- The updated AJCC TNGM Staging classification for soft tissue sarcomas.
- The most recent edition of the WHO Classification of Tumours of the Soft Tissue and Bone lists over 120 different histologic subtypes of soft tissue lesions… Based on data from a randomized trial coordinated by the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) and on retrospective studies demonstrating an association between treatment with neoadjuvant chemotherapy and improved disease-specific survival in patients with large, high-grade, extremity lesions, neoadjuvant chemotherapy is considered for patients with high-grade tumors that are larger than 10 cm.
- In most instances, neither computed tomography nor magnetic resonance imaging can define the histologic subtype, although they can be highly suggestive; for example, myxofibrosarcoma often has tail-like projections spreading along fascial planes and enhancing after administration of contrast.
Latest Updates
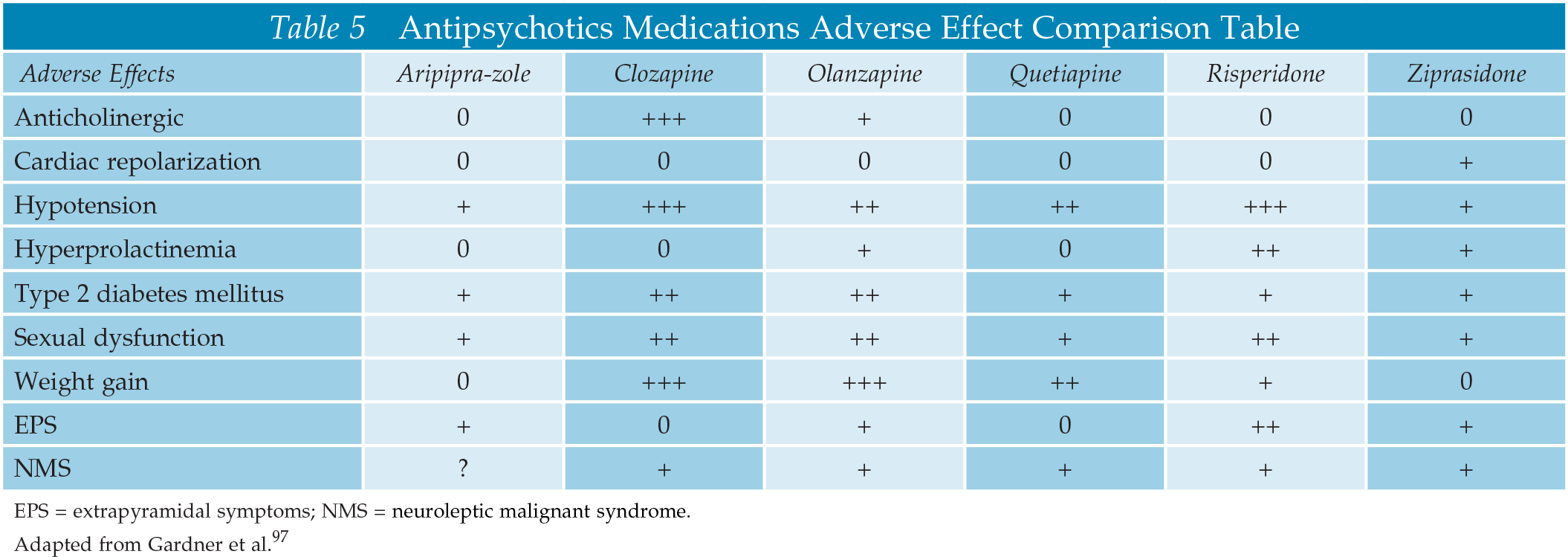
- The currently FDA-approved antipsychotics can be divided into two classes: typical antipsychotics and atypical antipsychotics.
- Antipsychotics are used to treat a variety of psychiatric disorders.
- Typical antipsychotics are effective for the treatment of positive symptoms, whereas atypical antipsychotics also have an effect on the negative symptoms of schizophrenia.
