- ATS guidelines for exercise-induced bronchoconstriction, asthma in the elderly, and asthma in the workplace
- ERS/ATS guideline for severe asthma discusses pharmacologic modalities of asthma management and bronchial thermoplasty.
- 2020 GINA practice guidelines no longer recommend treatment with SABA alone, without inhaled ICS. Recommend that all adults and adolescents with asthma should receive ICS-containing controller treatment.
- 2020 NAEPP practice guidelines delineating optimal treatment steps in adolescents and adults with asthma. This includes bronchial thermoplasty and immunotherapy.
Latest Updates
.png)
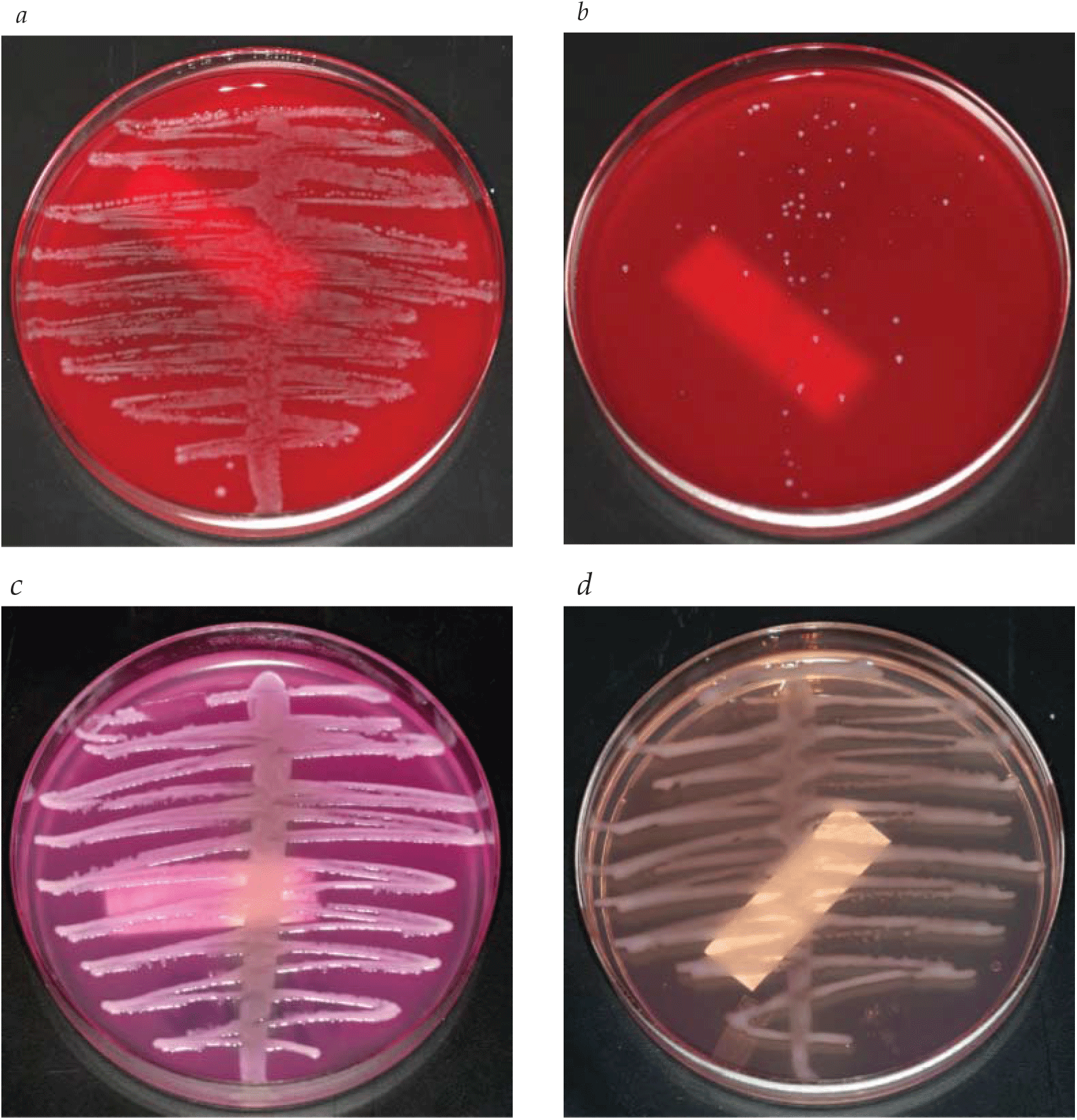
- Latest IDSA clinical practice guideline for management of candidiasis
- Latest ACR expert panel on urologic imaging of recurrent lower urinary tract infections in women

- Latest IDSA clinical practice guideline for management of candidiasis
- Latest ACR expert panel on urologic imaging of recurrent lower urinary tract infections in women
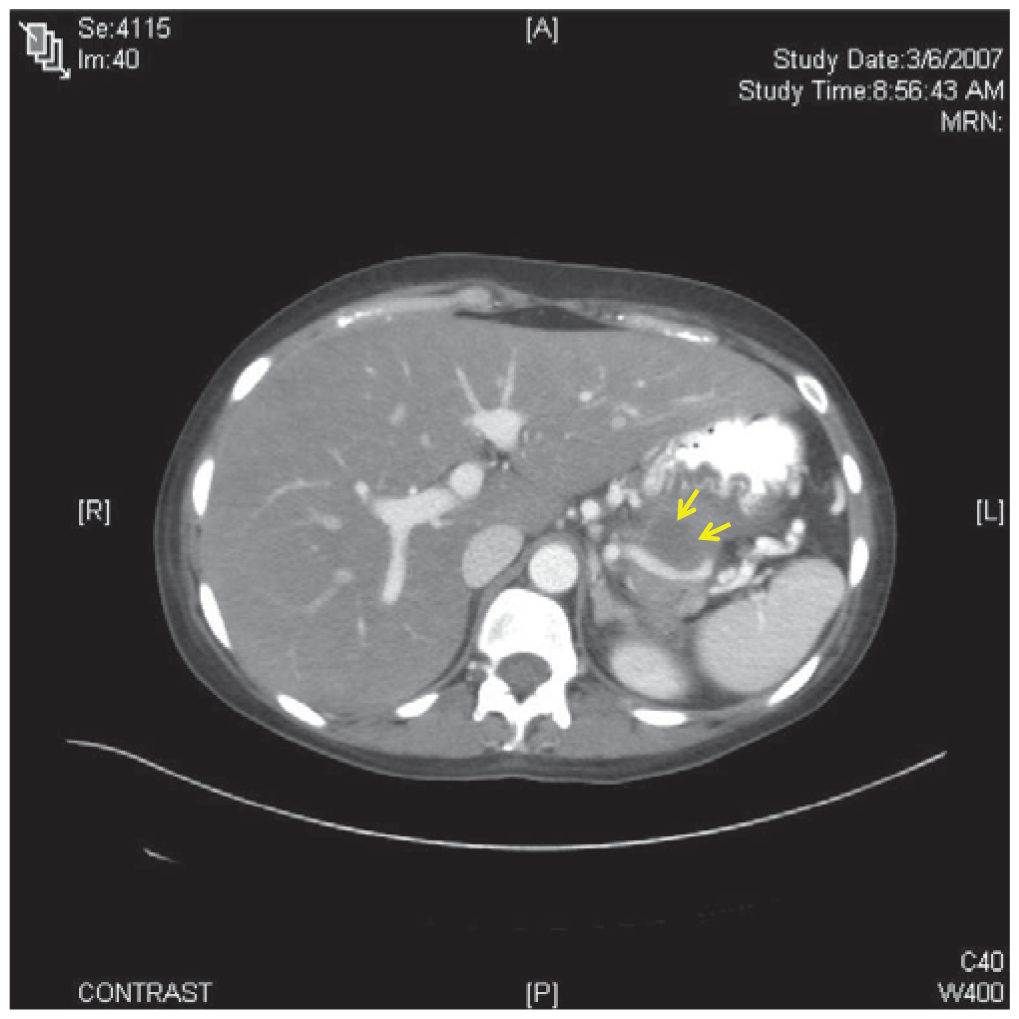
- The chief presenting complaint in acute pancreatitis is abdominal pain. The differential diagnosis for pancreatitis is broad, and includes abdominal, pulmonary, urologic and cardiovascular pathologies.
