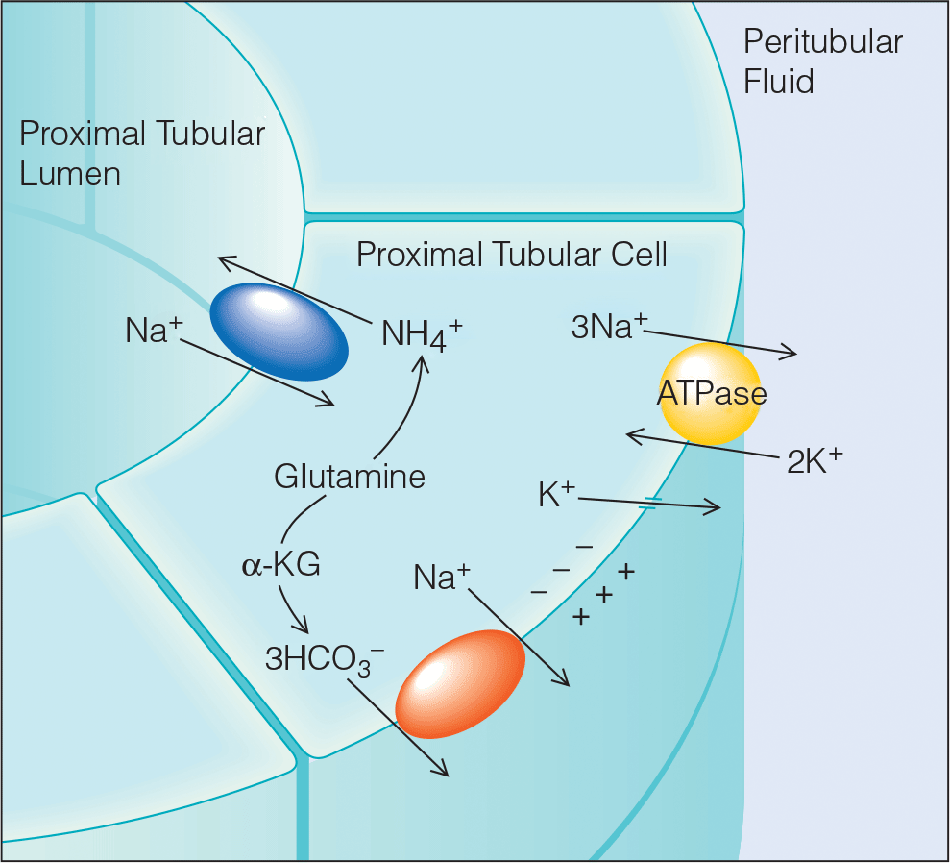
- Detailed physiology of acid-base homeostasis to provide a clearer understanding of the pathophysiology of acid-base disorders
- Updated information on the treatment of metabolic acidosis, including the use of tromethamine and bicarbonate
Latest Updates
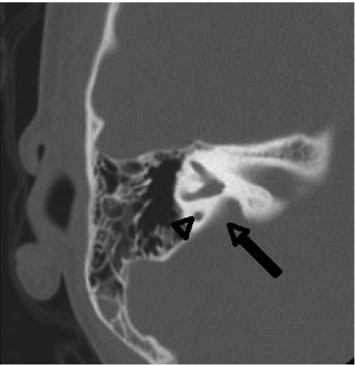
- The FDA first approved cochlear implantation in 1985, since then the criteria have expanded and now include infants as young as 9-months-old and single-sided deafness.
- All cochlear implant recipients should receive vaccination against Streptococcus pneumoniae according to guidelines set forth by the Center for Disease Control (CDC).
- The majority of cochlear implant surgeons utilize the round window insertion technique to minimize intracochlear trauma. Cochleostomy location and insertion technique may vary based on electrode design and patient anatomy.
