- When massive bleeding exists and direct control of the site of bleeding is under way, the decision to transfuse should be based primarily on hemodynamic status rather than on the hemoglobin or hematocrit level. These laboratory values do not reflect acute hemorrhage because there is a time lag before these levels equilibrate from fluid shift between the extravascular and vascular compartments and from administration of IV fluids.
- The concept of liberal, early use of plasma and platelets developed in large part from the recent US-led military campaigns in Iraq and Afghanistan. Initially in those conflicts, the lack of a reliable supply of blood products near the scene of injury—and platelets especially—led to the use of fresh whole blood transfusion. Although fresh whole blood would be impractical in the civilian setting because of logistical issues and the risk of transmitting transfusion-related infections, the perception of improved outcomes associated with its use prompted military surgeons to advocate 1:1:1 transfusion.
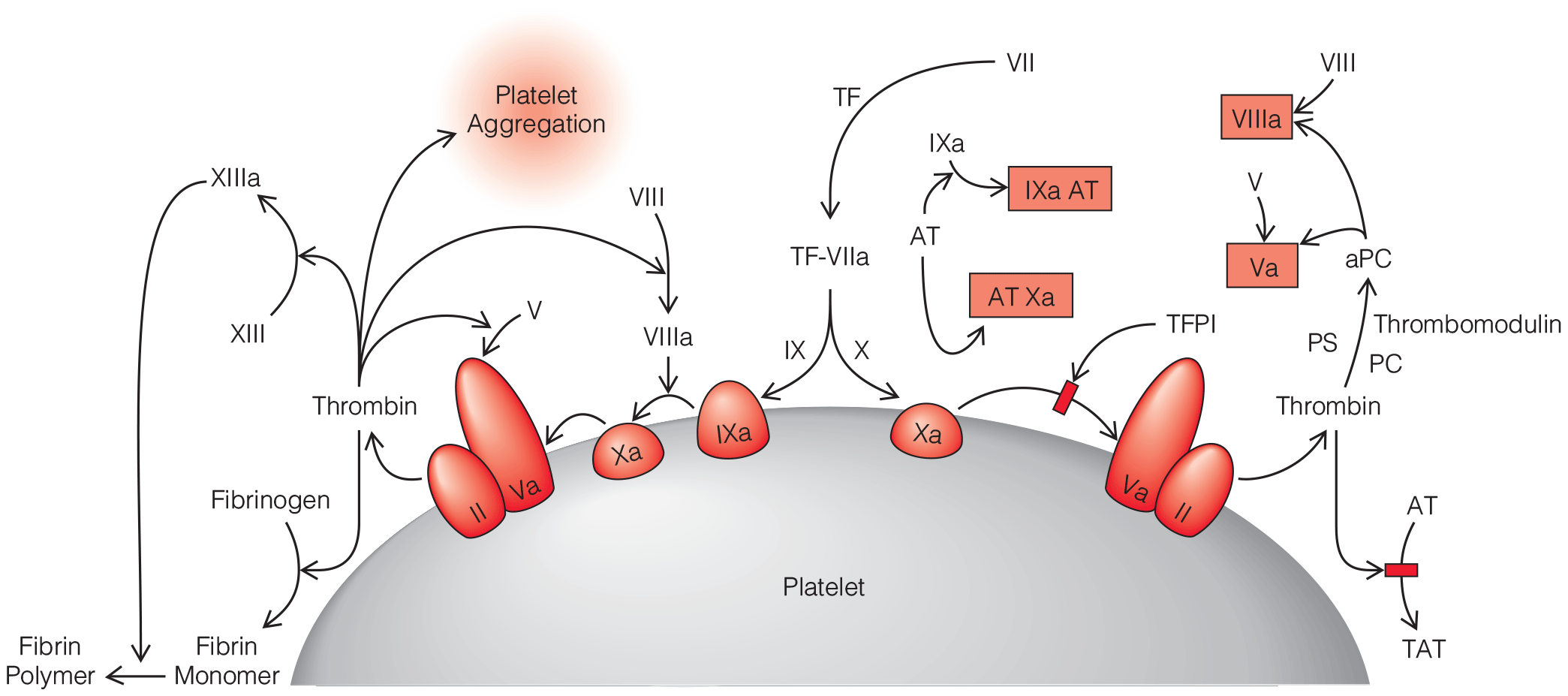
- Beyond recognition and correction of the underlying problem causing DIC and the associated coagulopathy, the diagnosis of DIC represents something of an academic exercise because there is no specific treatment for the condition. Scoring systems that assess the severity of DIC are most useful for distinguishing DIC from other causes of coagulopathy (e.g., hypothermia, dilution, and drug effects).