- Recent guidelines state that the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis should be established by meeting two of the following clinical, laboratory, or imaging criteria: abdominal pain and examination consistent with the disease, a serum amylase and/or lipase three times the upper limit of normal, and/or computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, or ultrasonography findings consistent with the disease.
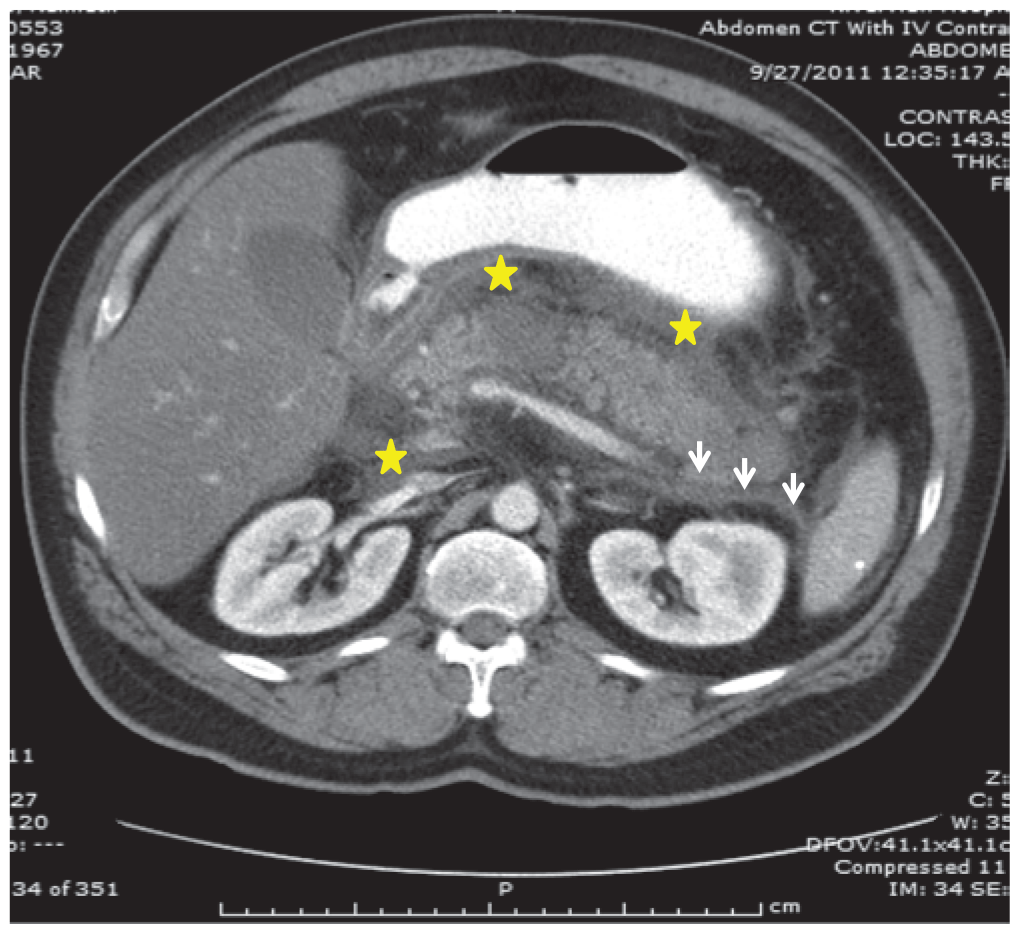
Unstable Angina and Non-ST Segment Elevation Acute Coronary Syndrome
- Beta blockers remain underused in clinical practice despite demonstrated efficacy in acute myocardial infarction (AMI). They have been shown to reduce myocardial oxygen demand and infarction size, and alleviate AMI-related pain. They also reduce the likelihood of developing mechanical and arrhythmogenic complications of AMI. They can be dosed in a wide range, and should be started at the lower end of the dosing range and titrated upward. The only relative contraindications to treatment with beta blockers are mild to moderate heart failure, obstructive airway disease (in the absence of asthma), peripheral vascular disease, diabetes mellitus and a history of cardiomyopathy.
