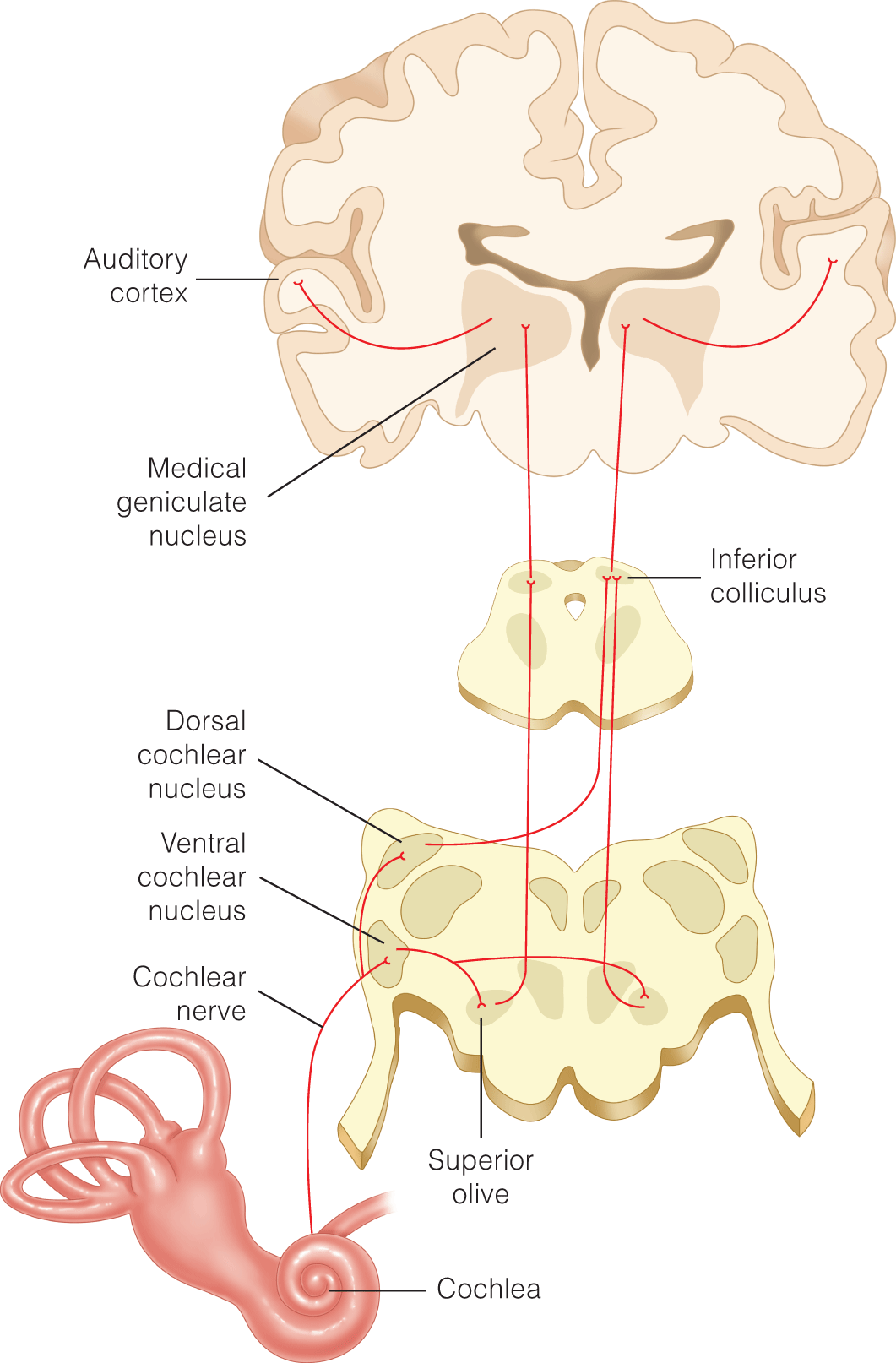
Audiometric and Vestibular Testing
Latest Updates
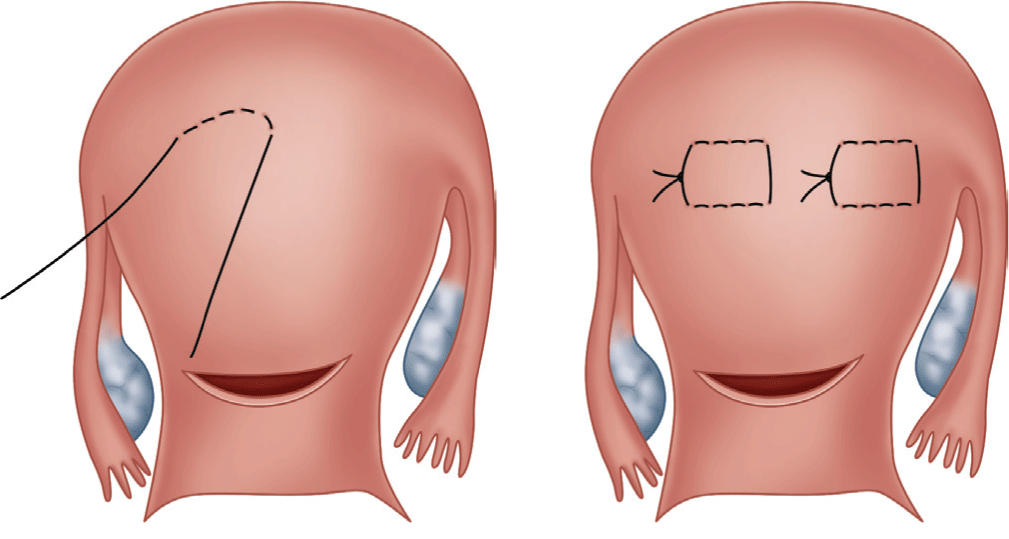
Management of Postpartum Hemorrhage
- In a 2015 population-based, cross-sectional study conducted by the United Kingdom Obstetric Surveillance System on women requiring massive postpartum transfusion for PPH, uterine atony was found to be responsible 40% of the time. Atony represents a large proportion of cases of PPH, and its incidence is on the rise. Over recent years, we have observed a significant rise in the rate of PPH attributed to uterine atony not only in the United States but also worldwide.
- Originally described in 1997, the B-Lynch compression suture is an effective and easily used tool for the management of PPH. This technique involves placing brace sutures over the fundus of the uterus to apply ongoing compression of the uterus.
- The correct ratio of packed red blood cells to fresh frozen plasma to platelets in the setting of obstetrical hemorrhage remains controversial. Most experts advocate for a 1:1:1 ratio in the setting of active bleeding, whereas others advocate for 6:4:1 or 2:1 (with platelets to be given after the first 4:2).

Management and Therapeutic Issues in the Dementias
- The cholinesterase inhibitors donepezil, galantamine, and rivastigmine have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of AD dementia.
- Patients with mild to moderate AD dementia are the appropriate candidates for cholinesterase inhibitor therapy. These patients need a designated caregiver to supervise the use of the medication.
- Support for and empowerment of the caregivers of dementia patients must be an integral part of management. The emotional and physical health of caregivers is critical to long-term outcomes.
