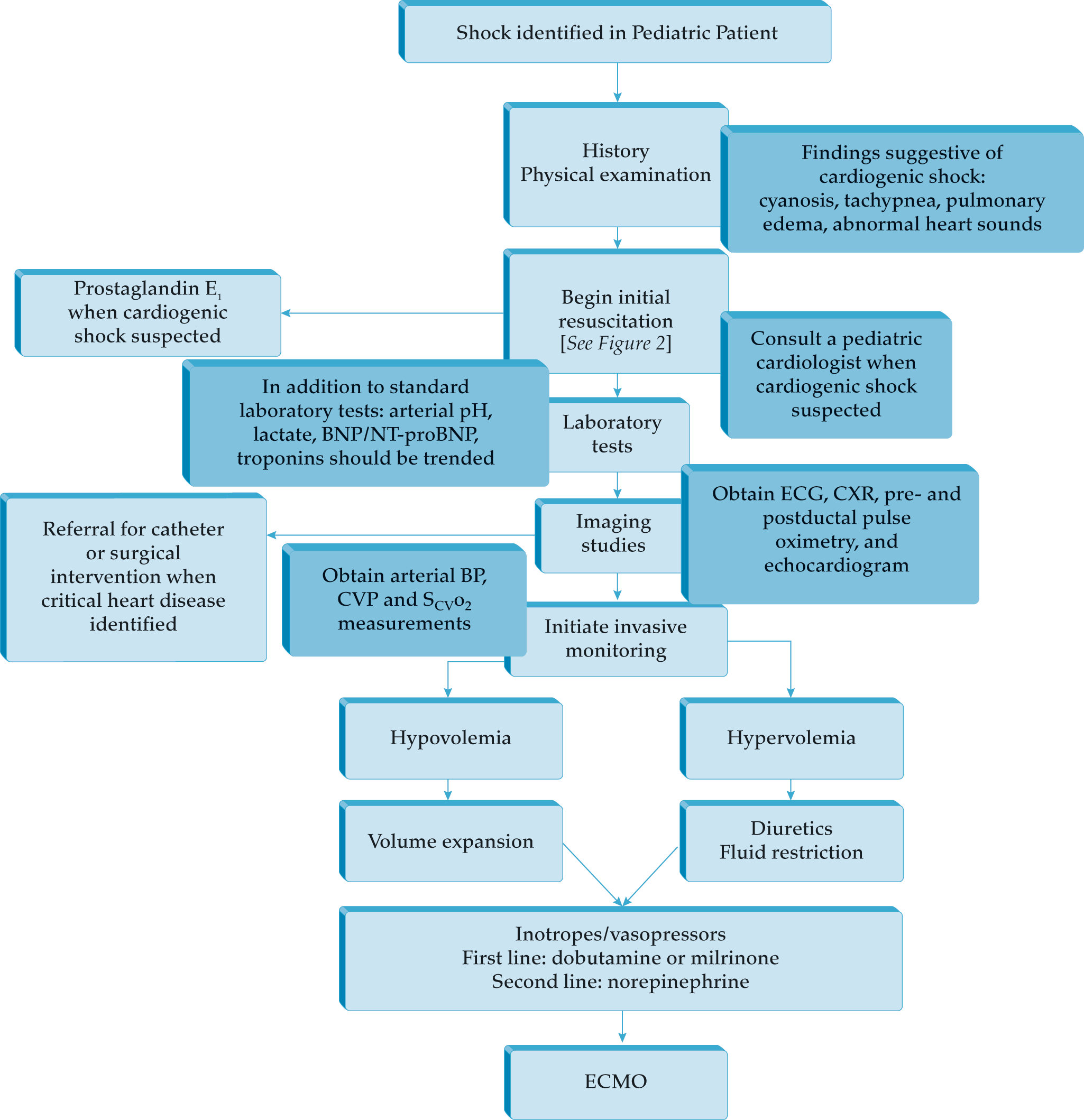
Cardiac Patients for Non-Cardiac Surgeries
- Improved survival of patients with congenital heart disease requires all anesthesiologists to be familiar with basic pathophysiological concepts and long term problems after repair or palliation of heart defects.
