Disorders of Water and Sodium Balance: Hypernatremia
- Hydrochlorothiazide is not beneficial in treating ICU-acquired hypernatremia
- Hypernatremia after hypertonic saline irrigation is rare, but might cause severe complications
- Hypercalcemia induces targeted autophagic degradation of aquaporin-2 at the onset of nephrogenic diabetes insipidus
- Hypernatremia identified as new predictor of worse clinical outcomes after percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy placement
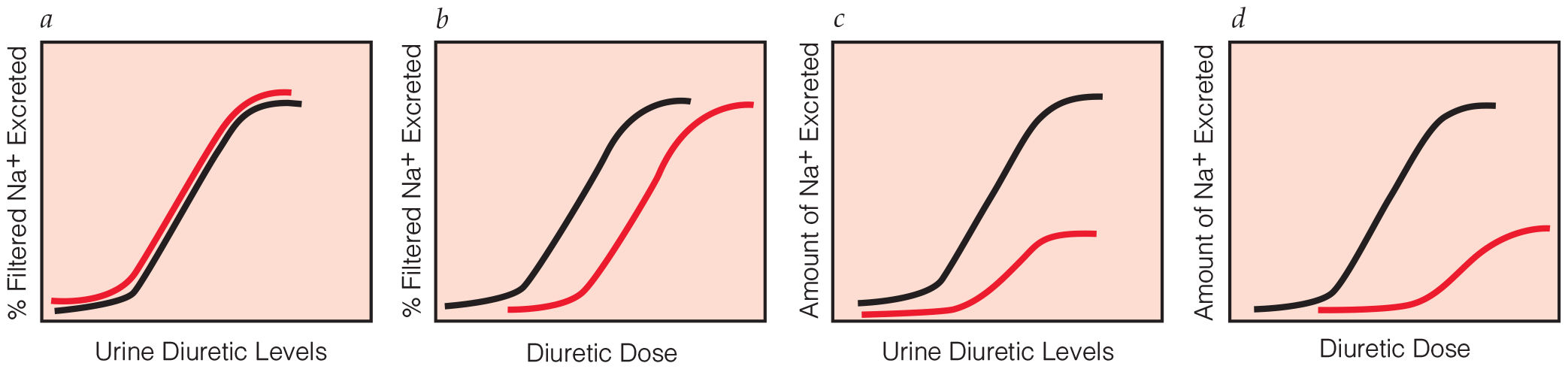
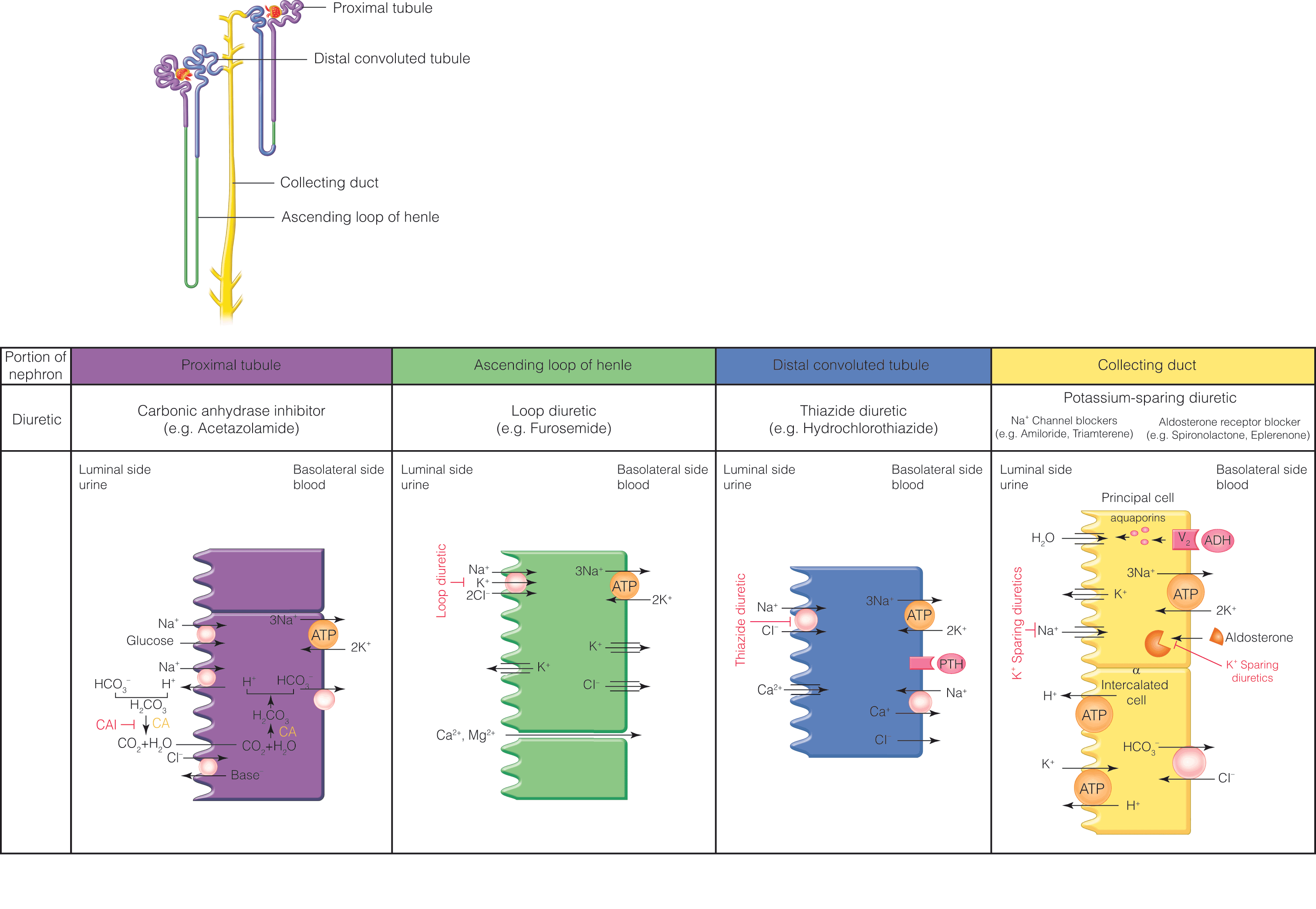


.png)