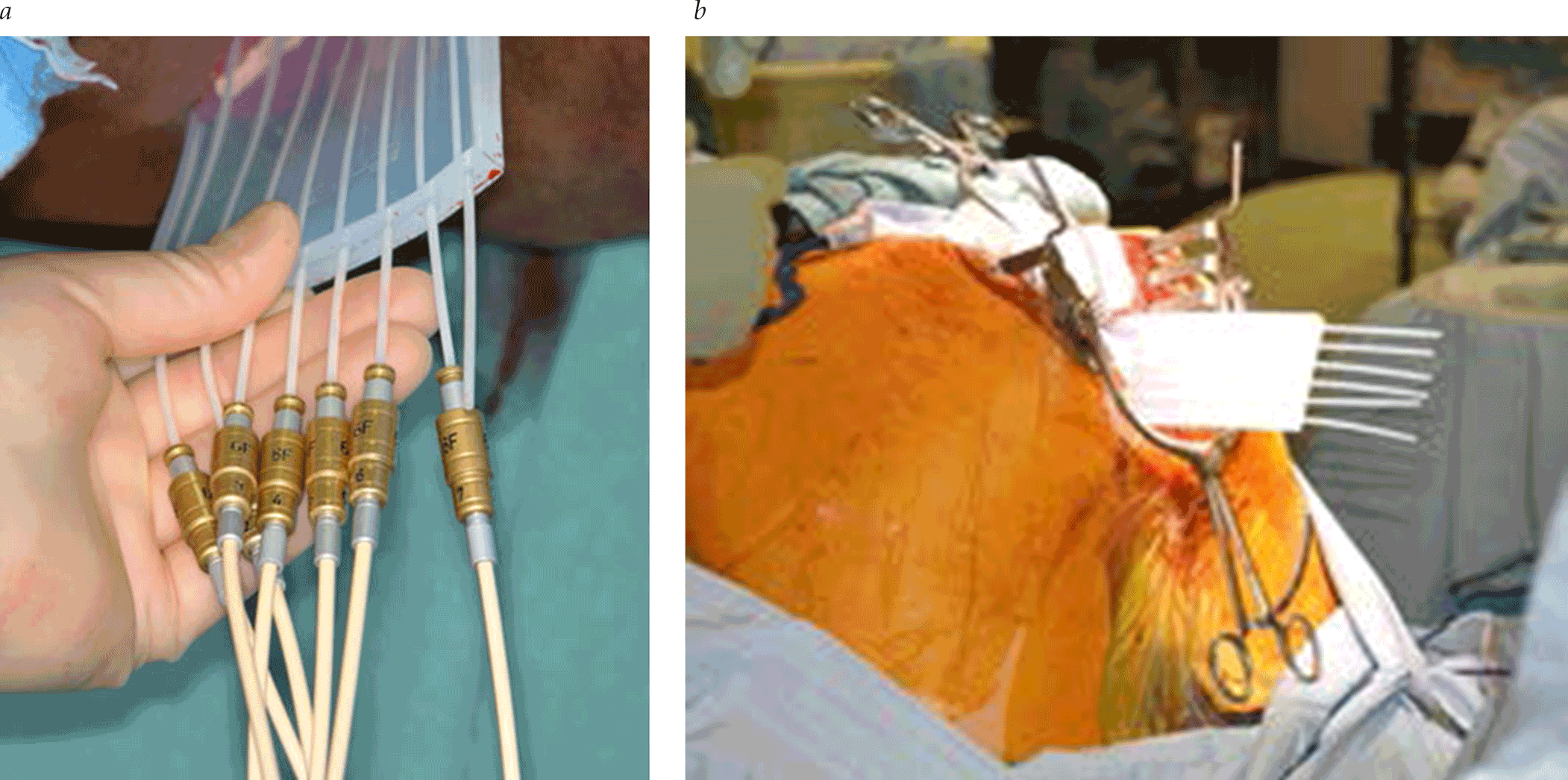
Advanced and Recurrent Rectal Cancer
- Patients with colorectal cancer, due to increased age and exposure to neoadjuvant therapy, are likely to have or obtain functional deficits prior to surgery. Optimizing patients is crucial for minimizing postoperative complications after radical resections. It has been established that patients with poor physical fitness experience a greater number of complications after surgery, are at greater risk for death, and have a significant delay in regaining their baseline functional status. Prehabilitation is an increasingly studied novel approach to patient optimization through a process of increasing functional capacity prior to colorectal surgery. Several small studies have shown beneficial functional outcomes, although the clinical impact, as far as decreased morbidity and mortality, has not been clearly demonstrated.