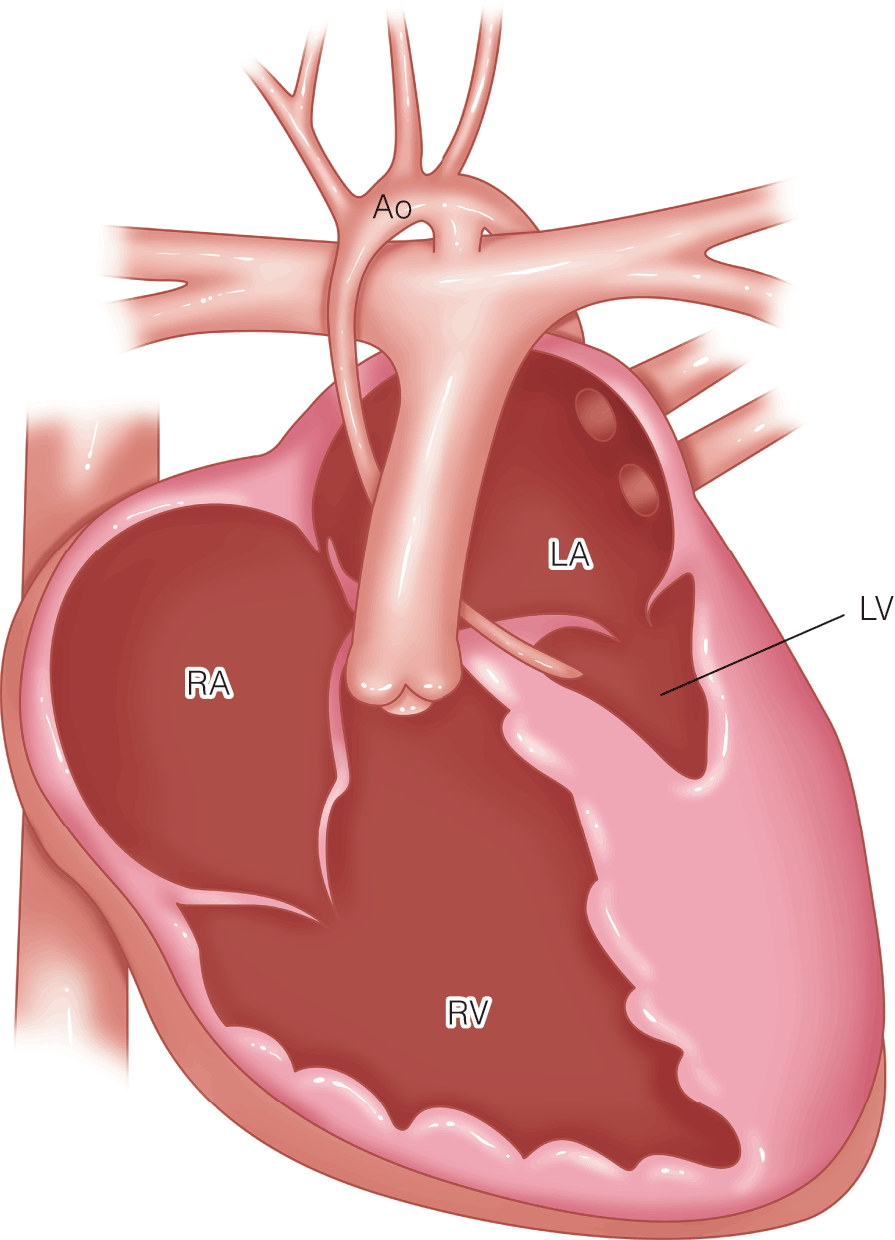
- Complex congenital heart defects are nowadays often managed with staged palliations and multiple interventions in the cardiac catheterization laboratory. A thorough understanding of the physiological implications for each of these stages is important for a safe anesthetic management.
- Minimal invasive surgical techniques can have major implications for patients with single ventricle physiology.
- Recent advances in the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension and heart transplantations will increase the number of imaging studies and interventions for surveillance and therapy adjustments.



.png)