- The typical antipsychotics are generally associated more with the side effects of the extrapyramidal movement, whereas the atypical antipsychotics have a higher risk for metabolic adverse effects.
- Decreasing adverse effects and improving adherence are the goals of treatment with antipsychotic medications.
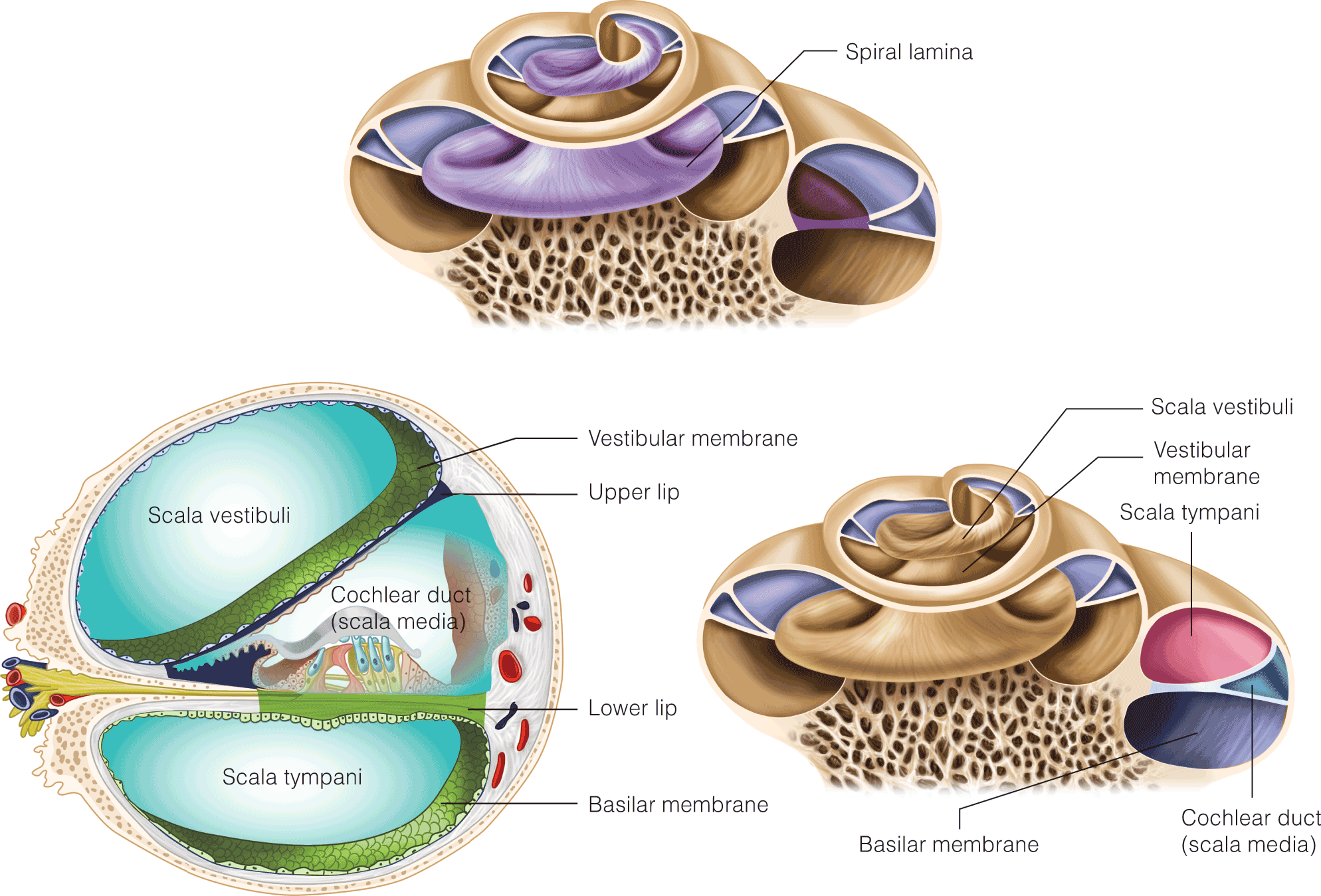
- Drug therapies for cochlear hair cell regeneration are currently being developed and tested in several labs and a few are in human clinical trials for SNHL treatment.
