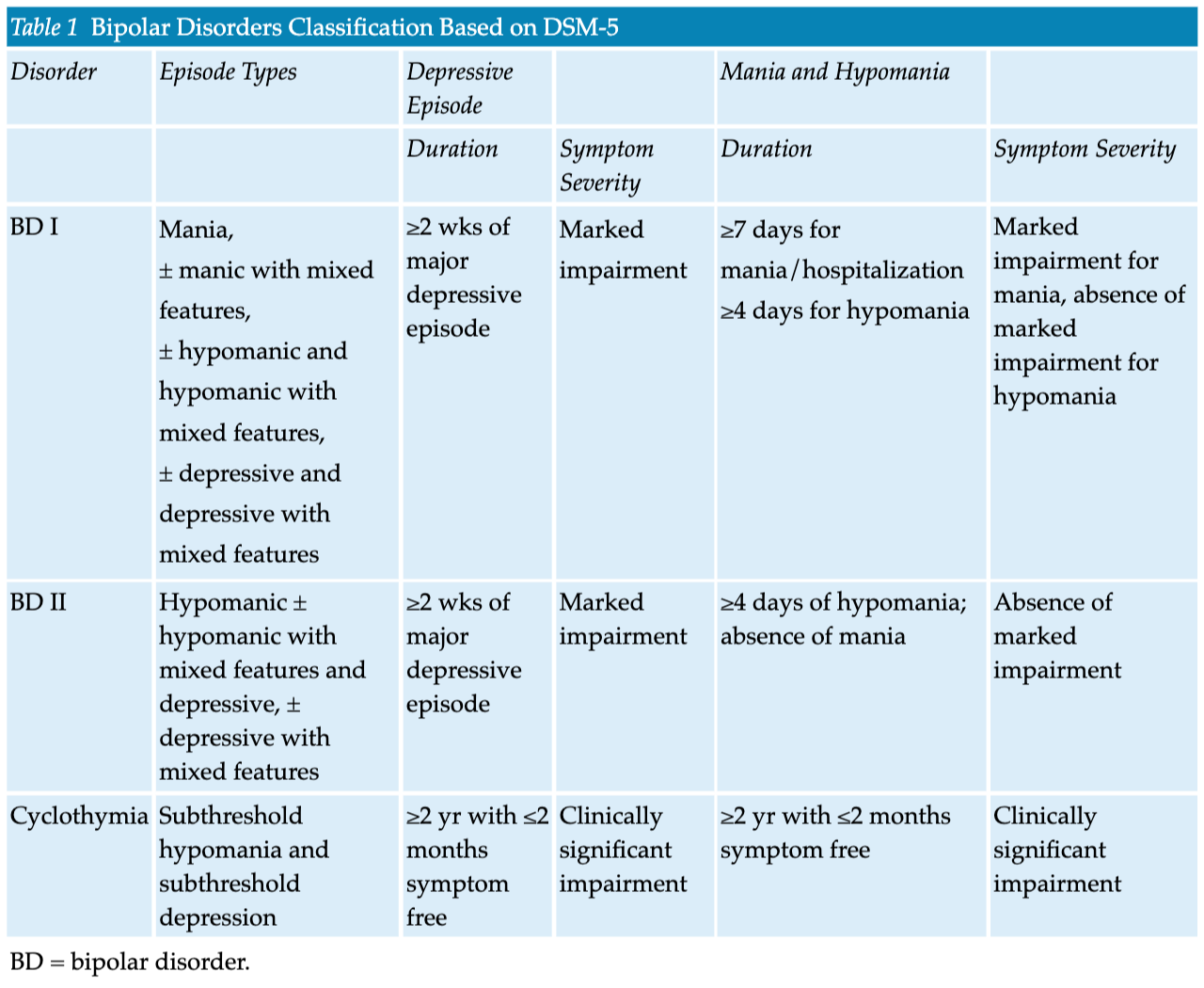
Initial Management of Life-Threatening Trauma
- Initial volume resuscitation should commence with 1 L isotonic crystalloid solution followed by blood products at 1:1:1 ratio (1 unit packed red blood cells to 1 unit fresh frozen plasma to 1 unit platelets) if the patient is not responsive to the initial fluid bolus.
- In patients with massive hemorrhage or evidence of fibrinolysis, tranexamic acid has demonstrated improved survival if administered within 3 hours of injury.
- Use of resuscitative endovascular balloon occlusion of the aorta may be an important adjunct in the control of life-threatening abdominal or pelvic hemorrhage.
- In cases of external hemorrhage of an extremity, a tourniquet should be used to control bleeding.

