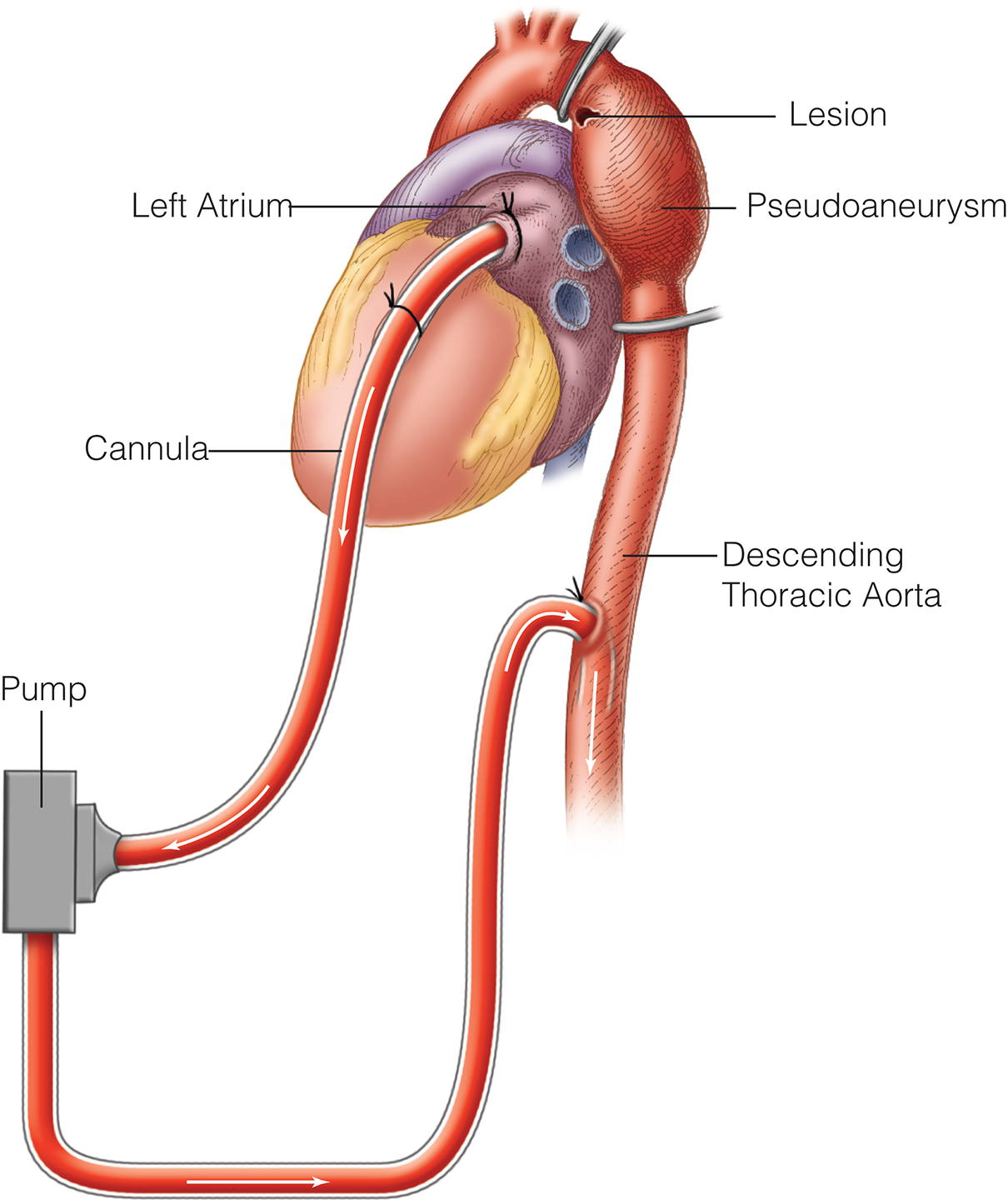
- BTAI is now the gold standard n treating patients with these problems
- The grade of injury with these lesions has been defined and there is controversy on which lesion should be treated and how emergently
- Recently in the US a device changed its IFU because of complications after TEVAR for BTAI. It was being used outside its IFU.