Latest Updates

- When massive bleeding exists and direct control of the site of bleeding is under way, the decision to transfuse should be based primarily on hemodynamic status rather than on the hemoglobin or hematocrit level. These laboratory values do not reflect acute hemorrhage because there is a time lag before these levels equilibrate from fluid shift between the extravascular and vascular compartments and from administration of IV fluids.
- The concept of liberal, early use of plasma and platelets developed in large part from the recent US-led military campaigns in Iraq and Afghanistan. Initially in those conflicts, the lack of a reliable supply of blood products near the scene of injury—and platelets especially—led to the use of fresh whole blood transfusion. Although fresh whole blood would be impractical in the civilian setting because of logistical issues and the risk of transmitting transfusion-related infections, the perception of improved outcomes associated with its use prompted military surgeons to advocate 1:1:1 transfusion.
- Beyond recognition and correction of the underlying problem causing DIC and the associated coagulopathy, the diagnosis of DIC represents something of an academic exercise because there is no specific treatment for the condition. Scoring systems that assess the severity of DIC are most useful for distinguishing DIC from other causes of coagulopathy (e.g., hypothermia, dilution, and drug effects).
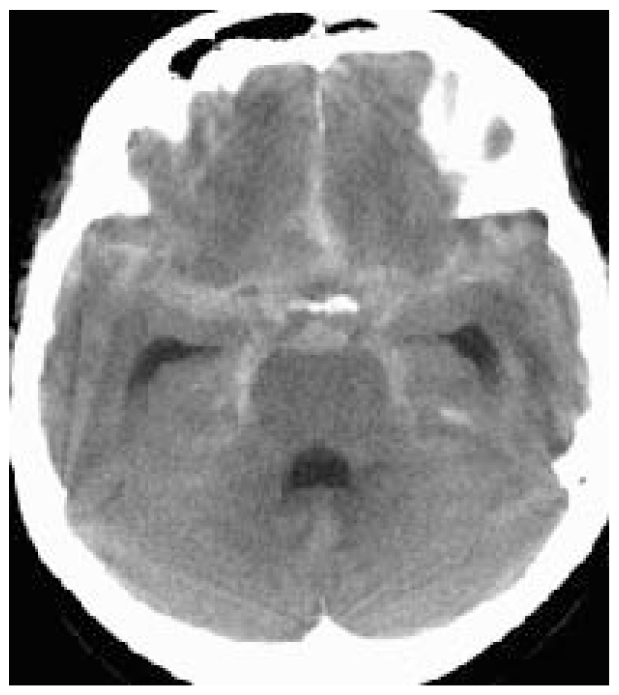
- Computed tomographic angiography (CTA) has the advantage of being noninvasive, but there are very limited data to compare a CTA approach with the current standard diagnostic approach. A methodological review supported CTA in patients presenting within 48 hours of symptoms and with a neurologically intact examination. CTA has not replaced the current approach but has gained more acceptance; its use is center specific and more prevalent in continued management than initial diagnosis. CTA sensitivity decreases with aneurysms less than 4 mm in size and carries the risk of contrast-induced nephropathy, especially if digital subtraction angiography is performed after CTA.
- Current data suggest that very short courses of antifibrinolytics may reduce rebleeding without causing ischemia. Rapid diagnosis of SAH and early definitive repair probably remain the best strategy for prevention. Fibrinolytics should be used in consultation with the neurosurgeon and may be most beneficial in instances of delayed definitive repair.
- The mortality from aSAH appears to have declined in industrialized nations over the past 25 years. The case-fatality rate for aSAH, although still high worldwide, appears globally to be minimally on the decline despite significant regional differences in reporting of mortality.
