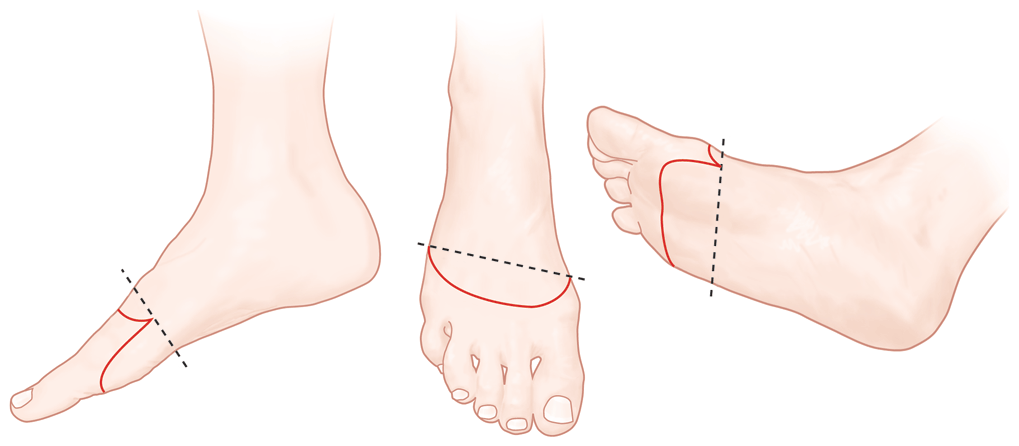
Lower Extremity Amputation for Ischemia
- Amputations on the foot require normal or near-normal arterial supply to heal.
- Pulsatile flow into the deep femoral artery is typically adequate to heal a below-the-knee amputation.
- Prosthetic limb rehabilitation is more likely in case of below-the-knee amputation than above-the-knee amputation.
- Above-the-knee amputation is preferred in nonfunctional extremities.



.png)