- Recent advancement on sizing and device differences between BTAI and other pathologies treated with TEVAR
Latest Updates

- BTAI is now the gold standard n treating patients with these problems
- The grade of injury with these lesions has been defined and there is controversy on which lesion should be treated and how emergently
- Recently in the US a device changed its IFU because of complications after TEVAR for BTAI. It was being used outside its IFU.
- Recent advancement on sizing and device differences between BTAI and other pathologies treated with TEVAR
Part 1: Borderline Personality Disorder and Its Clinical Features
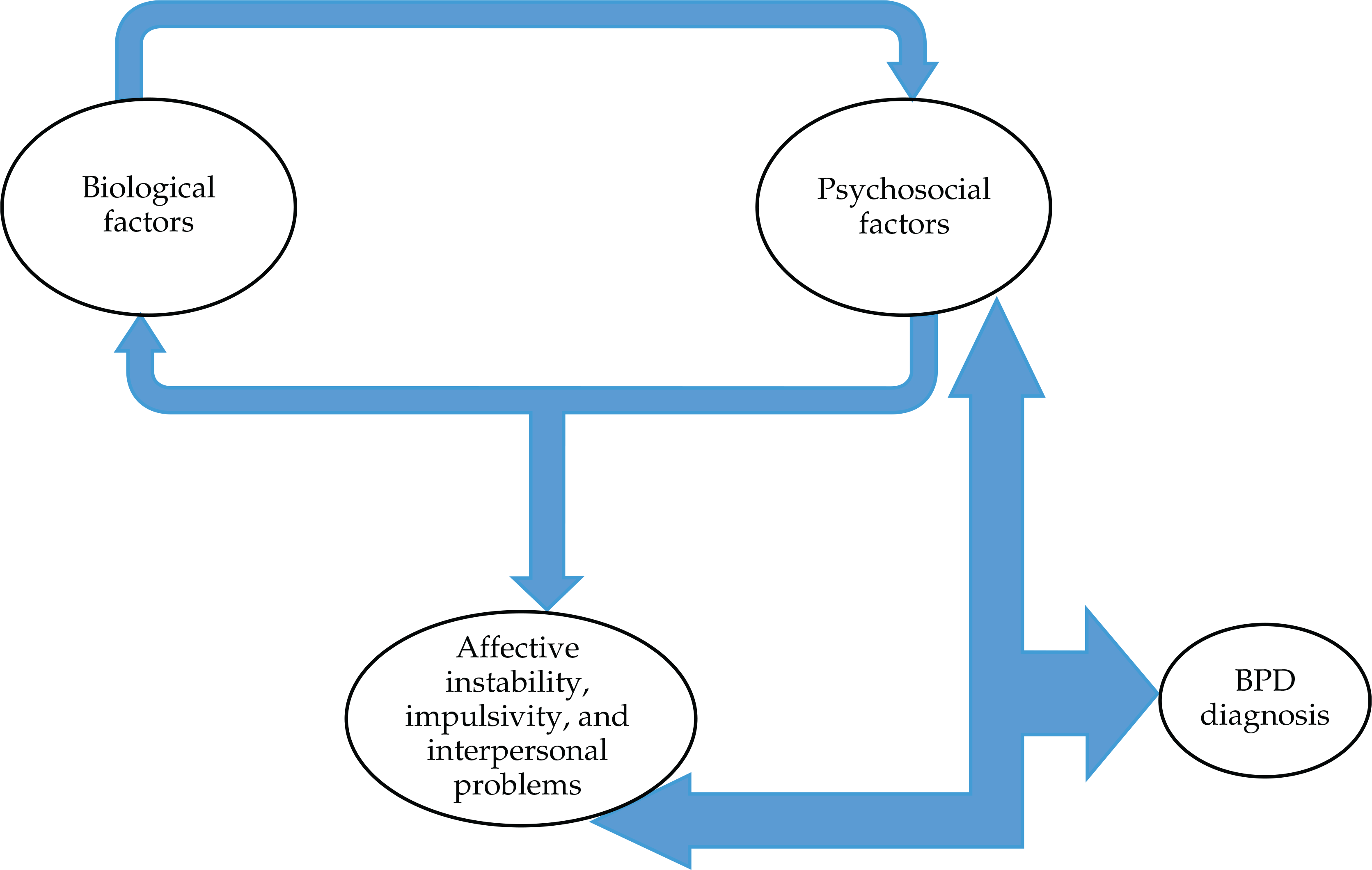
- Diagnosing borderline personality disorder (BPD) is focused on identifying patterns of symptoms that are consistent over time across several domains.