- Gene interventions such as gene editing and gene silencing have been shown to improve hair cell survival rates in mice and have the potential for the development of gene therapy for SNHL.
- Many novel immunotherapeutic agents used for cancer treatment such as immune checkpoint inhibitors and T-cell therapies have been implicated in SNHL as a side effect.
- Several studies have discovered that inner ear inflammation triggered by the release of IL-1β from macrophages in response to unknown stimuli is responsible for SNHL secondary to autoinflammatory diseases.
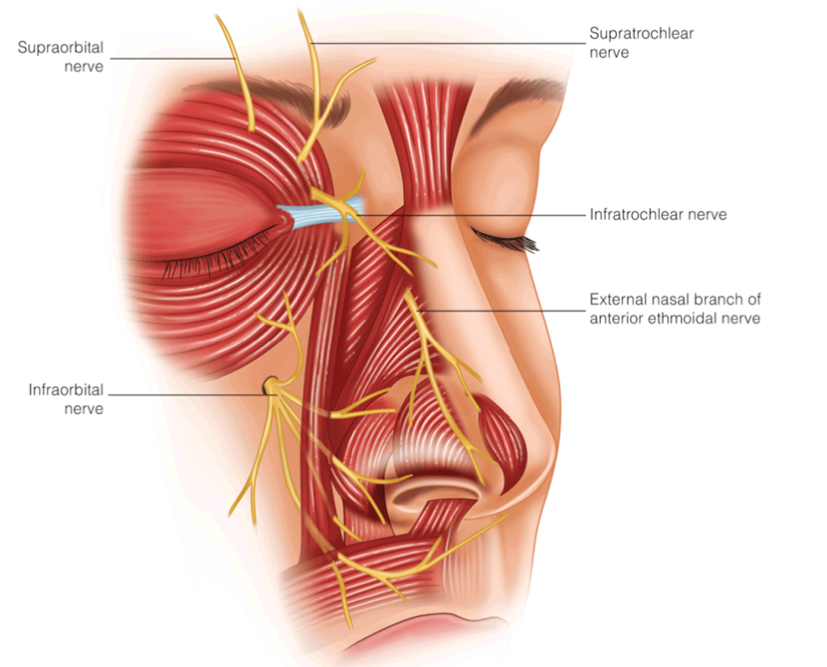
- Tranexamic acid may help with bleeding in rhinoplasty and has been used in craniofacial literature to stop bleeding.
- Preoperative discussion and evaluation is crucial when discussing and planning rhinoplasty for patient satisfaction.
- Free tissue transfer can be utilized if the latter methods have failed in a persistent septal perforation.
