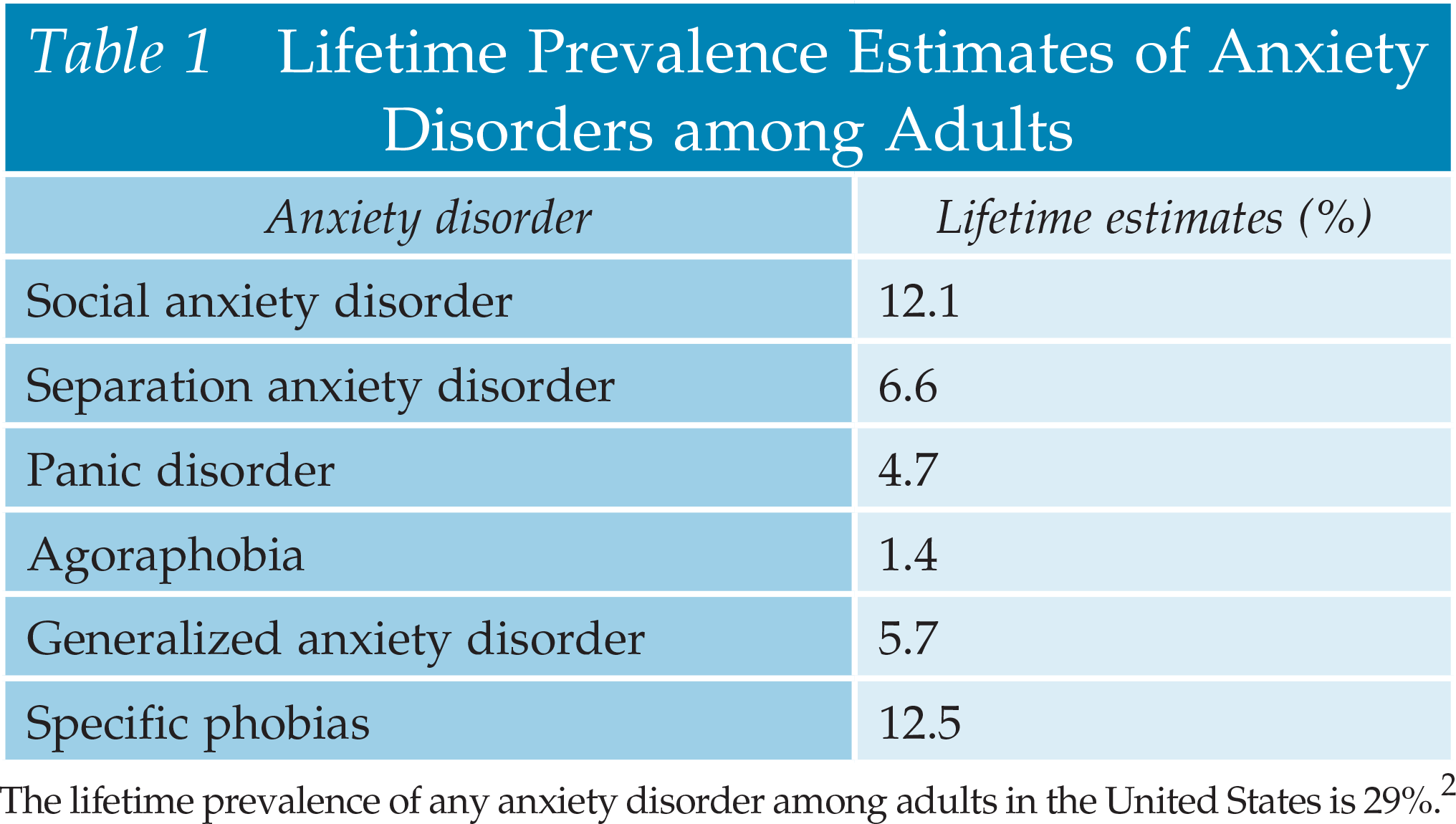
- Anxiety disorders are common and disabling conditions.
- Most anxiety disorders affect almost twice as many women as men.
- If untreated, anxiety disorders tend to recur chronically.
