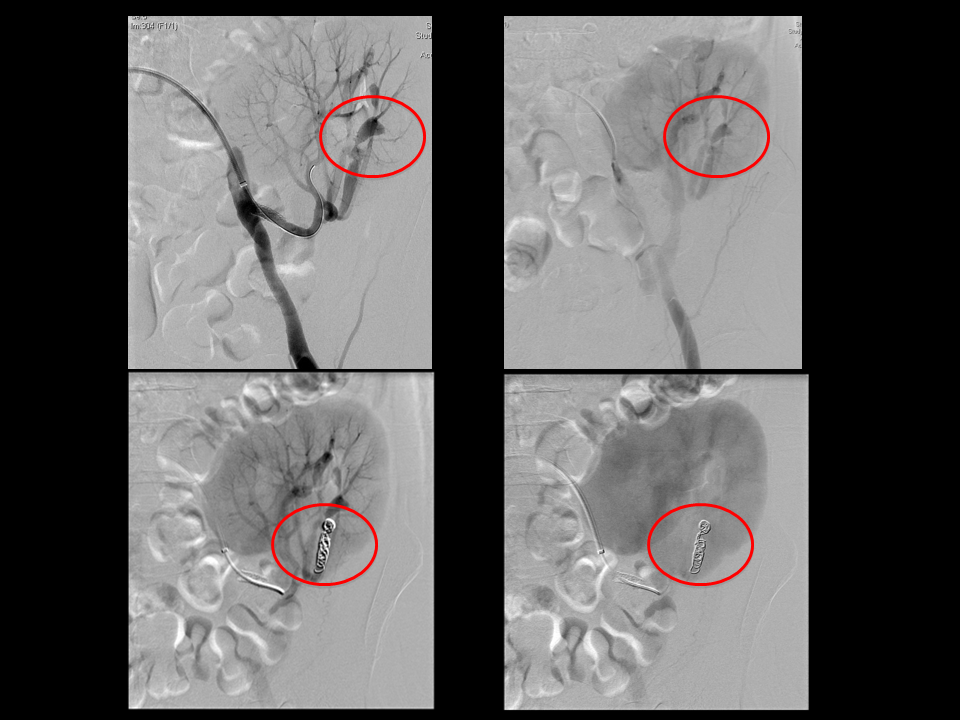
Urogenital Fistulas and Female Urethral Diverticula
- For iatrogenic vesicovaginal fistula, delaying repair until healing has occurred is no longer mandatory, and outcomes for immediate repair are comparable to delayed repairs.
- Concomitant stress incontinence surgery with autologous fascial pubovaginal sling at the same time as repair of complex urethral diverticula appears to be safe and effective.
- MRI is a valuable tool for surgical planning and is recommended prior to urethral diverticulectomy.


.png)







