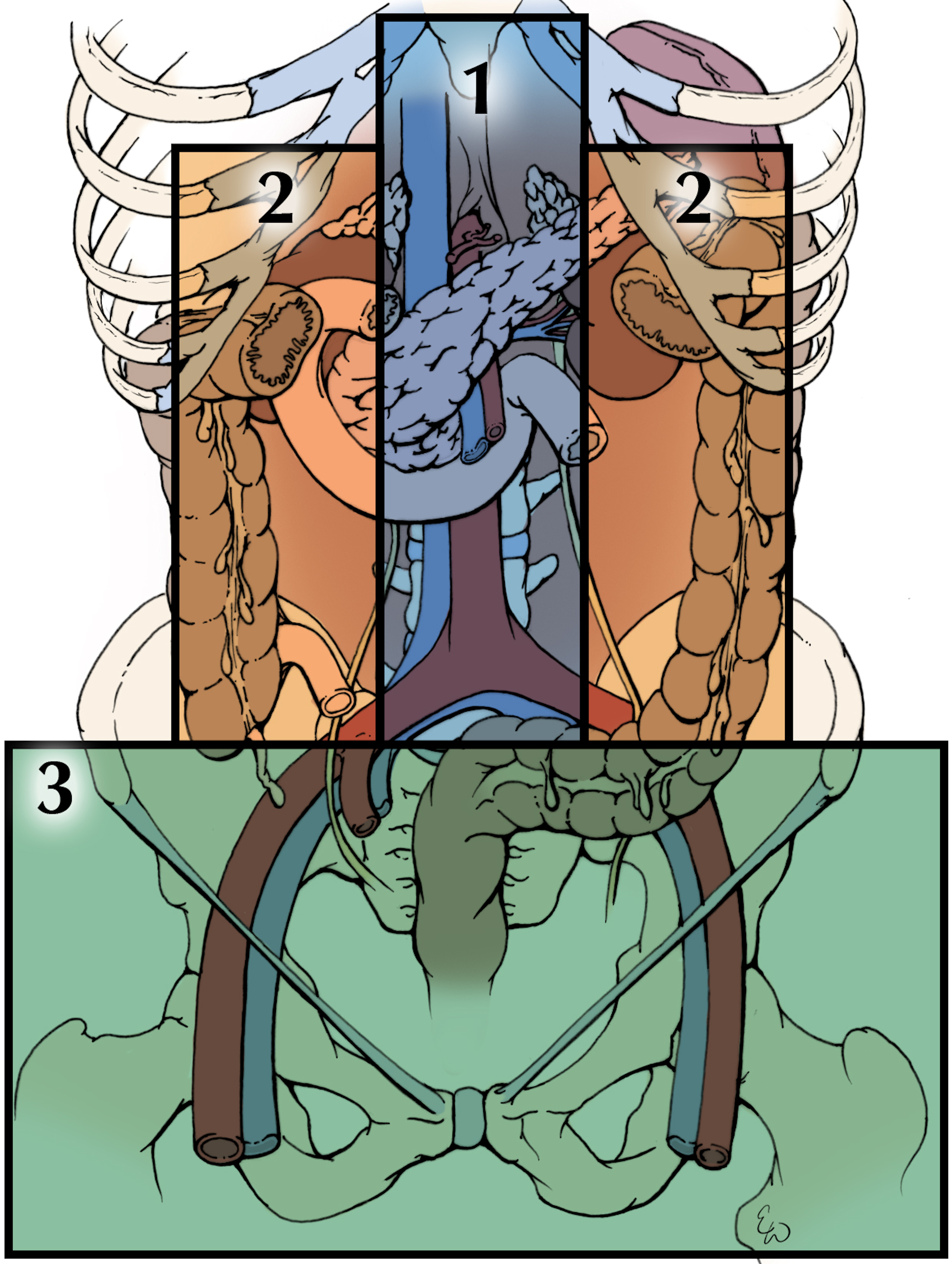
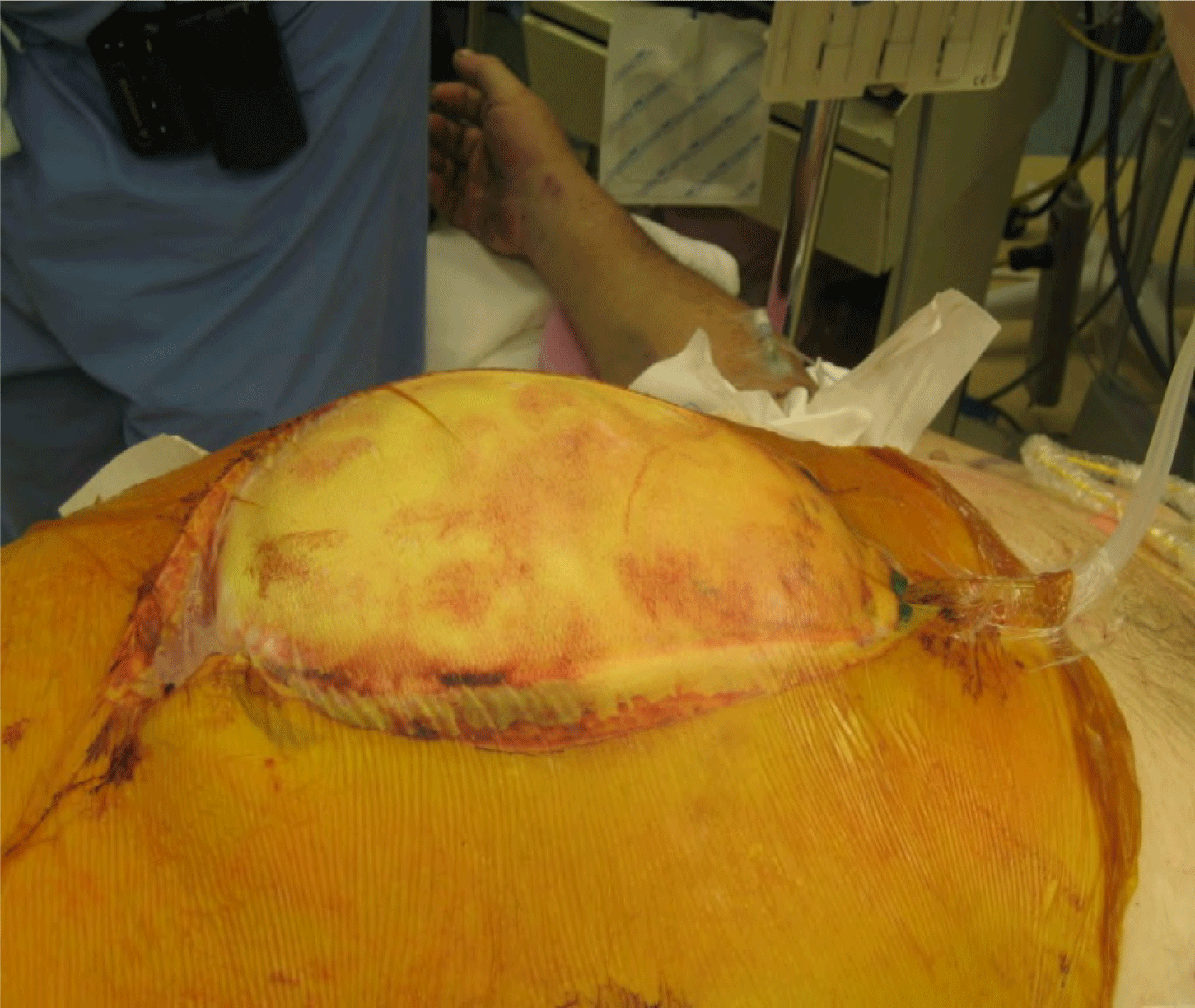
Operative Exposure of Abdominal Injuries and Closure of the Abdomen
- Prehospital control of bleeding with tourniquets, and permissive hypotension until operative bleeding control improve survival.
- Damage control resuscitation and surgical principles improve outcomes in patients with abdominal trauma, impaired physiology.
- Resuscitative Endovascular Balloon Occlusion of the Aorta, may aid the hemorrhaging abdominal trauma patient.


.png)