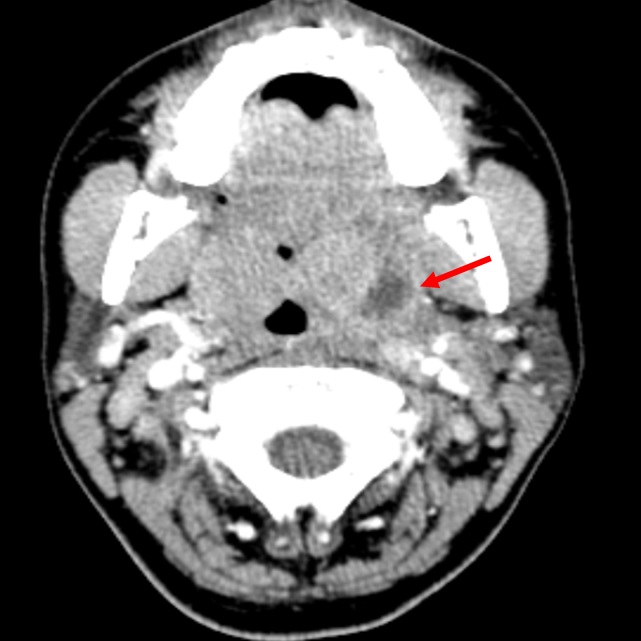
Pediatric Head and Neck Masses
- Ultrasound is being increasingly used in the diagnosis of peritonsillar abscesses
- SIST score (septae+ irregular wall + solid components (1 point each)= TGDC) may be used to distinguish thyroglossal duct cysts from dermoid cysts on ultrasonography
- Quantiferon-TB testing may distinguish non-Tuberculosis mycobacterial infection from tuberculosis mycobacterial infections
- Sirolimus is used in unresectable or difficult to resect microcystic lymphatic malformations
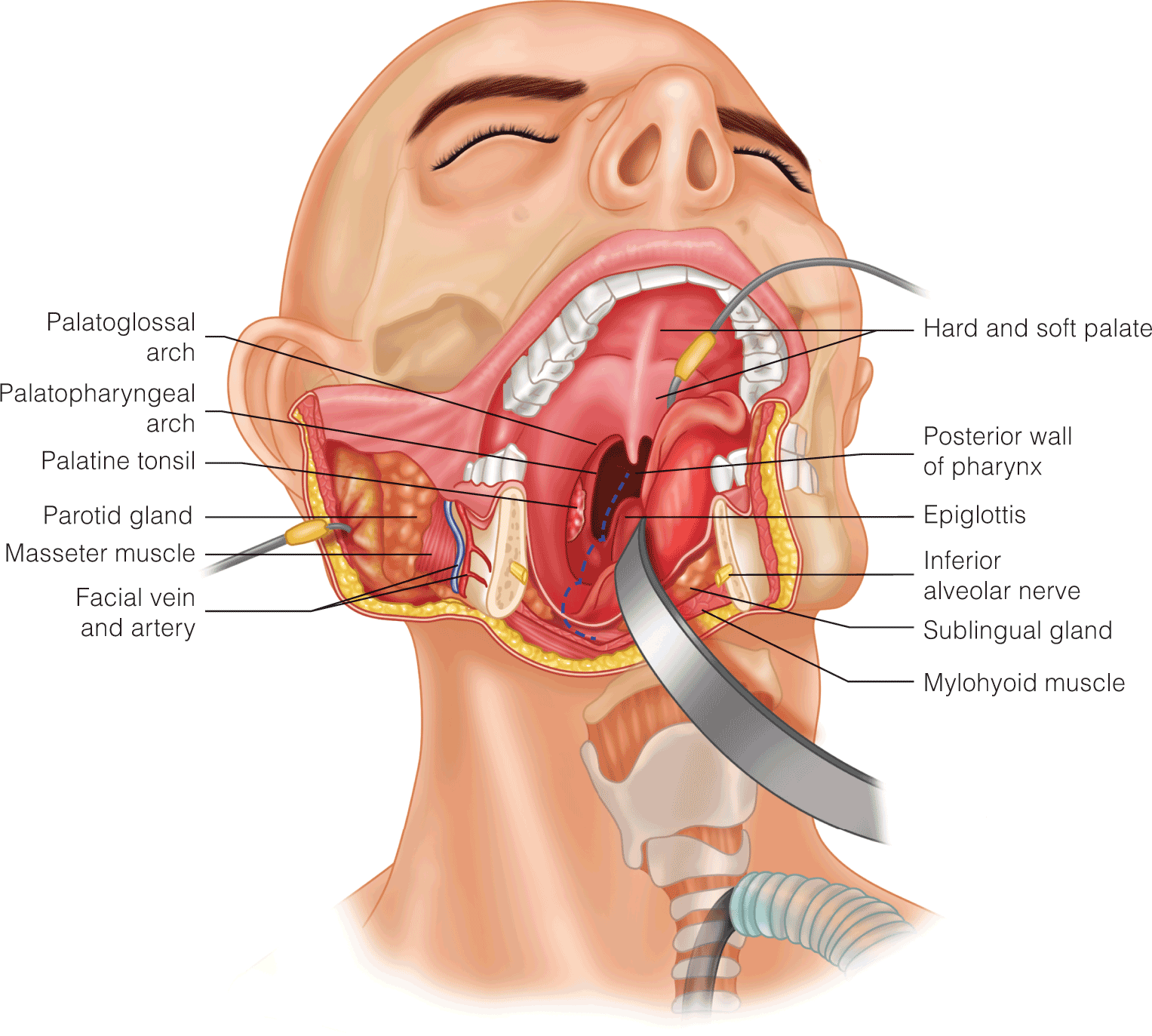
- Virtual surgical planning: computer assisted reconstructive planning or virtual surgical planning (VSP) involves virtually mapping the planned surgical site and defect, producing cutting guides for use when actively harvesting and insetting the osseous free flap and pre-shaping of the reconstruction plates