- With an aggressive multidisciplinary approach, the overall 5-year survival rate of LRRC is 25 to 67%. The quality of the surgery has a large impact on patient survival; therefore, an aggressive surgical strategy to gain a negative resection margin is vital to patient outcomes
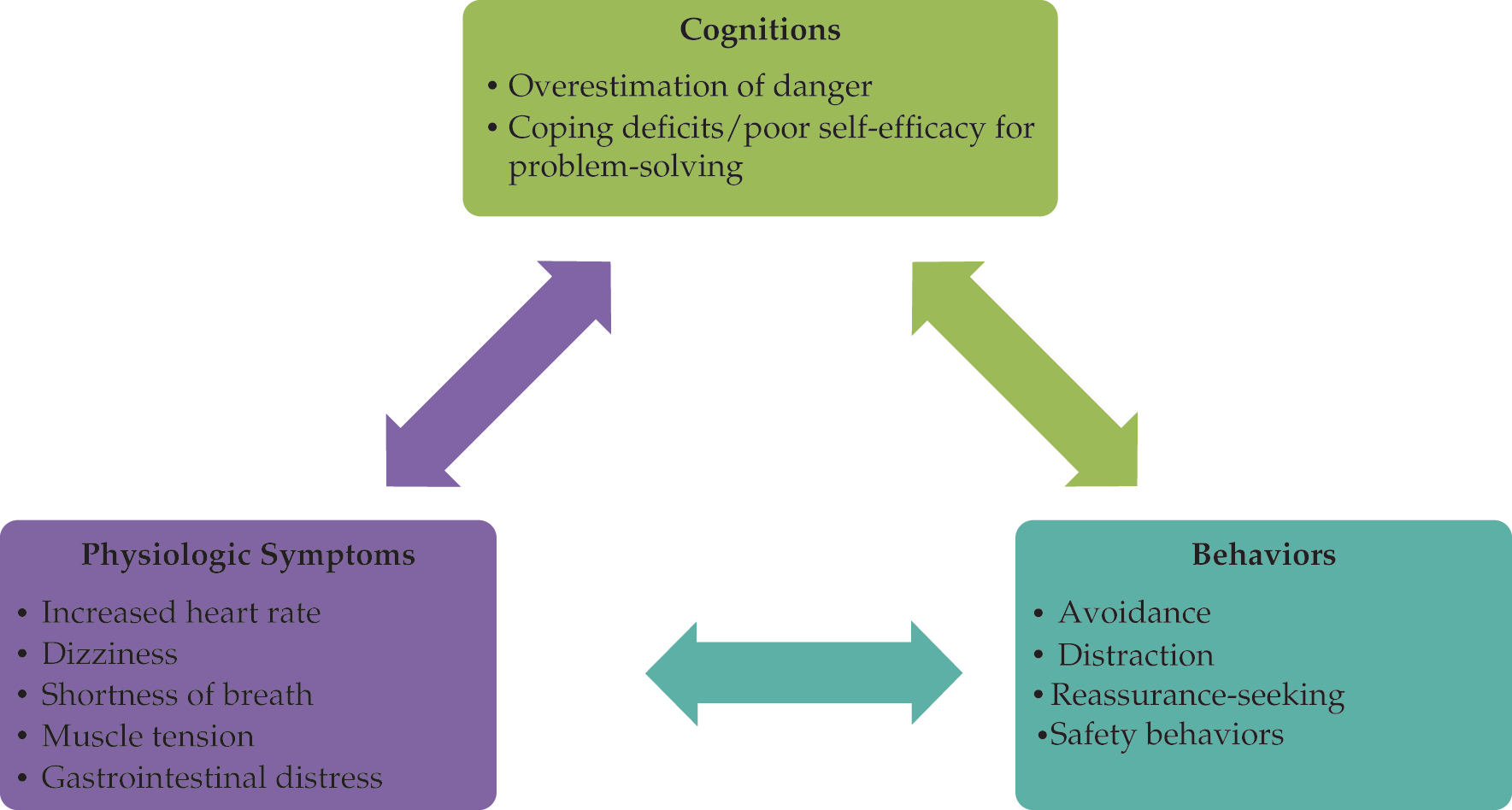
Clinical Management of Anxiety Disorders
- Identification of major anxiety disorders observed in adults according to the DSM-5
- Description of physiologic, cognitive, and behavioral components of anxiety and their relevance to diagnosis and treatment