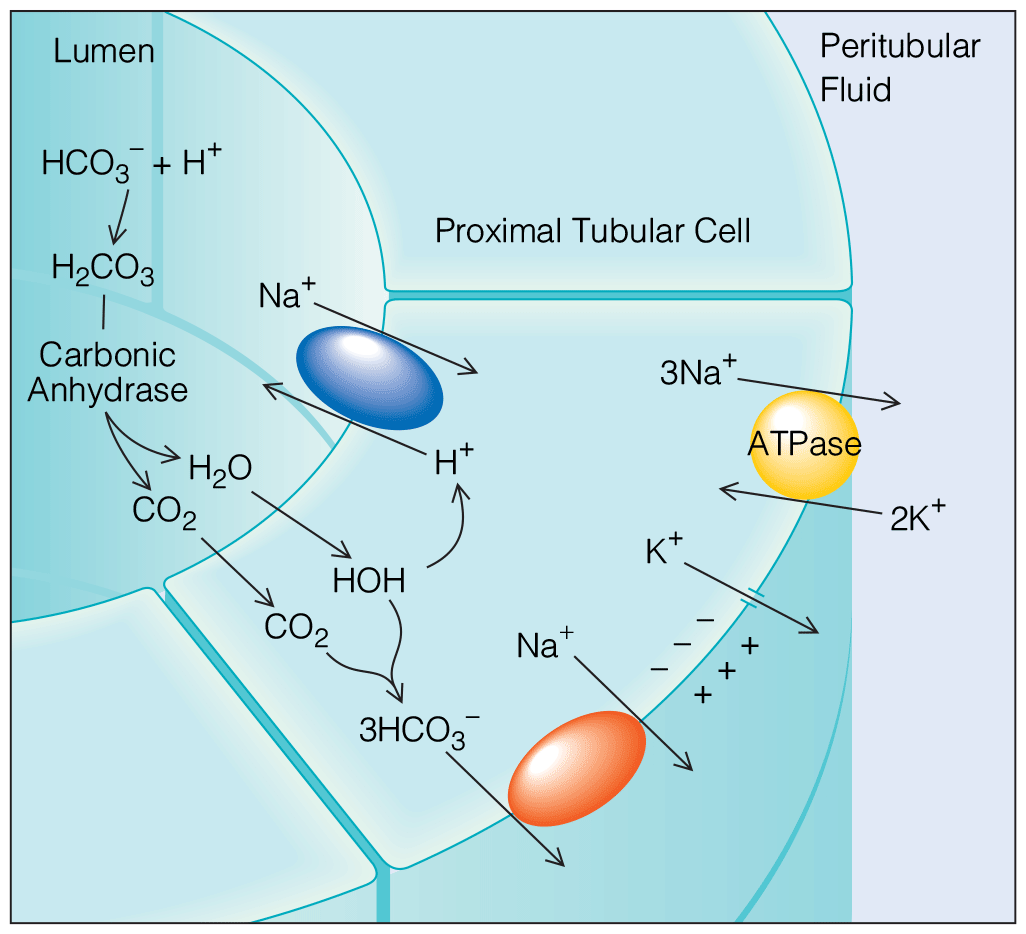
Disorders of Acid-Base and Potassium Balance
- Latest evidence-based management of potassium disorders.