- Psychological and pharmacologic treatments are often effective
Latest Updates

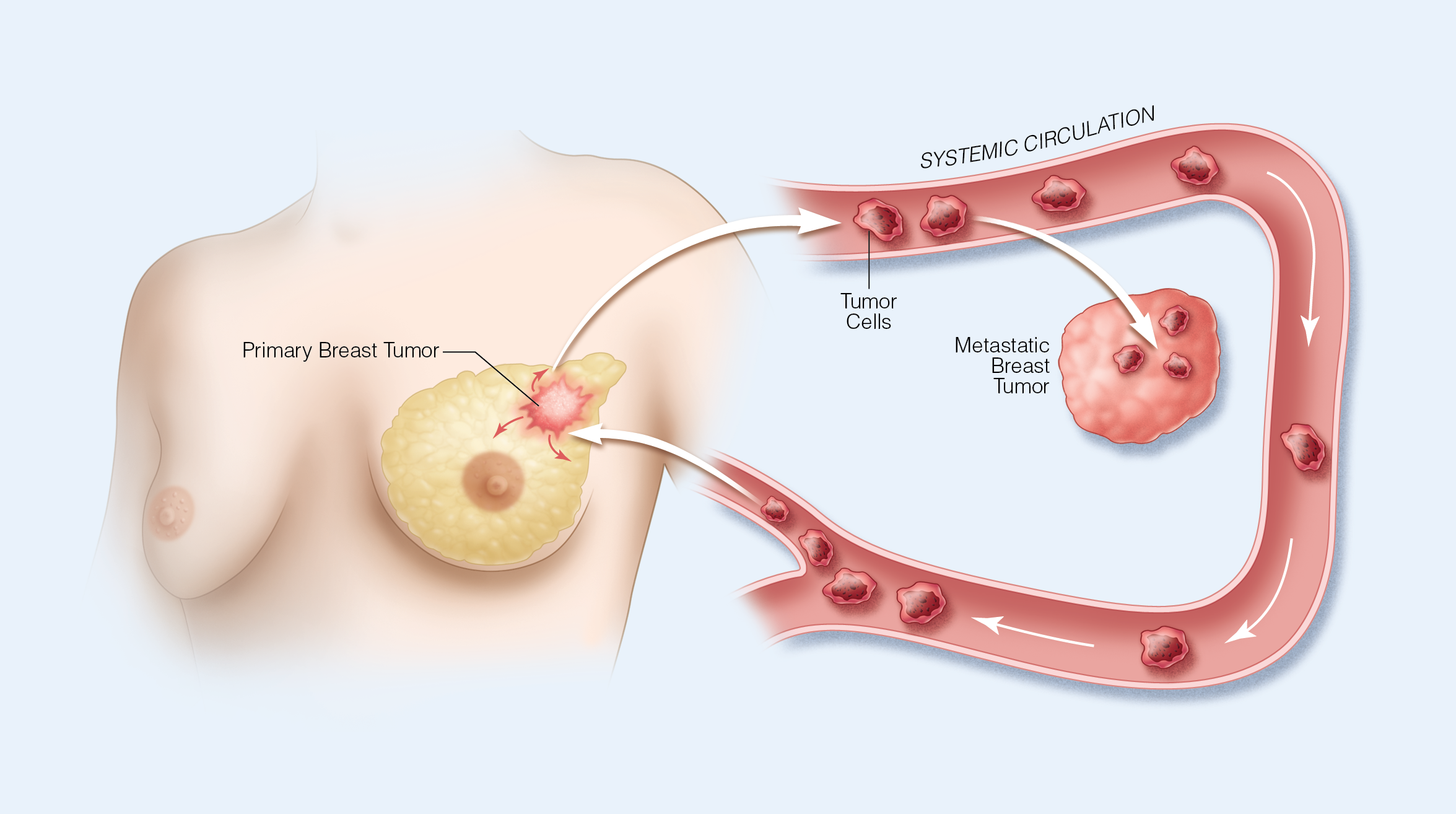
Locoregional Therapy for the Primary Tumor in Stage IV Breast Cancer
- Expanding indications for surgery for the primary tumor in stage IV breast cancer
- Defining extent of locoregional therapy in stage IV breast cancer
- Biological implications for removing the primary tumor in stage IV breast cancer

Locoregional Therapy for the Primary Tumor in Stage IV Breast Cancer
- Expanding indications for surgery for the primary tumor in stage IV breast cancer
- Defining extent of locoregional therapy in stage IV breast cancer
- Biological implications for removing the primary tumor in stage IV breast cancer
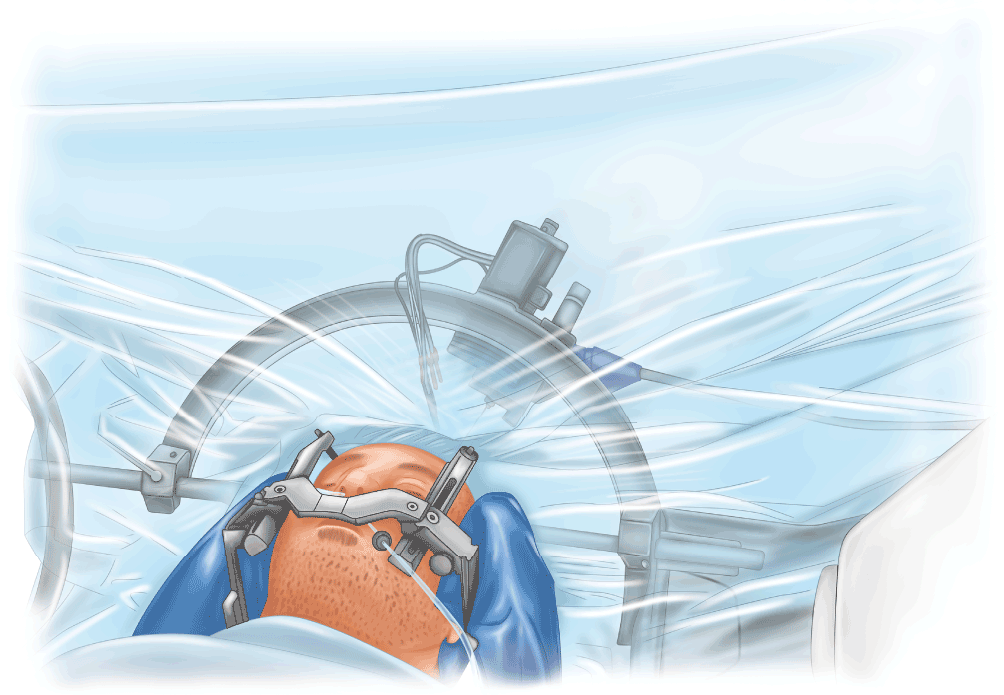
- The indications for awake neurosurgery have grown substantially over time, requiring anesthesiologists to maintain and improve the unique skill set needed to care for these patients.