- Review of cognitive-behavioral treatments and their efficacy for anxiety disorders in adults
- Review of pharmacologic treatments and their efficacy for anxiety disorders in adults
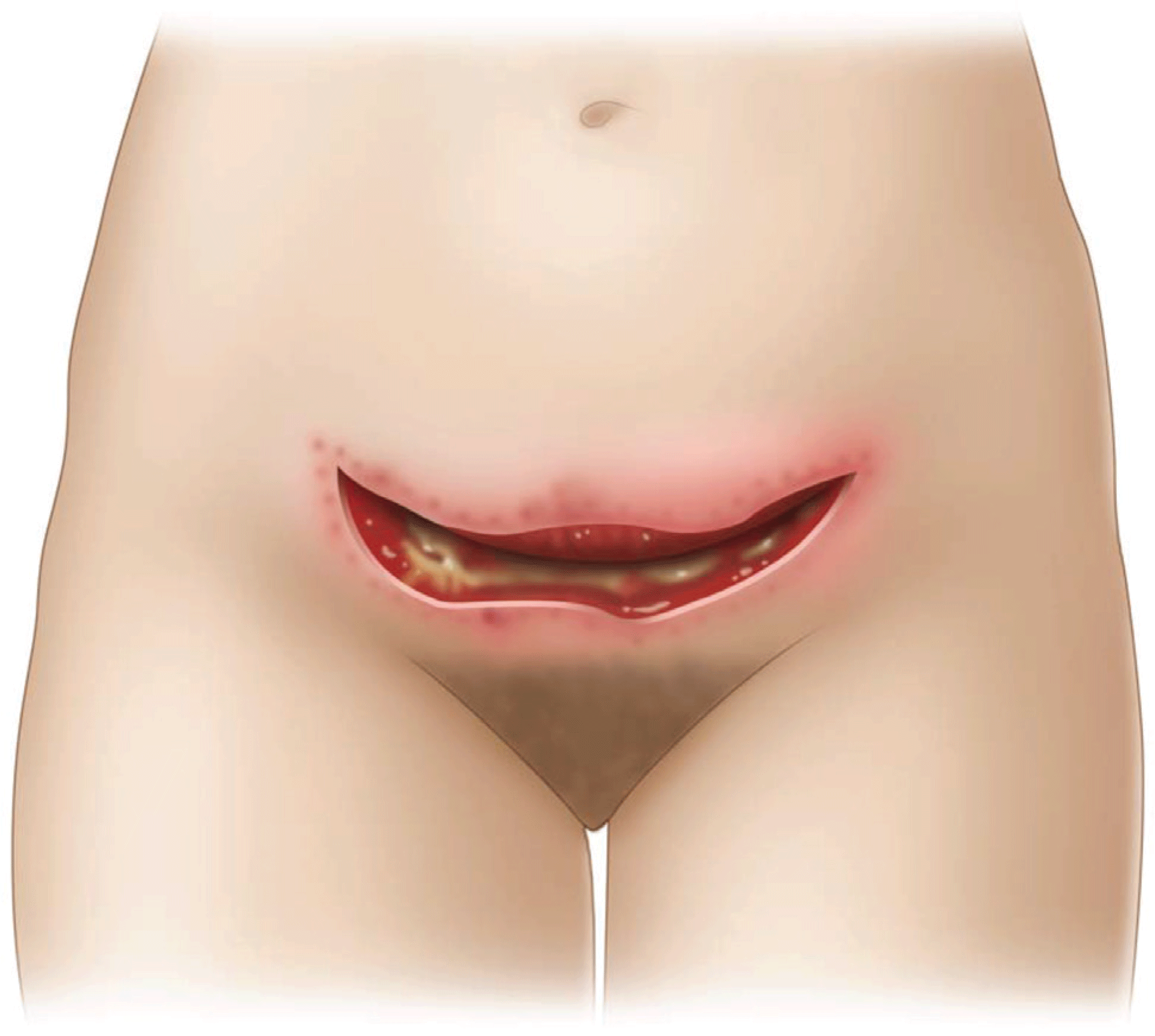
Scientific Foundations: Infection Control in Surgical Practice
- For patients undergoing surgical procedures requiring the implantation of foreign bodies, colonization with MRSA should be assessed. Hospitalized hemodialysis patients and their health care workers are frequently colonized.