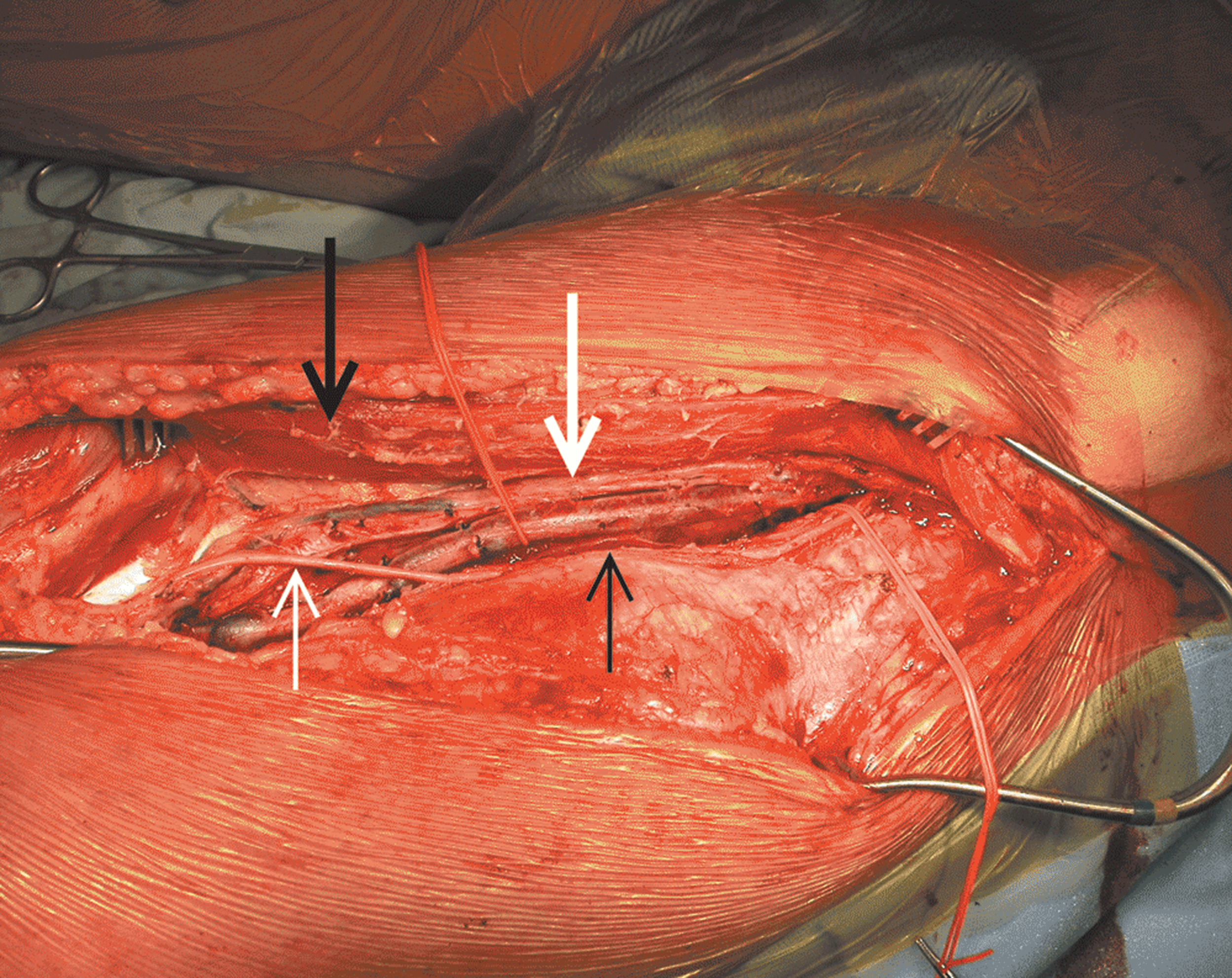
Surgical Treatment of the Infected Aortic Graft
- Discussion of the management of aortic endograft infections, which are increasing in incidence and prevalence and represent a particularly technically challenging subset of aortic graft infections (AGIs)
- Discussion of the management of aortoenteric fistula, with special attention paid to the disastrous effects of gastrointestinal complications
- Updated review of the various methods of arterial reconstruction for AGI, with updated summary of outcomes
- Although hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) is the second most common HAI in hospitalized patients, the diagnosis is far from straightforward in many cases. More than 80% of HAP is ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP), defined as pneumonia diagnosed within 24 hours of any duration of mechanical ventilation. Unfortunately, there is no diagnostic gold standard, and other common conditions, such as acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), chest trauma, and even volume overload, share the key features of VAP.