- Prefabricated fibulas with dental implants - this novel surgical technique involves the placing the dental implants into the fibula several weeks prior to harvesting the fibula to allow for additional osseointegration
- Jaw-in-a-day - this technique involves complete reconstruction and dental implantation / rehabilitation in a single surgery, and requires precise virtual surgical planning but can speed up dental rehabilitation by several months
- Tissue-engineered vascularized bone graft - experimental technique where 3D-CT and computer-aided design techniques were used to create a titanium mesh cage filled with bone blocks and infiltrated with BMP-7, then implanted into the latissimus dorsi muscle and is transferred weeks later as a prefabricated free flap
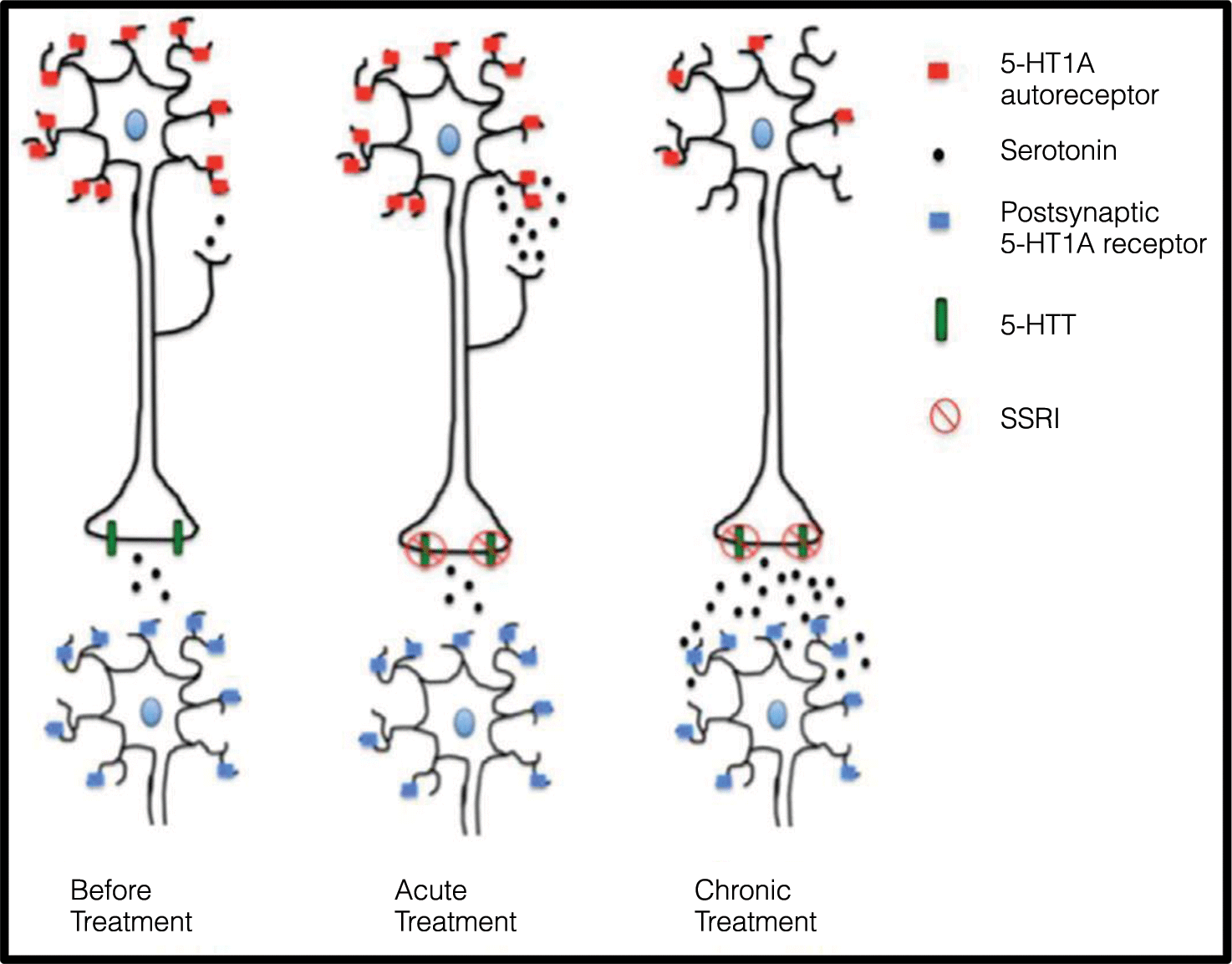
- Antidepressants have clinical utility for many psychiatric conditions, including major depressive disorder and anxiety disorders.