- A variety of anesthetic approaches to awake craniotomy have evolved over time. There is an increasing prevalence of dexmedetomidine in anesthetic regimens described. Also, the trend toward using shorter-acting medications is only likely to continue.
- The many pitfalls of anesthetic management of awake craniotomy patients requires keen awareness of issues such as patient inclusion/exclusion criteria, intraoperative management of co-morbid diseases and airway emergencies.
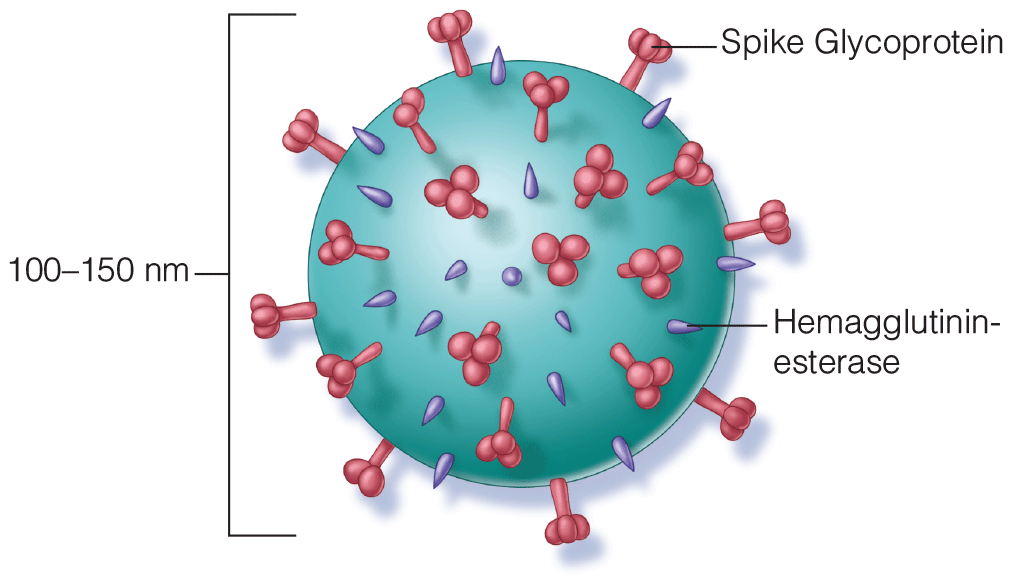
Coronaviruses: HCoV, SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, and COVID-19
- Specific features on high resolution CT imaging for the more severe coronavirus syndromes are now accepted for clinical diagnosis in the appropriate context, followed by RT-PCR confirmation. This includes ground-glass opacity, with lower-lobe and bilateral involvement, and septal thickening. Other characteristics make diagnosis more or less likely.
