- Members of the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer–Invasive Fungal Infection Cooperative Group and National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Mycoses Study Group formed a consensus committee to develop standard definitions for invasive fungal infections for clinical research.
- The development of standardized methodology for antifungal susceptibility testing is another recent advance in the laboratory evaluation of Aspergillus species. Although azole resistance by Aspergillus species is unusual, patients exposed chronically to antifungal triazoles have been reported to have refractory infection caused by isolates with elevated minimum inhibitory concentrations.
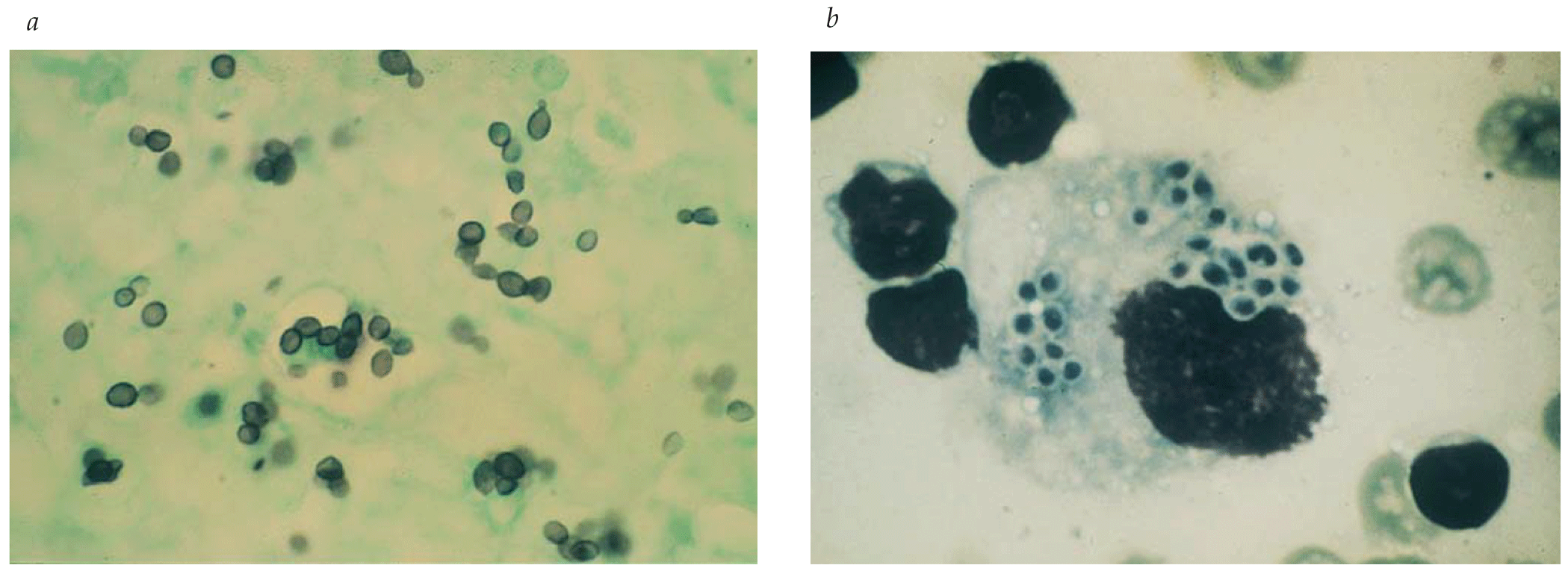
- Fusarium and Scedosporium species are increasingly common causes of infections in surgical patients, especially in recipients of stem cell or organ transplants.
