- 2017 Japan Society for Equilibrium Research guideline on classification, diagnostic criteria, and management of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo
- Latest American Physical Therapy Association guideline on vestibular rehabilitation for peripheral vestibular hypofunction
- 2017 American Physical Therapy Association practice guidelines on dizziness
- 2017 American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery Practice Guideline included
Latest Updates
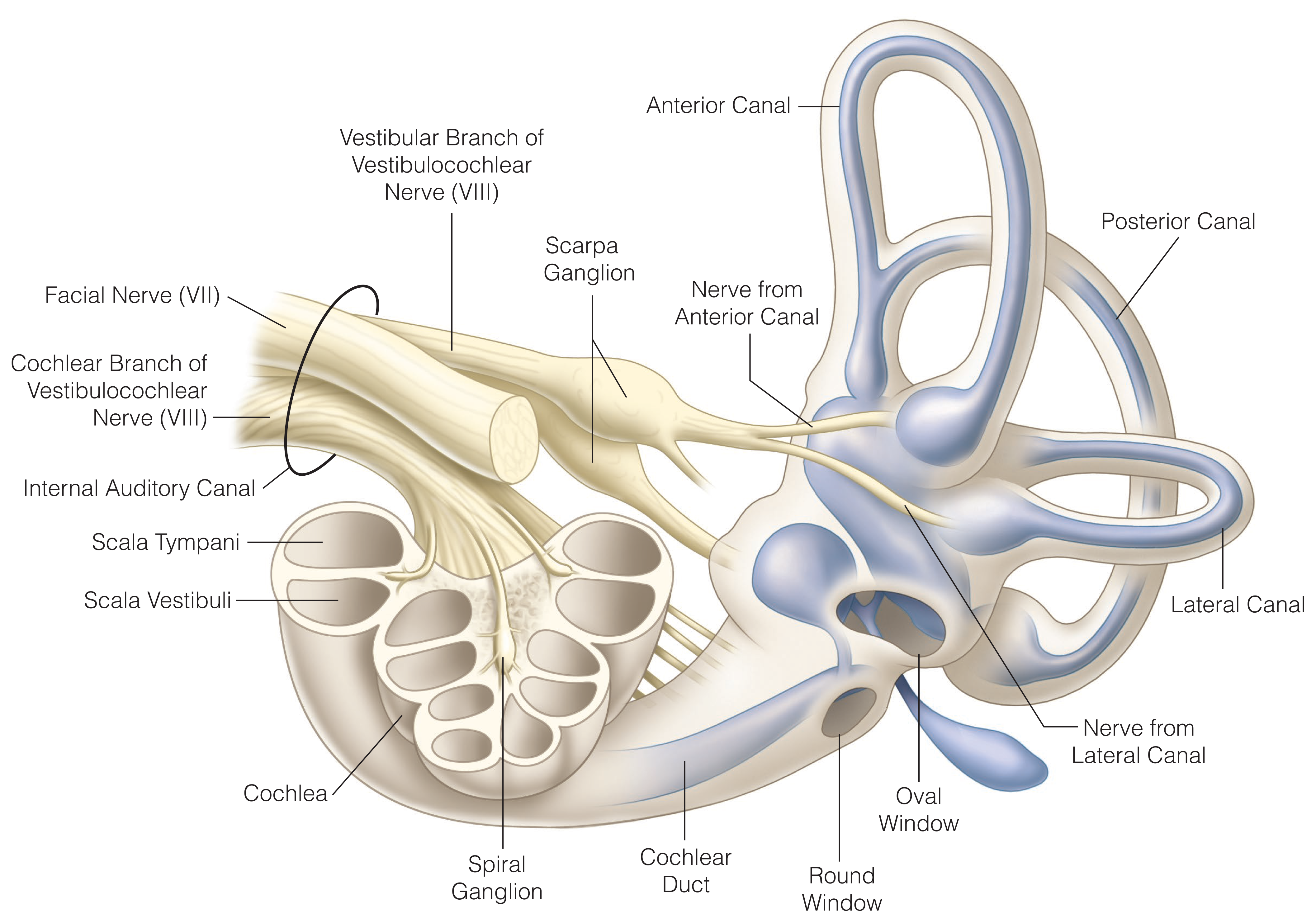

- 2017 Japan Society for Equilibrium Research guideline on classification, diagnostic criteria, and management of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo
- Latest American Physical Therapy Association guideline on vestibular rehabilitation for peripheral vestibular hypofunction
- 2017 American Physical Therapy Association practice guidelines on dizziness
- 2017 American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery Practice Guideline included

- 2017 Japan Society for Equilibrium Research guideline on classification, diagnostic criteria, and management of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo
- Latest American Physical Therapy Association guideline on vestibular rehabilitation for peripheral vestibular hypofunction
- 2017 American Physical Therapy Association practice guidelines on dizziness
- 2017 American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery Practice Guideline included