- Development of BPD depends on an interactive combination of temperamental factors and environment stresses.
- Distinguishing BPD from other psychiatric disorders, such as bipolar disorder, is essential in providing effective treatment.
- Patients with BPD are highly stigmatized in the mental health system and receive poorer quality of care than patients with some other disorders.
- BPD has a positive prognosis, with improvements typically seen within several years.
Gastrointestinal: Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding
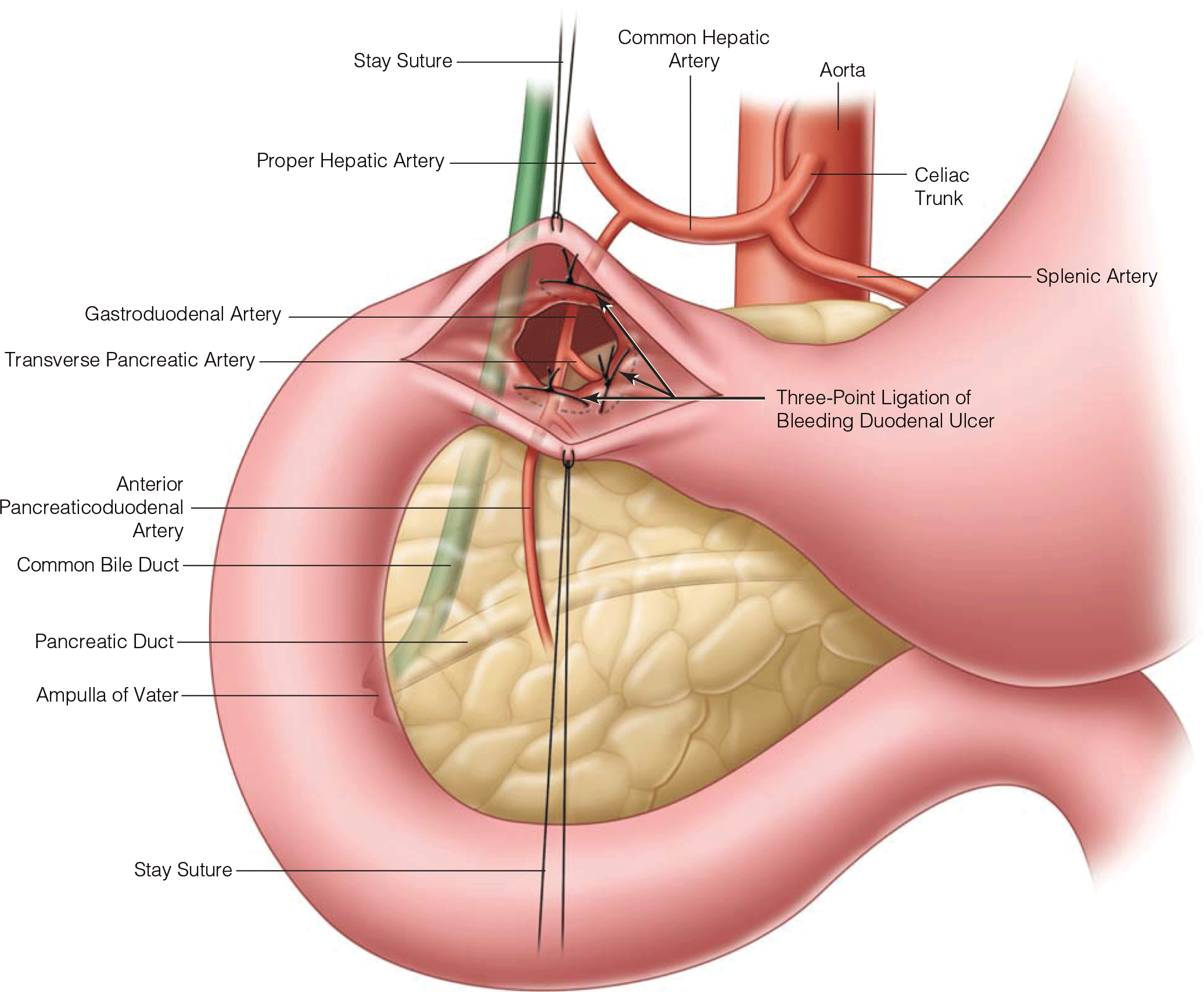
- Several clinical prediction scores have been developed to risk-stratify patients presenting with upper gastrointestinal bleeding (UGIB) and can help guide the sequence of diagnostic tests and subsequent management. The two most commonly used are the Glasgow-Blatchford score and Rockall score. These scoring systems are designed to aid in the identification of patients who will require acute interventions and determine the risk of rebleeding and mortality.
- Endoscopic intervention is beneficial in high-risk patients with UGIB, reducing the rate of rebleeding, the need for surgical intervention, and mortality. Recent advances in the use of combination therapies and newer mechanical means of hemostasis have increased the success of endoscopic management.