- Updated CDC diagnostic criteria for surgical site infection, catheter-associated urinary tract infection, central line–associated bloodstream infection, and ventilator-associated pneumonia
- Although no single surveillance system captures all HAIs that occur within US acute care hospitals, recent Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates suggest that 648,000 patients experienced at least one HAI during their hospital stay in 2011. This represents 4.0% of the hospitalized population. Among surgical patients, the rate of reported HAIs is even higher at 10.6%
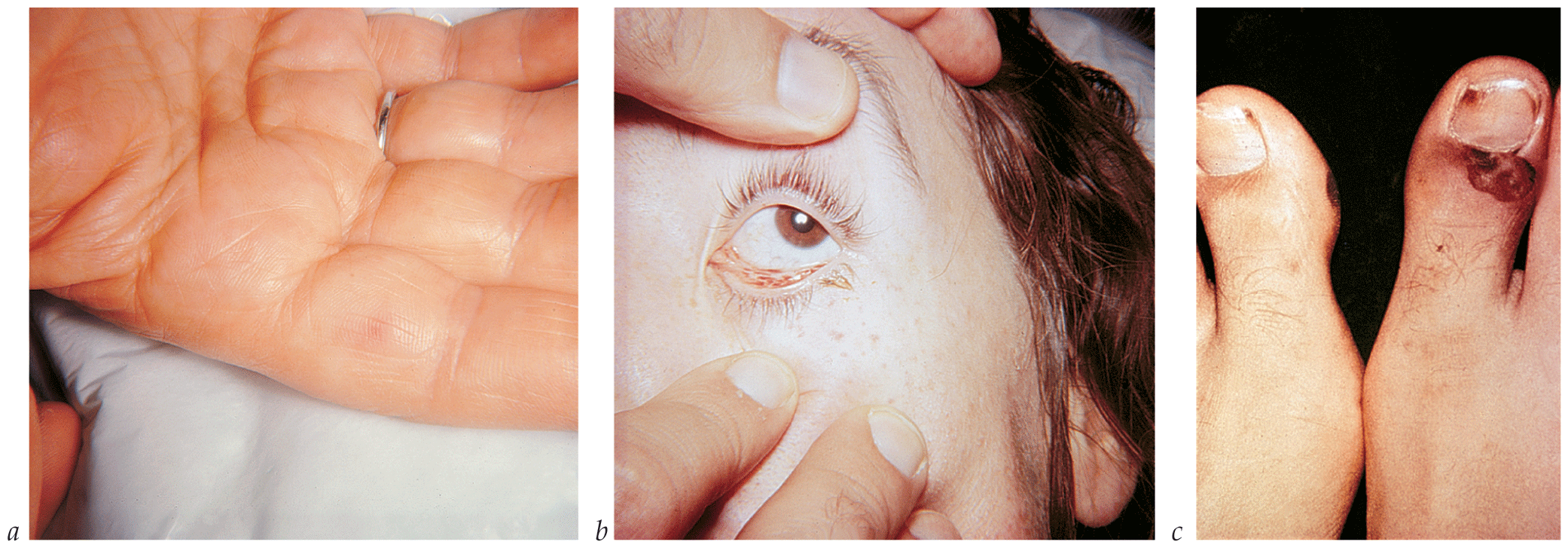
- Bactericidal antibiotics are used parenterally in high doses. With the exception of PVE caused by staphylococci, antimicrobial therapy for PVE caused by a specific organism uses the same drugs recommended for native valve endocarditis.
- Endocarditis caused by relatively penicillin-resistant (MIC = 0.2 to 0.5 µg/mL) viridans or other nonenterococcal streptococci is treated with a higher dose of penicillin G combined with gentamicin. If the strain is even more resistant to penicillin (MIC > 0.5 µg/mL), the infection is treated with one of the standard regimens for enterococcal endocarditis.
- Operative intervention to débride infected perivalvular tissue or to replace or reconstruct a dysfunctioning valve is important in the management of complicated infective endocarditis that involves either a native or a prosthetic valve. Overall, surgery is indicated in 25 to 40% of patients with infective endocarditis, and up to 45% of patients undergo surgery during the active phase of their disease.

Management and Therapeutic Issues in the Dementias
- The cholinesterase inhibitors donepezil, galantamine, and rivastigmine have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of AD dementia.
- Patients with mild to moderate AD dementia are the appropriate candidates for cholinesterase inhibitor therapy. These patients need a designated caregiver to supervise the use of the medication.
- Support for and empowerment of the caregivers of dementia patients must be an integral part of management. The emotional and physical health of caregivers is critical to long-term outcomes.


.png)