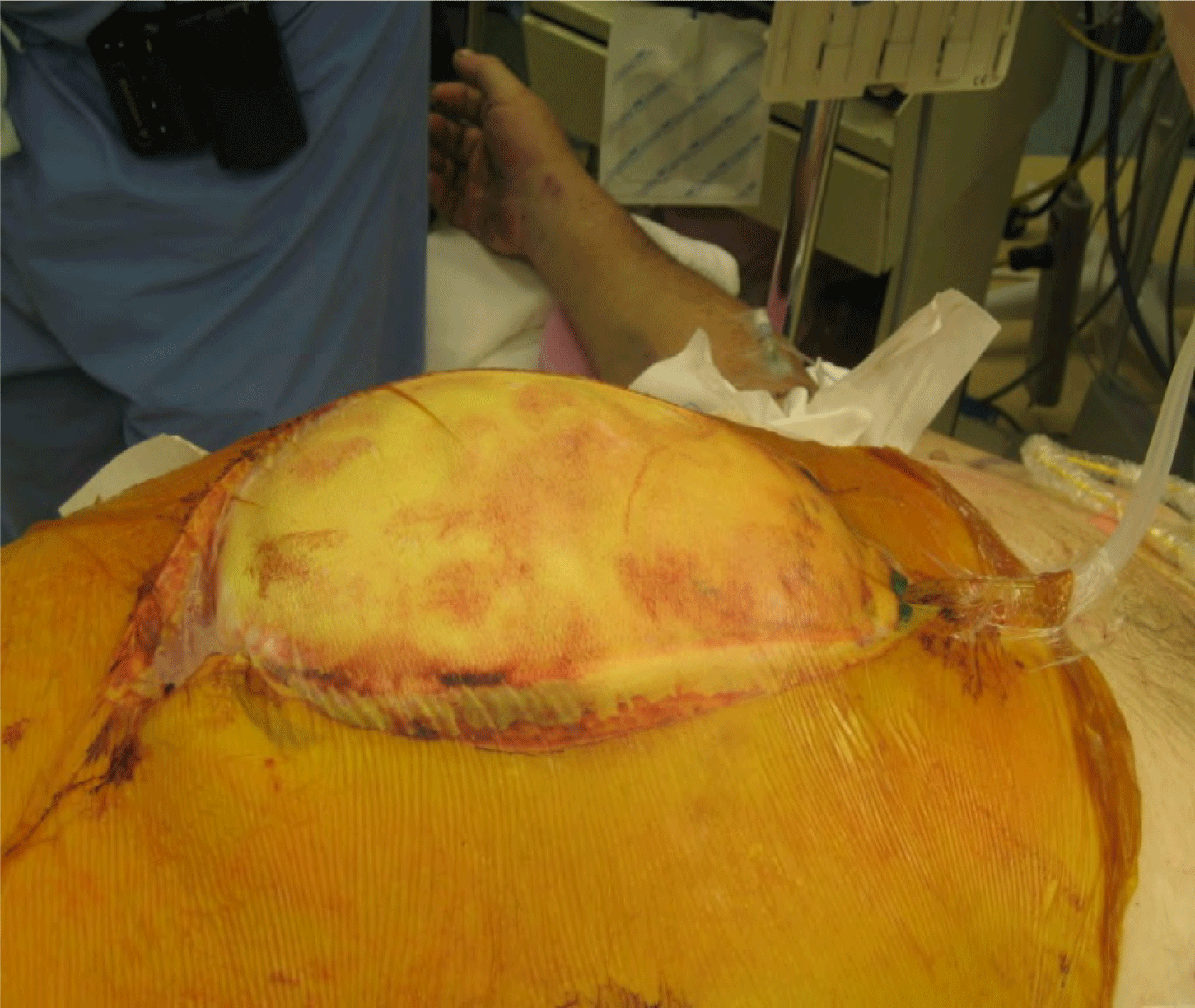
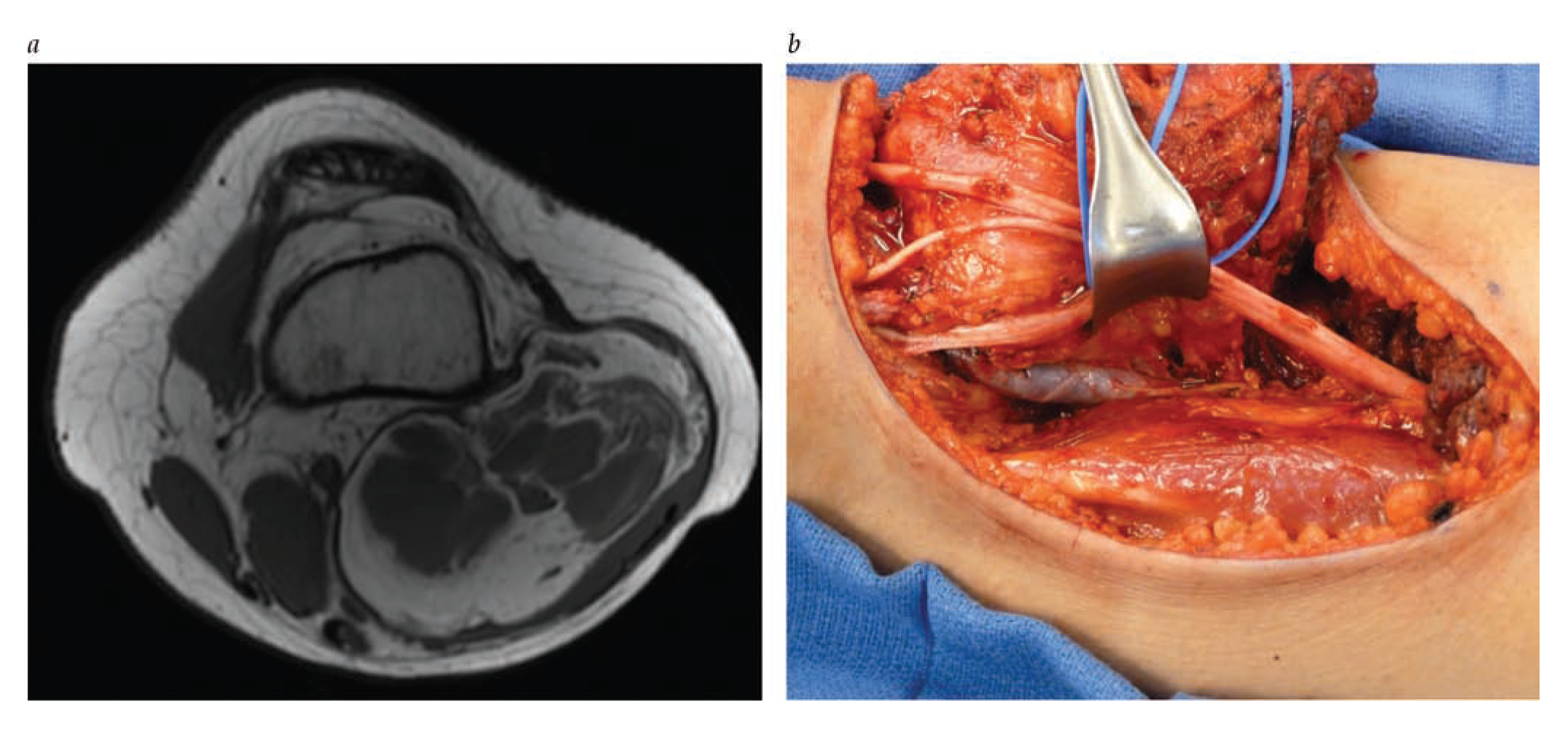
- Compartment syndrome of the extremity is a clinical diagnosis in an awake and alert patient.
- Measurement of intracompartmental pressures should be performed in the obtunded patient or if clinical assessment is inconclusive.
- Once the diagnosis is made, emergent fasciotomy is the treatment of choice as time to fasciotomy is the most important factor determining outcome.
- Any patient with risk factors for developing abdominal hypertension should have intra-abdominal pressure assessed, preferably via intermittent or continuous transbladder pressure.
- Patients diagnosed with abdominal compartment syndrome require emergent decompressive laparotomy and the creation of a temporary abdominal closure.