- Contrast-enhanced, multiphase computed tomography (CT) techniques have improved dramatically over the last decade. CT serves as an excellent complementary test to endoscopic techniques in the management of the hemodynamically stable patient.
- Transcatheter angiographic embolization is an attractive alternative to surgical intervention in select patients. Advances in catheter-based delivery systems have increased the success rate of angiographic embolization, particularly in patients who have a failed second attempt at endoscopic hemostasis.
Practicing Evidence-Based Medicine
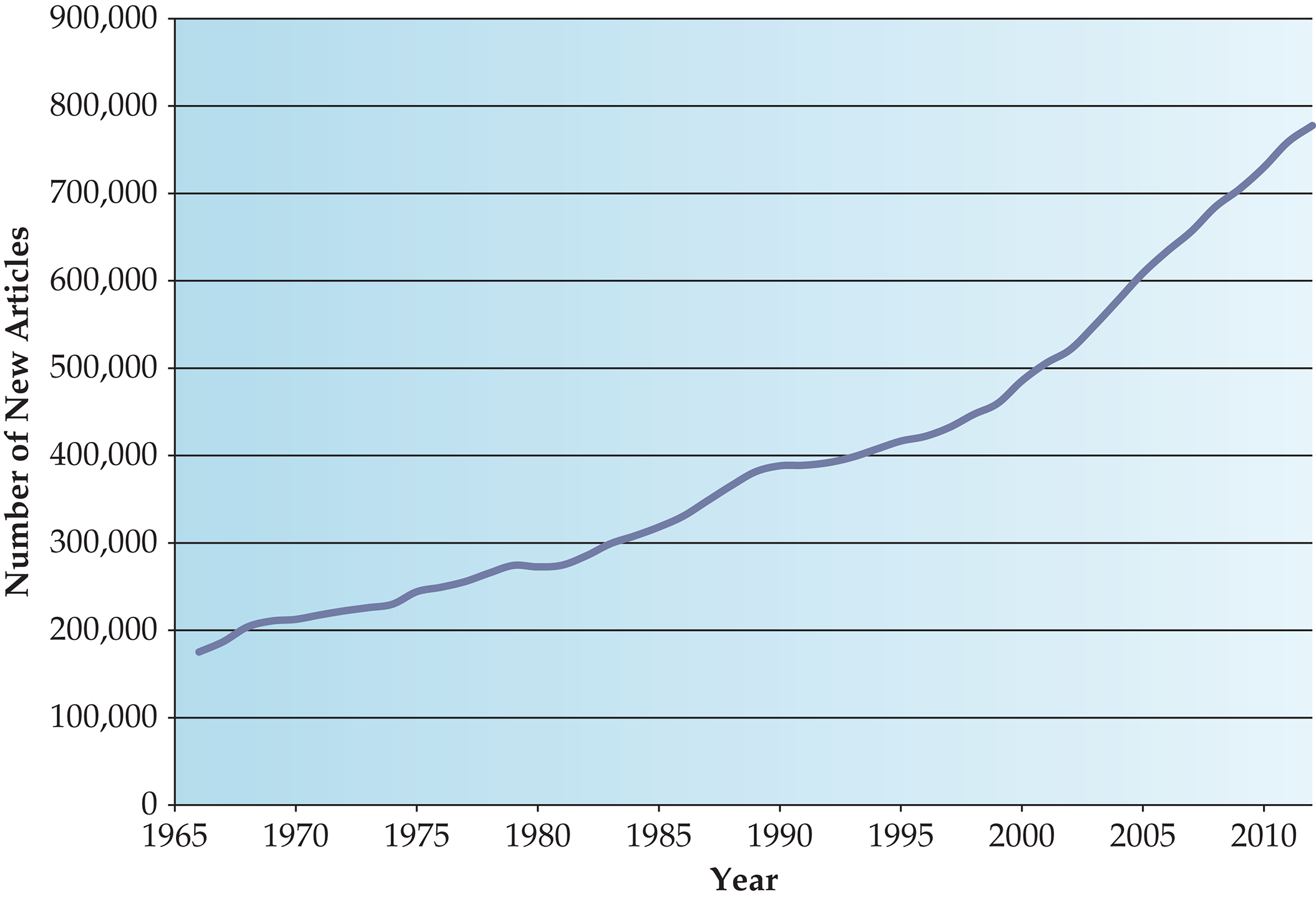
- Even the most competent physician can be prone to misusing epidemiologic concepts. An example of inaccurate decision making, resting on Bayes’s theorem, occurred in a recent study in which primary care physicians were given clinical scenarios. Although the clinicians confidently provided their estimates of the probabilities of given disorders, no consensus could be found among the estimates. Another study assessed the ability of medical students, residents, and attending physicians to correctly determine the positive predictive value of a hypothetical screening test. The vast majority of respondents not only got the question wrong but also had an answer that would have led to the opposite clinical conclusions, guessing an incorrect positive predictive value of 95% when the true answer was 2%.

Injection Sclerotherapy and Ablation