Latest Updates
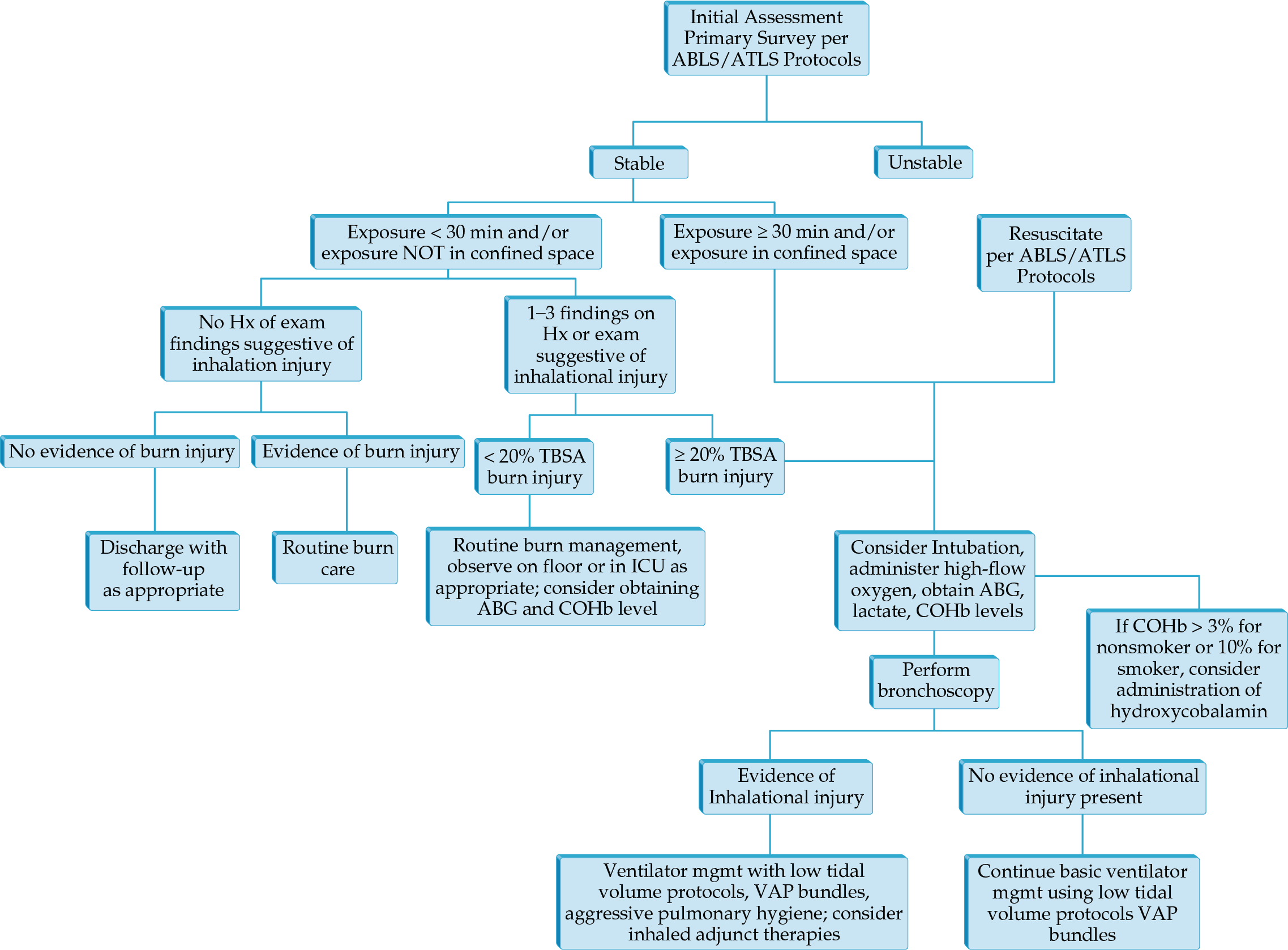
- CT of the chest has taken a greater role in determining injury severity in inhalation injury.
- Airway control and ventilator management remain the mainstays of treatment in those with severe injury.
- Volumetric diffusive respiration is a mode specifically developed for inhalation injury that has been shown to decrease use of other rescue modes of ventilation.