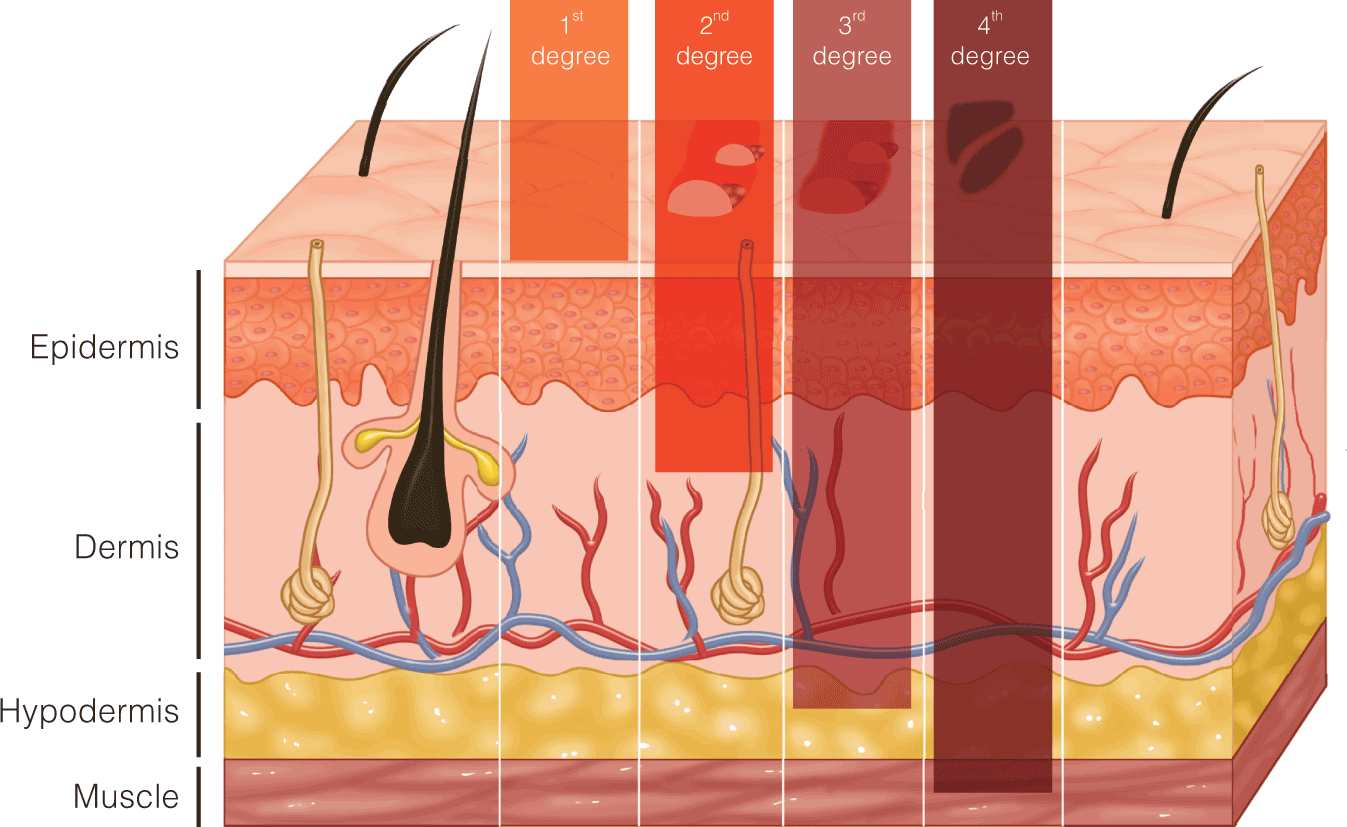
Evaluation and Management of Facial Burns
- Synthetic biodegradable dermal matrices are a recent innovation which regenerates a neodermis, with implications for wound coverage in burns and may confer benefits including decreased risk of infection and lower cost.
- 3-D printing of skin is a new frontier in tissue engineering, involving suspension and growth of keratinocytes and fibroblasts in a collagen matrix, with promising results in early animal studies.
- Although face transplantation has been previously performed for debilitating burns of the head and neck, the number of face transplants has declined; reasons for this are multifactorial.