- 2017 Japan Society for Equilibrium Research guideline on classification, diagnostic criteria, and management of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo
- Latest American Physical Therapy Association guideline on vestibular rehabilitation for peripheral vestibular hypofunction
- 2017 American Physical Therapy Association practice guidelines on dizziness
- 2017 American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery Practice Guideline included

- 2017 Japan Society for Equilibrium Research guideline on classification, diagnostic criteria, and management of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo
- Latest American Physical Therapy Association guideline on vestibular rehabilitation for peripheral vestibular hypofunction
- 2017 American Physical Therapy Association practice guidelines on dizziness
- 2017 American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery Practice Guideline included
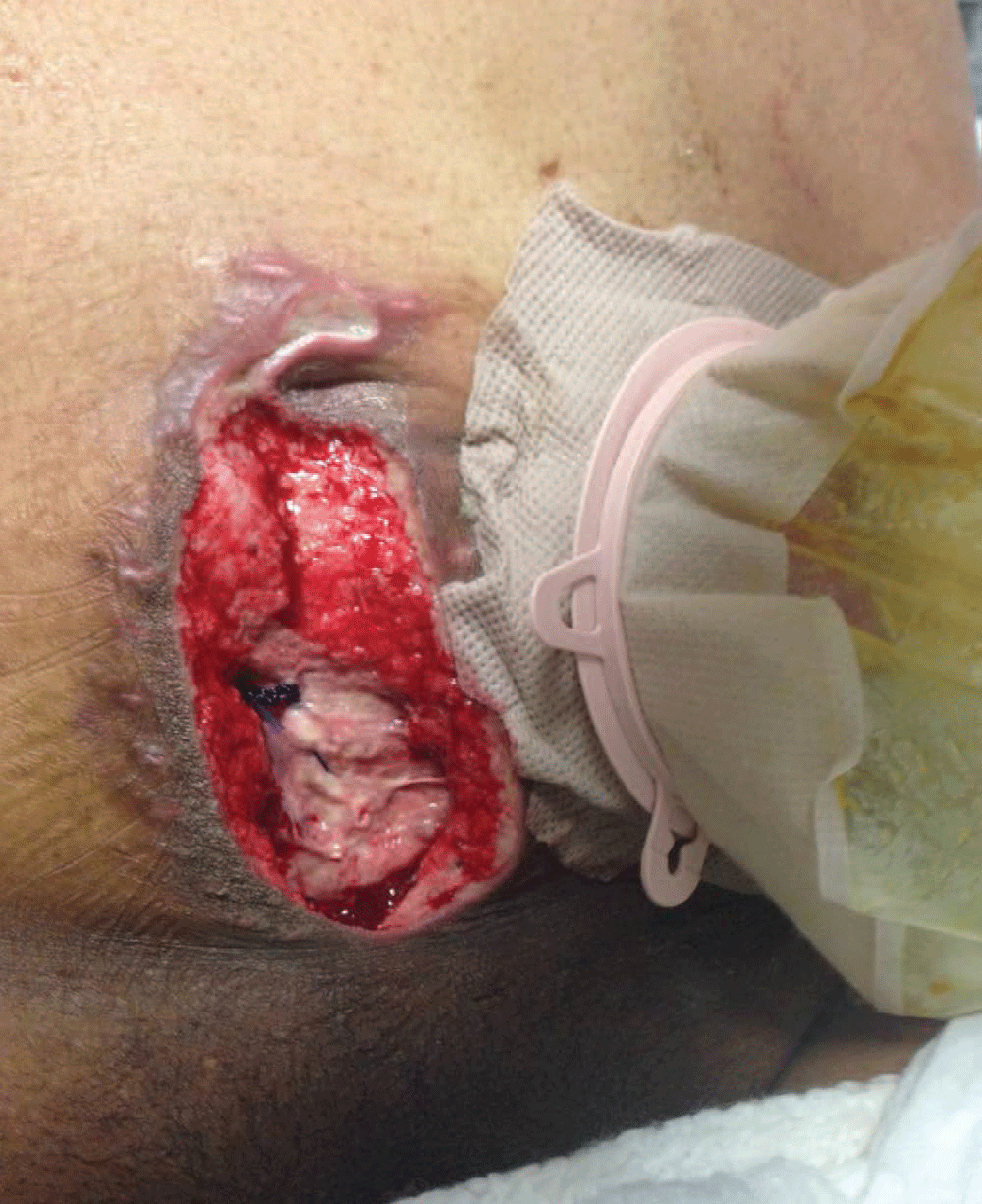
Surgical Management of Benign and Malignant Colorectal Disease in the Immunocompromised Patient
- Immunosuppression alters colorectal disease
- Immunosuppressive therapy for inflammatory bowel disease may worsen postoperative outcomes
- Diverticulitis, even if uncomplicated, should be treated with a surgical resection in patients who have had a solid-organ transplantation
- Typhlitis may mimic appendicitis in immunocompromised patients but should not be managed with surgery
- Certain neoplasms are increased in the setting of immunosuppression