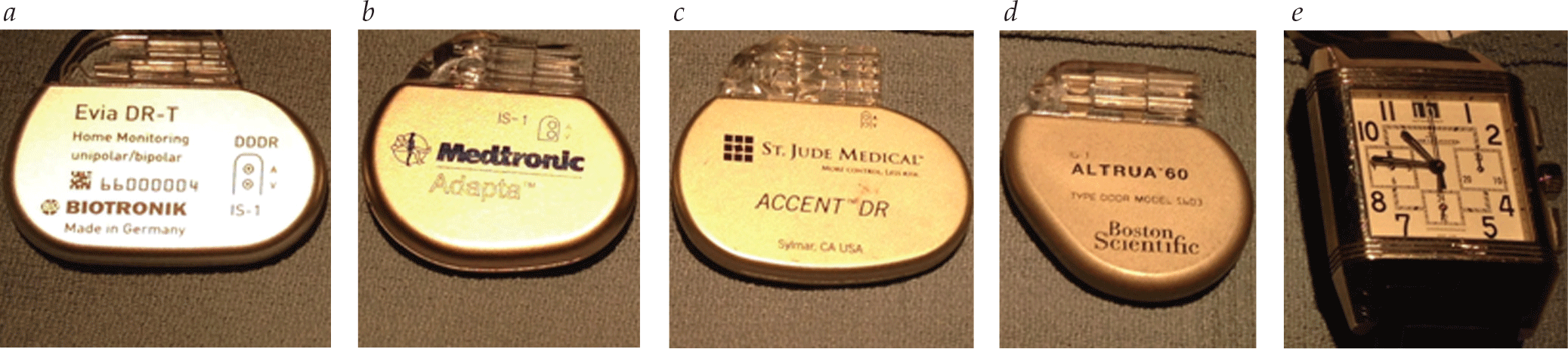
- The number of permanent pacemakers implanted per year increased by 55.6% between 1993 and 2009, and is continuing to rise. Accordingly, the number of patients treated in the emergency department who have permanent pacemakers is increasing, and it is important for physicians in the emergency department to be familiar with the operation and potential complications of these devices.
- Genetic testing of first-degree relatives is recommended according to 2018 ACC/AHA/HRS guidelines on evaluation of bradycardia and conduction delay.
- Permanent pacing is reasonable intervention for patients with tachy-brady syndrome and symptoms attributable to bradycardia.
- 2018 ACC/AHA/HRS specific guideline considerations for genetic disorders, neuromuscular disorders, and infiltrative disorders (e.g., cardiac sarcoidosis and amyloidosis).
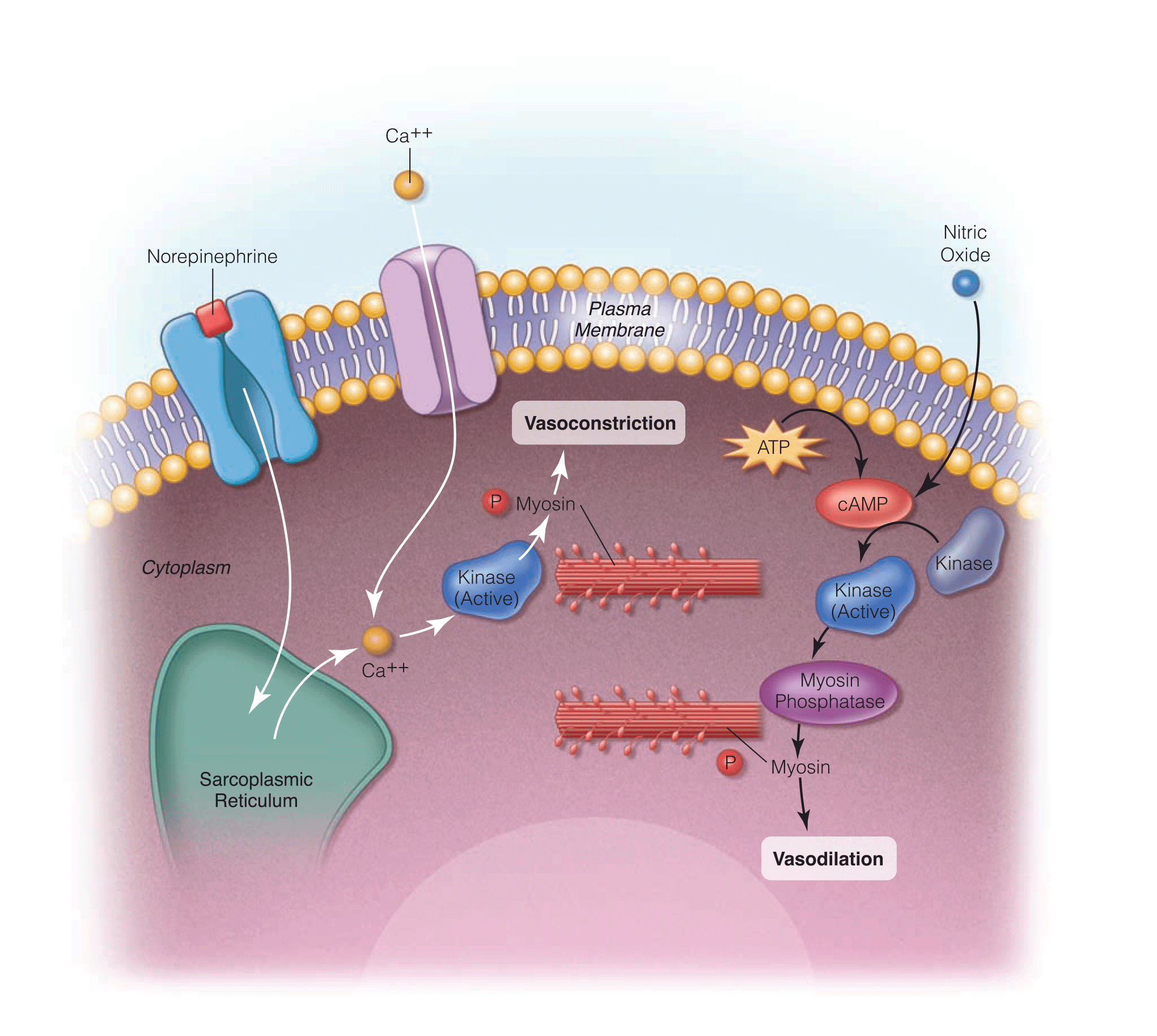
- Pulmonary hypertension can be treated with single or combination therapy employing calcium channel blockers, phosphodiesterase inhibitors, guanylate cyclase stimulators, endothelin receptor antagonists, and prostanoids.
- Levosimendan is a calcium sensitizer used to treat cardiogenic shock and right heart failure.
- Clevidipine is an ultra-rapid acting calcium channel blocker used for perioperative hypertension management in cardiovascular and vascular diseases, neurosurgery, and surgery for pheochromocytoma.

- Radiofrequency ablation as a treatment modality has revolutionized therapy for many SVTs; acts as a first-line alternative to drug therapy in some circumstances, with a high acute success rate and relatively low complication rate.
- Cryoablation therapy emerging as an alternative in ablative therapies. Investigation of this modality for SVTs is ongoing.
- Detailed drug regimens optimized for acute and chronic management of specific SVTs; detailed in the 2015 ACC/AHA/HRS practice guidelines.

- The REVERT trial concluded that a modified valsalva maneuver has a higher rate of cardioversion than historical vagal maneuvers.
- In a patient with stable SVT where vagal maneuvers have failed, IV adenosine remains the first-line pharmacologic agent.
- Combining adenosine and saline in a single syringe, rather than administration of adenosine followed by a saline flush, has been proven to be an effective form of administration.