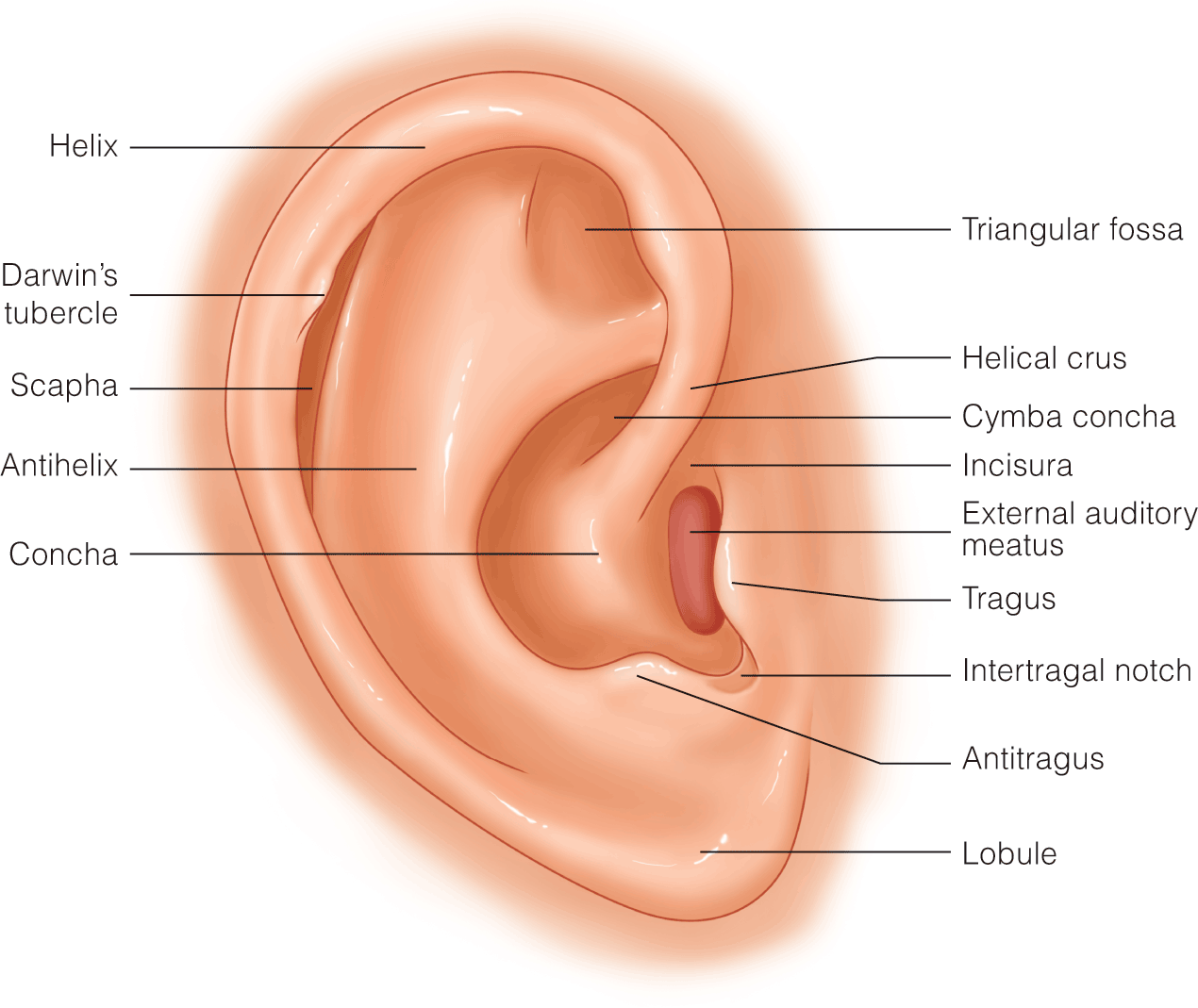
Congenital Malformations of the Ear
- There remains controversy on the true origin and developmental stages of the external ear
- Auricular reconstruction for microtia is complex and constantly evolving
- Classification of auricular anomalies should focus on describing the anatomic subunits involved
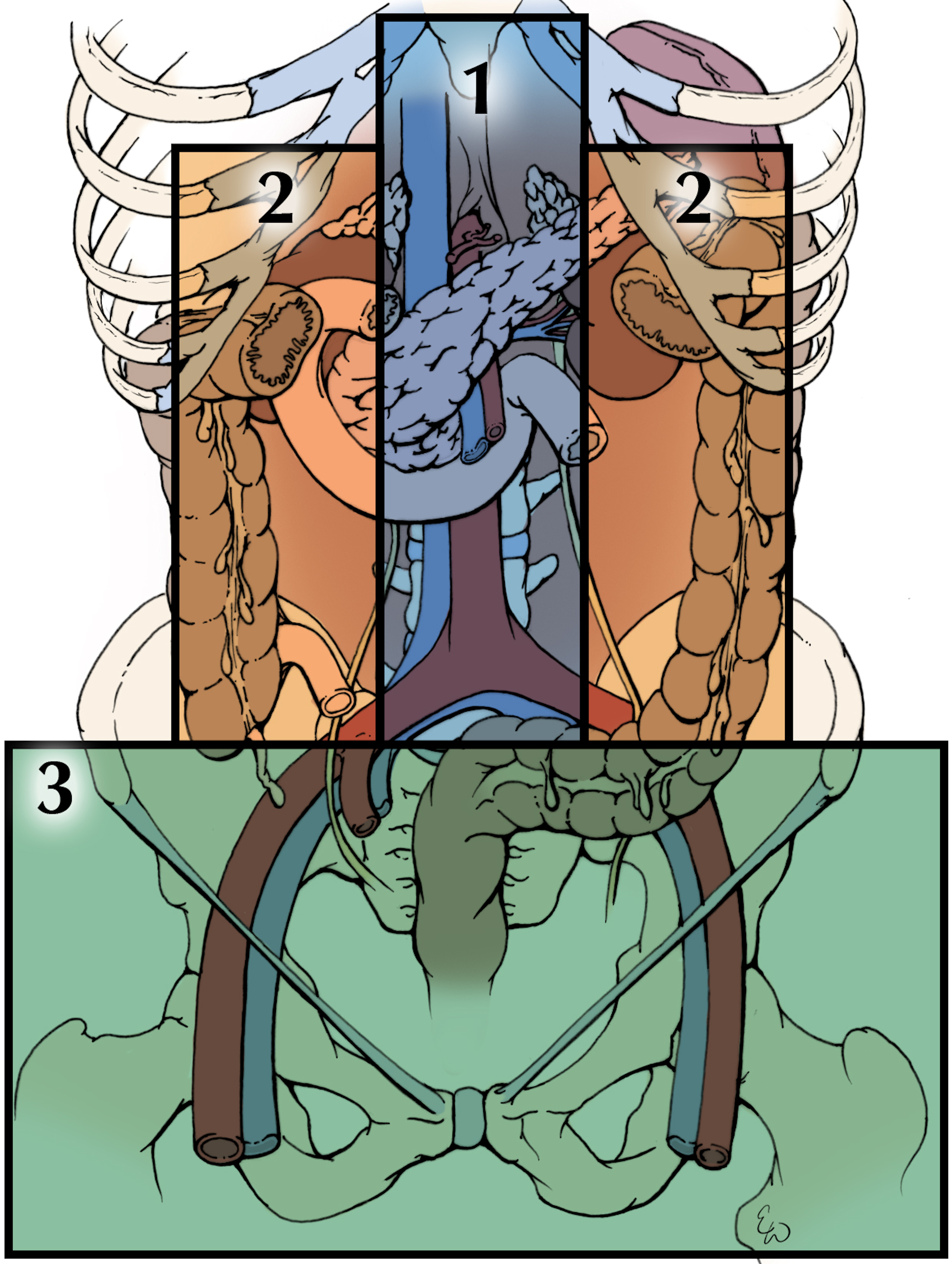
Operative Exposure of Abdominal Injuries and Closure of the Abdomen
- Prehospital control of bleeding with tourniquets, and permissive hypotension until operative bleeding control improve survival.
- Damage control resuscitation and surgical principles improve outcomes in patients with abdominal trauma, impaired physiology.
- Resuscitative Endovascular Balloon Occlusion of the Aorta, may aid the hemorrhaging abdominal trauma patient.


.png)