Surgical Management of Benign and Malignant Colorectal Disease in the Immunocompromised Patient
- Immunosuppression alters colorectal disease
- Immunosuppressive therapy for inflammatory bowel disease may worsen postoperative outcomes
- Diverticulitis, even if uncomplicated, should be treated with a surgical resection in patients who have had a solid-organ transplantation
- Typhlitis may mimic appendicitis in immunocompromised patients but should not be managed with surgery
- Certain neoplasms are increased in the setting of immunosuppression
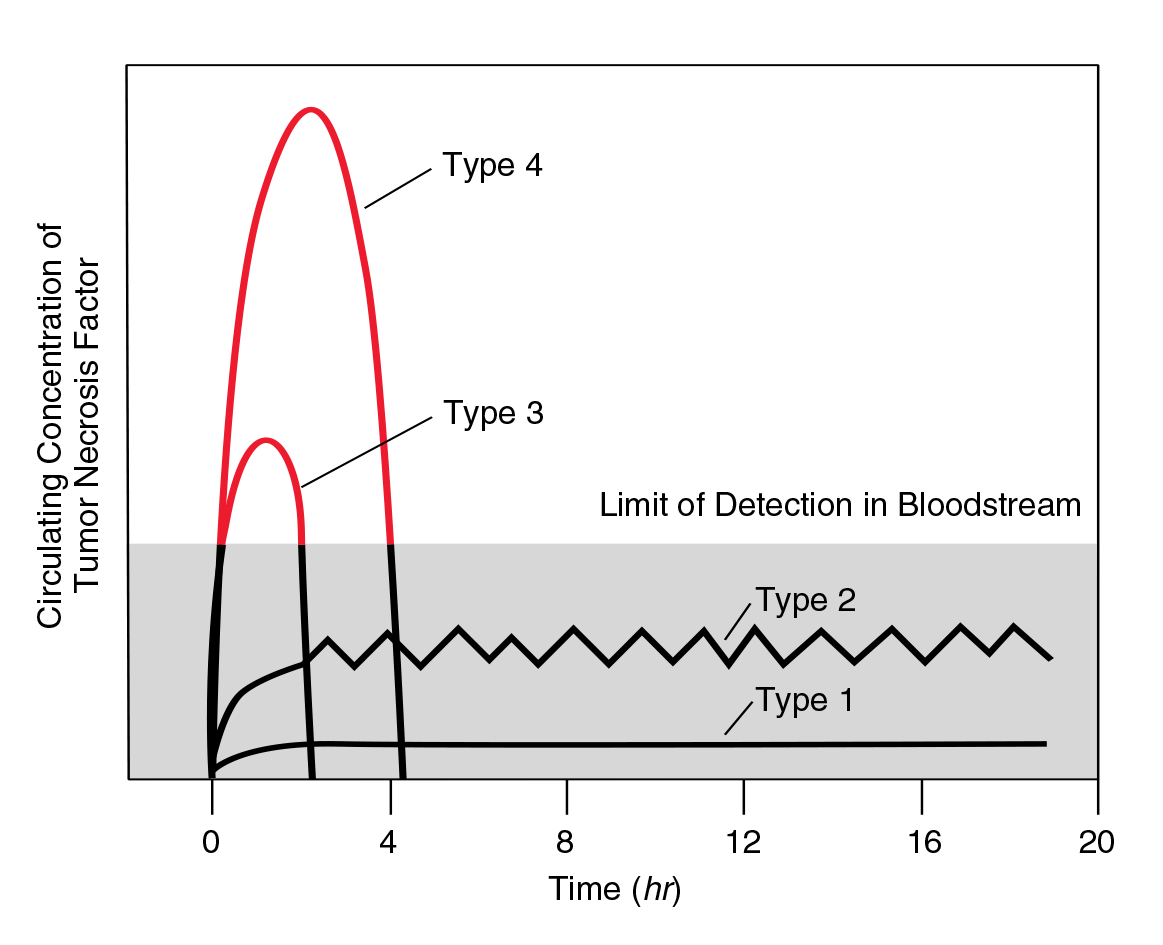
Metabolic Response to Critical Illness - Part 2
- Use of growth hormone for manipulation of metabolic response and muscle characteristics. This in combination with early physical therapy/exercise aids in preservation.
- Anti-cytokine antibodies for partial attenuation of metabolic response. These approaches have elucidated the complexity of mechanisms leading to the metabolic response of critically ill patients.
- Relatively recent adoption of the important role of the gut in metabolic response. This includes production of mediators and functioning as a barrier to bacteria which dramatically affect severity of metabolic response.


.png)