- Molecular studies of the evolution of the S protein affinity for COVID-19 allow more complete understanding of the mechanism of transmission and predisposing factors. These attachment proteins have highest affinity for ACE2 receptors on type II pneumocytes. What remains to be explained is the presence of virus in saliva, blood, urine and gastrointestinal tract: Are these potential modes of transmission?
- Two clinical trials have demonstrated promise for SARS-CoV-2 immunization; humoral and cellular immune responses are elicited. The preliminary data of these studies were published on July 20, 2020.

Coronaviruses: HCoV, SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, and COVID-19
- Specific features on high resolution CT imaging for the more severe coronavirus syndromes are now accepted for clinical diagnosis in the appropriate context, followed by RT-PCR confirmation. This includes ground-glass opacity, with lower-lobe and bilateral involvement, and septal thickening. Other characteristics make diagnosis more or less likely.
- Molecular studies of the evolution of the S protein affinity for COVID-19 allow more complete understanding of the mechanism of transmission and predisposing factors. These attachment proteins have highest affinity for ACE2 receptors on type II pneumocytes. What remains to be explained is the presence of virus in saliva, blood, urine and gastrointestinal tract: Are these potential modes of transmission?
- Two clinical trials have demonstrated promise for SARS-CoV-2 immunization; humoral and cellular immune responses are elicited. The preliminary data of these studies were published on July 20, 2020.

Coronaviruses: HCoV, SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, and COVID-19
- Specific features on high resolution CT imaging for the more severe coronavirus syndromes are now accepted for clinical diagnosis in the appropriate context, followed by RT-PCR confirmation. This includes ground-glass opacity, with lower-lobe and bilateral involvement, and septal thickening. Other characteristics make diagnosis more or less likely.
- Molecular studies of the evolution of the S protein affinity for COVID-19 allow more complete understanding of the mechanism of transmission and predisposing factors. These attachment proteins have highest affinity for ACE2 receptors on type II pneumocytes. What remains to be explained is the presence of virus in saliva, blood, urine and gastrointestinal tract: Are these potential modes of transmission?
- Two clinical trials have demonstrated promise for SARS-CoV-2 immunization; humoral and cellular immune responses are elicited. The preliminary data of these studies were published on July 20, 2020.

Coronaviruses: HCoV, SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, and COVID-19
- Specific features on high resolution CT imaging for the more severe coronavirus syndromes are now accepted for clinical diagnosis in the appropriate context, followed by RT-PCR confirmation. This includes ground-glass opacity, with lower-lobe and bilateral involvement, and septal thickening. Other characteristics make diagnosis more or less likely.
- Molecular studies of the evolution of the S protein affinity for COVID-19 allow more complete understanding of the mechanism of transmission and predisposing factors. These attachment proteins have highest affinity for ACE2 receptors on type II pneumocytes. What remains to be explained is the presence of virus in saliva, blood, urine and gastrointestinal tract: Are these potential modes of transmission?
- Two clinical trials have demonstrated promise for SARS-CoV-2 immunization; humoral and cellular immune responses are elicited. The preliminary data of these studies were published on July 20, 2020.


.png)