- Sterile technique is always required for catheter insertion. However, current data support a surgical approach to preparation of the insertion site, with the operator wearing a gown, gloves, a mask, and a hat for the procedure, for all central line.
- The gold standard for detecting CDAD is to send a stool sample for cytotoxin determination, a procedure that has a sensitivity of 70 to 100%. This labor- intensive cell culture assay has been largely replaced in laboratories for enzyme immunoassays for toxins A and B with same-day results, but at a cost of decreased sensitivity (39 to 73%). At the time of this publication, polymerase chain reaction testing for the presence of toxin B is emerging as a rapid, more sensitive and specific test that will likely become the new standard for clinical screening.

- Although hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) is the second most common HAI in hospitalized patients, the diagnosis is far from straightforward in many cases. More than 80% of HAP is ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP), defined as pneumonia diagnosed within 24 hours of any duration of mechanical ventilation. Unfortunately, there is no diagnostic gold standard, and other common conditions, such as acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), chest trauma, and even volume overload, share the key features of VAP.
- Sterile technique is always required for catheter insertion. However, current data support a surgical approach to preparation of the insertion site, with the operator wearing a gown, gloves, a mask, and a hat for the procedure, for all central line.
- The gold standard for detecting CDAD is to send a stool sample for cytotoxin determination, a procedure that has a sensitivity of 70 to 100%. This labor- intensive cell culture assay has been largely replaced in laboratories for enzyme immunoassays for toxins A and B with same-day results, but at a cost of decreased sensitivity (39 to 73%). At the time of this publication, polymerase chain reaction testing for the presence of toxin B is emerging as a rapid, more sensitive and specific test that will likely become the new standard for clinical screening.

- Although hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) is the second most common HAI in hospitalized patients, the diagnosis is far from straightforward in many cases. More than 80% of HAP is ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP), defined as pneumonia diagnosed within 24 hours of any duration of mechanical ventilation. Unfortunately, there is no diagnostic gold standard, and other common conditions, such as acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), chest trauma, and even volume overload, share the key features of VAP.
- Sterile technique is always required for catheter insertion. However, current data support a surgical approach to preparation of the insertion site, with the operator wearing a gown, gloves, a mask, and a hat for the procedure, for all central line.
- The gold standard for detecting CDAD is to send a stool sample for cytotoxin determination, a procedure that has a sensitivity of 70 to 100%. This labor- intensive cell culture assay has been largely replaced in laboratories for enzyme immunoassays for toxins A and B with same-day results, but at a cost of decreased sensitivity (39 to 73%). At the time of this publication, polymerase chain reaction testing for the presence of toxin B is emerging as a rapid, more sensitive and specific test that will likely become the new standard for clinical screening.

- Although hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) is the second most common HAI in hospitalized patients, the diagnosis is far from straightforward in many cases. More than 80% of HAP is ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP), defined as pneumonia diagnosed within 24 hours of any duration of mechanical ventilation. Unfortunately, there is no diagnostic gold standard, and other common conditions, such as acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), chest trauma, and even volume overload, share the key features of VAP.
- Sterile technique is always required for catheter insertion. However, current data support a surgical approach to preparation of the insertion site, with the operator wearing a gown, gloves, a mask, and a hat for the procedure, for all central line.
- The gold standard for detecting CDAD is to send a stool sample for cytotoxin determination, a procedure that has a sensitivity of 70 to 100%. This labor- intensive cell culture assay has been largely replaced in laboratories for enzyme immunoassays for toxins A and B with same-day results, but at a cost of decreased sensitivity (39 to 73%). At the time of this publication, polymerase chain reaction testing for the presence of toxin B is emerging as a rapid, more sensitive and specific test that will likely become the new standard for clinical screening.


.png)