- Bedside right lower quadrant ultrasonography to assess for acute appendicitis is rapid and noninvasive and does not involve ionizing radiation. Studies have validated that nonradiologist clinicians, when trained properly, can safely and accurately perform this examination, with sensitivities and specificities similar to those achieved by radiologists.
- Ultrasonographic detection of either a complex fluid collection or abscess is reported to be 99% specific for diagnosis of a perforated appendix but only 36% sensitive.
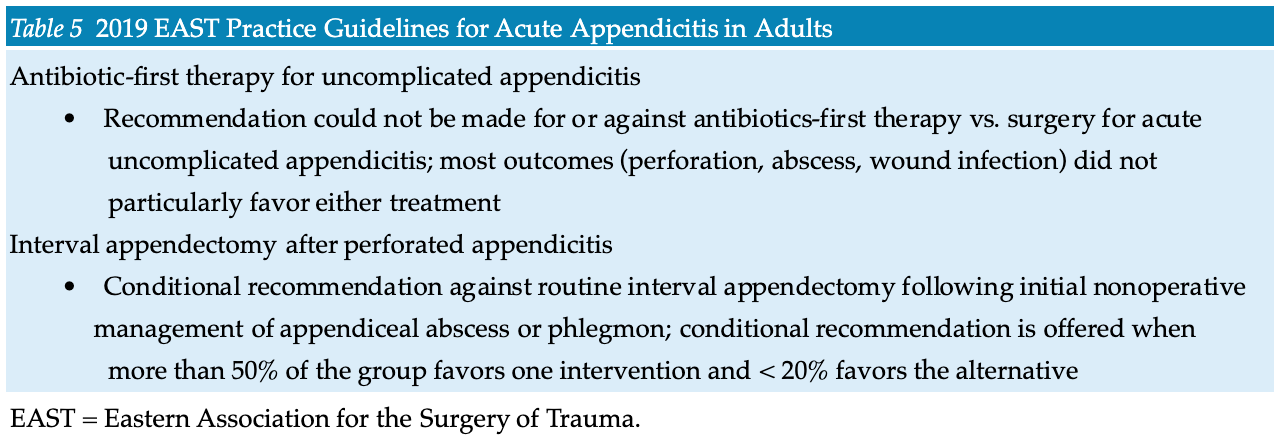
- A recent randomized controlled trial of amoxicillin-clavulanate versus appendectomy demonstrated the noninferiority of antibiotics for treatment of acute noncomplicated appendicitis but did not demonstrate an increased rate of complications in the appendectomy group. However, a Cochrane review of antibiotic therapy versus operative management did not find conclusive data to support antibiotic therapy and concluded that appendectomy remains the gold standard treatment.

- Bedside right lower quadrant ultrasonography to assess for acute appendicitis is rapid and noninvasive and does not involve ionizing radiation. Studies have validated that nonradiologist clinicians, when trained properly, can safely and accurately perform this examination, with sensitivities and specificities similar to those achieved by radiologists.
- Ultrasonographic detection of either a complex fluid collection or abscess is reported to be 99% specific for diagnosis of a perforated appendix but only 36% sensitive.
- A recent randomized controlled trial of amoxicillin-clavulanate versus appendectomy demonstrated the noninferiority of antibiotics for treatment of acute noncomplicated appendicitis but did not demonstrate an increased rate of complications in the appendectomy group. However, a Cochrane review of antibiotic therapy versus operative management did not find conclusive data to support antibiotic therapy and concluded that appendectomy remains the gold standard treatment.


.png)