- Endovenous laser ablation (EVLA) has many similarities to radiofrequency ablation (RFA), with the primary differences related to the catheter and mechanism used to ablate the vein. EVLA uses a bare-tipped or jacket-tipped fiber to deliver laser energy to a target area.
- The thermal energy generates heat and steam bubbles within the lumen of the target vessel, destroying the endothelial lining of the vessel. This causes an inflammatory and constricting reaction that leads to fibrosis and occlusion of the treated vein.
- Of note, the incidence of severe postprocedure pain and bruising has been significantly decreased with the advent of the new-generation covered fibers and hemoglobin-targeted chromophore, such that these adverse events are now comparable to those seen with RFA.
- Latest available ACC/AHA guidelines and ongoing controversy around optimal heart rate targets
- Updated classification for patients with valvular and nonvalvular AF algorithm for maintenance of sinus rhythm
- 2019 AHA/ACC/HRS and 2020 ESC/EACTS practice guidelines delineated new and modified anticoagulation recommendations pertaining to NOACs.


- Latest available ACC/AHA guidelines and ongoing controversy around optimal heart rate targets
- Updated classification for patients with valvular and nonvalvular AF algorithm for maintenance of sinus rhythm
- 2019 AHA/ACC/HRS and 2020 ESC/EACTS practice guidelines delineated new and modified anticoagulation recommendations pertaining to NOACs.


.png)