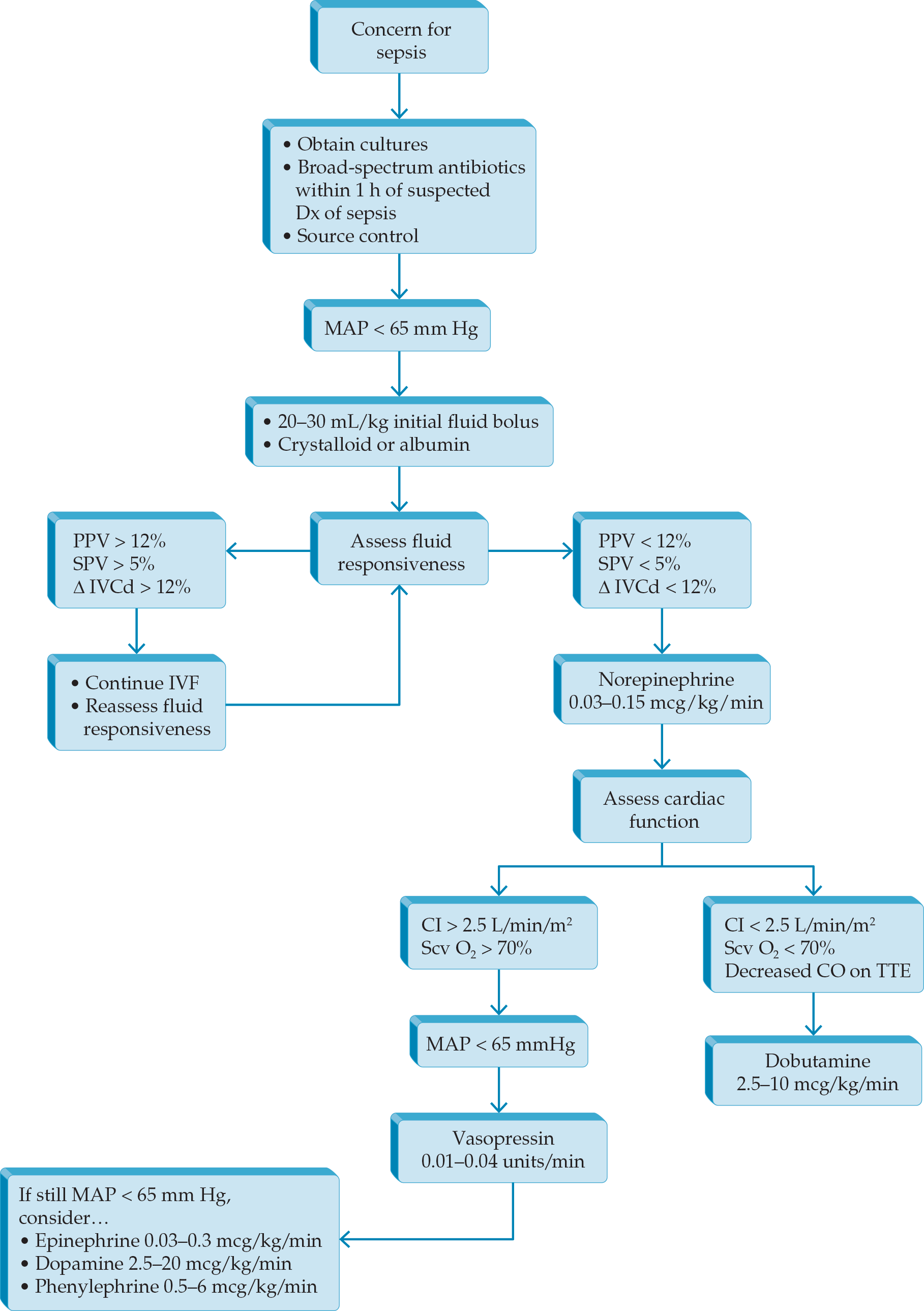
- Sepsis syndromes have been redefined (Sepsis-3 definitions) by international experts, based on sepsis mortality data extracted large administrative databases.