- Review of emerging genetics and etiologic theories of bipolar disorders
- Correlation between recent neurobiologic findings and clinical manifestations of bipolar disorders
- Discussion of the role of endocrine and immune alterations in metabolic derangements associated with bipolar disorders
- Zika virus: Delayconception if potential exposure: 8 weeks: females or 3 months: males
- Subclinical hypothyroid: Treatment is associated with improved pregnancy outcomes when TSH levels are above 4 mIU/L.
- Tubal patency: Hysterosalpingo-contrast sonography was recently introduced as an additional screening method to assess tubal patency.

- Review of emerging genetics and etiologic theories of bipolar disorders
- Correlation between recent neurobiologic findings and clinical manifestations of bipolar disorders
- Discussion of the role of endocrine and immune alterations in metabolic derangements associated with bipolar disorders

Initial Management of Life-Threatening Trauma
- Initial volume resuscitation should commence with 1 L isotonic crystalloid solution followed by blood products at 1:1:1 ratio (1 unit packed red blood cells to 1 unit fresh frozen plasma to 1 unit platelets) if the patient is not responsive to the initial fluid bolus.
- In patients with massive hemorrhage or evidence of fibrinolysis, tranexamic acid has demonstrated improved survival if administered within 3 hours of injury.
- Use of resuscitative endovascular balloon occlusion of the aorta may be an important adjunct in the control of life-threatening abdominal or pelvic hemorrhage.
- In cases of external hemorrhage of an extremity, a tourniquet should be used to control bleeding.

Initial Management of Life-Threatening Trauma
- Initial volume resuscitation should commence with 1 L isotonic crystalloid solution followed by blood products at 1:1:1 ratio (1 unit packed red blood cells to 1 unit fresh frozen plasma to 1 unit platelets) if the patient is not responsive to the initial fluid bolus.
- In patients with massive hemorrhage or evidence of fibrinolysis, tranexamic acid has demonstrated improved survival if administered within 3 hours of injury.
- Use of resuscitative endovascular balloon occlusion of the aorta may be an important adjunct in the control of life-threatening abdominal or pelvic hemorrhage.
- In cases of external hemorrhage of an extremity, a tourniquet should be used to control bleeding.
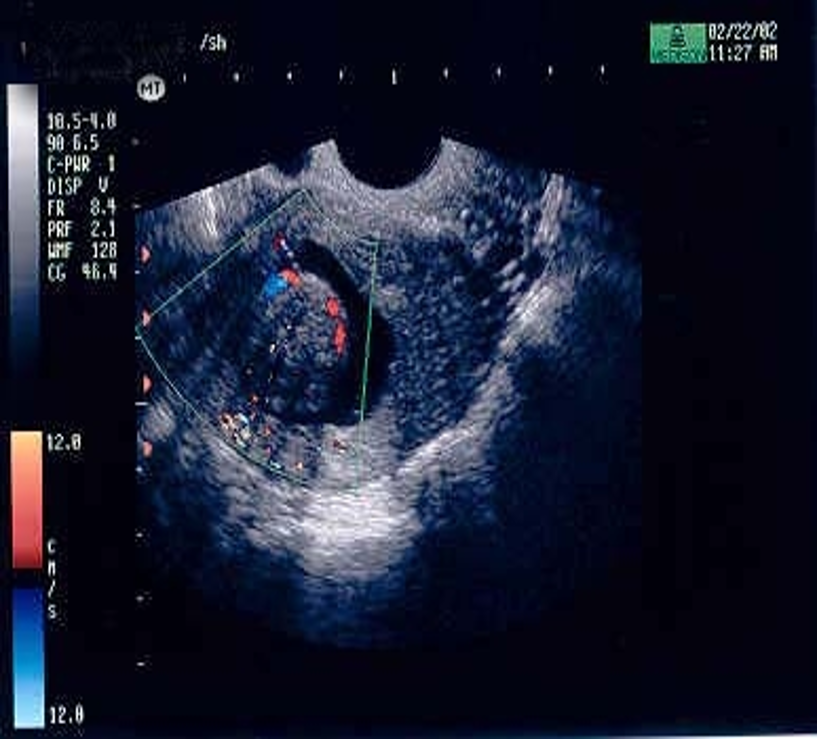
Pathophysiology of Alzheimer Disease
- Amyloid positron emission tomography (PET) has greatly expanded our knowledge of Alzheimer disease (AD), from its preclinical to its clinical manifestations.
- Tau PET has become available as a research tool and is providing new insights into the evolution of AD.
- A conceptual scheme that classifies the imaging and cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers of AD into amyloid, tau, and neurodegeneration has been adopted.


.png)