- National focus has turned to early identification of sepsis as a key determinant of outcomes. International critical care experts have recommended using the qSOFA criteria in the Emergency Department setting to identify sepsis risk in patients prior to obtaining diagnostics.
- The Center for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) has added a sepsis quality measure (SEP-1) as a reporting requirement for all US hospital tied to Medicare & Medicaid reimbursement. This measure has increased awareness of sepsis performance and focused quality efforts on improvement.
- 2018 update to bundles to simplify to 1-hour bundle.
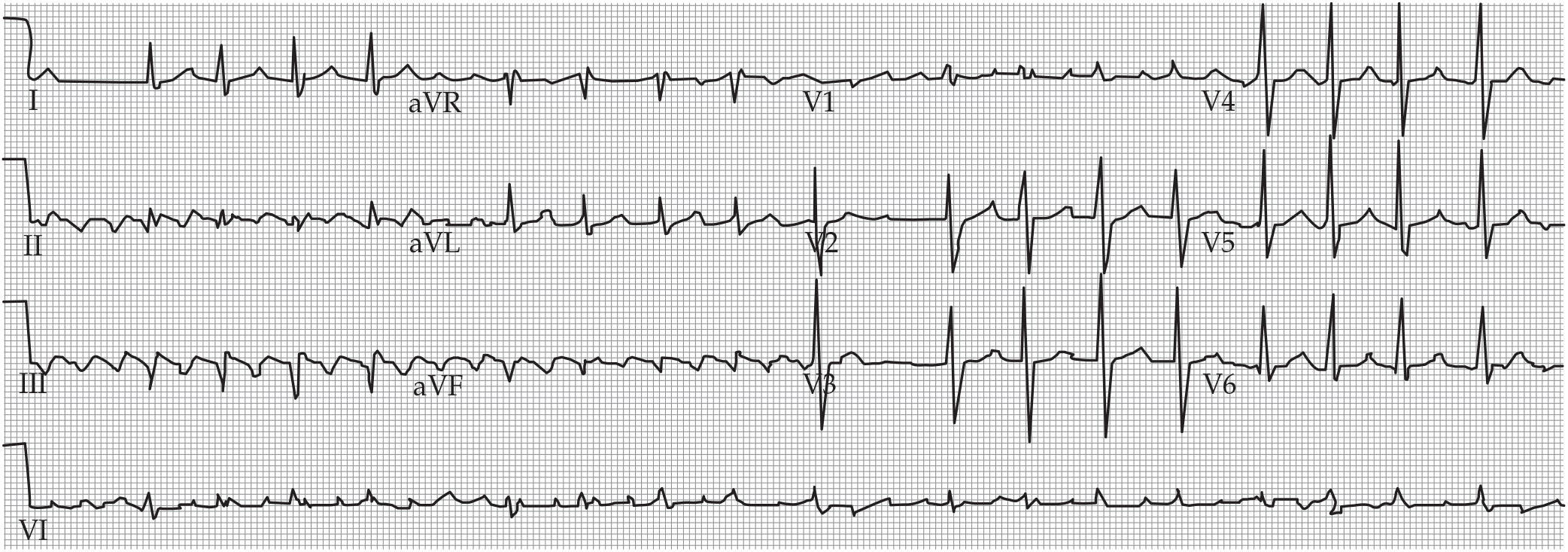
- Latest available ACC/AHA guidelines and ongoing controversy around optimal heart rate targets
- Updated classification for patients with valvular and nonvalvular AF algorithm for maintenance of sinus rhythm
- 2019 AHA/ACC/HRS and 2020 ESC/EACTS practice guidelines delineated new and modified anticoagulation recommendations pertaining to NOACs.


.png)