- Multiple classes of antidepressants are currently FDA-approved, including selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, tricyclic antidepressants, and antidepressants with multiple mechanisms of action.
- Adverse effects from antidepressants typically occur earlier than symptom resolution and may result in nonadherence.
- Patients should be counseled on the timeline of onset of therapeutic effects.
- Factors such as side effect profile, age, and past history of response guide the selection of antidepressants.
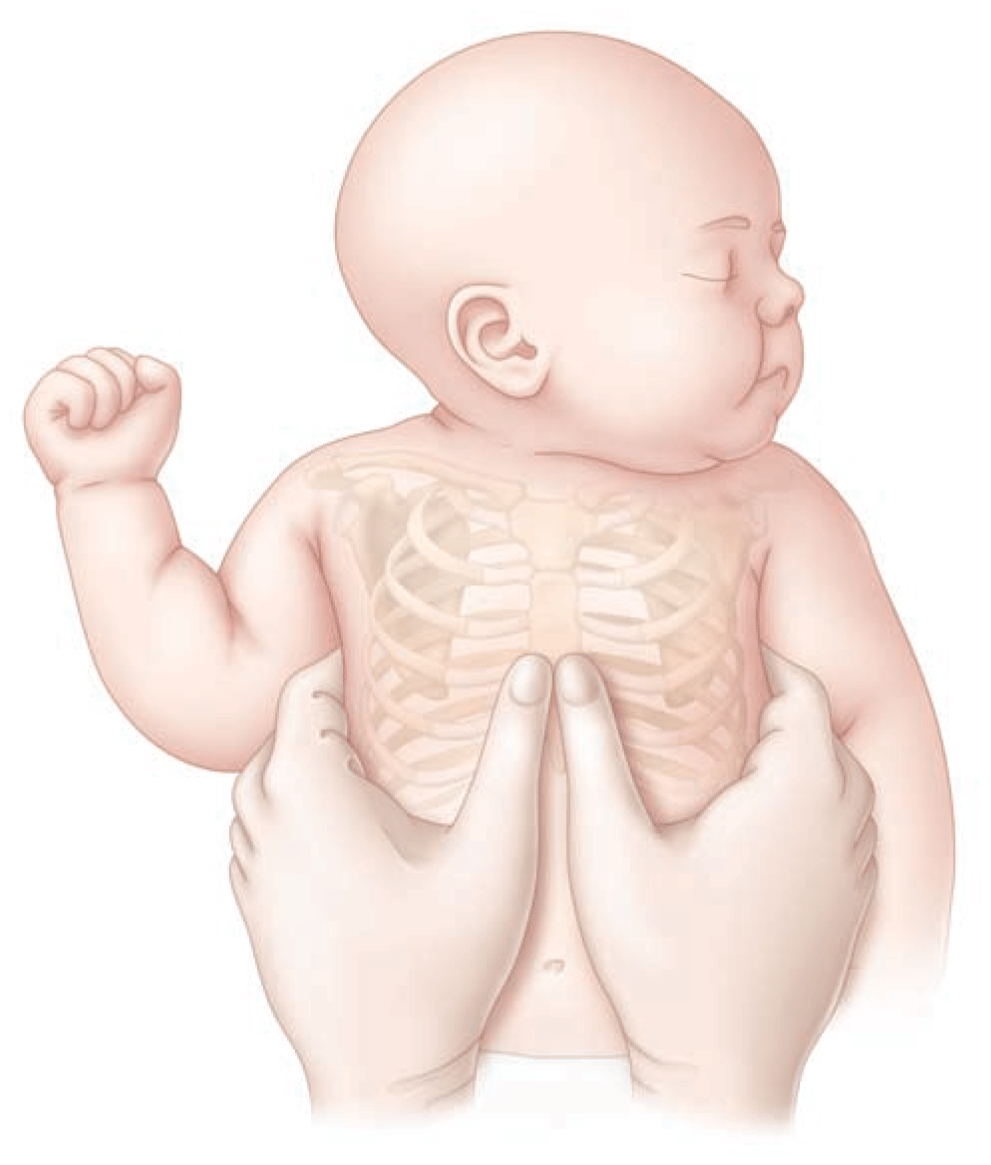
- Use of ECG monitoring to assess the neonate’s heart rate
- Use food grade plastic bag placed to level of neck to aid in keeping infant warm
- Initiating resuscitation with oxygen levels of 21-30% is recommended while high oxygen levels of 65-100% are not recommended
- Two thumb encircling hands technique is recommended over lower 1/3 of sternum compressing at 1/3 of the A-P diameter
- Routine intubation and suctioning is no longer recommended for all cases of meconium
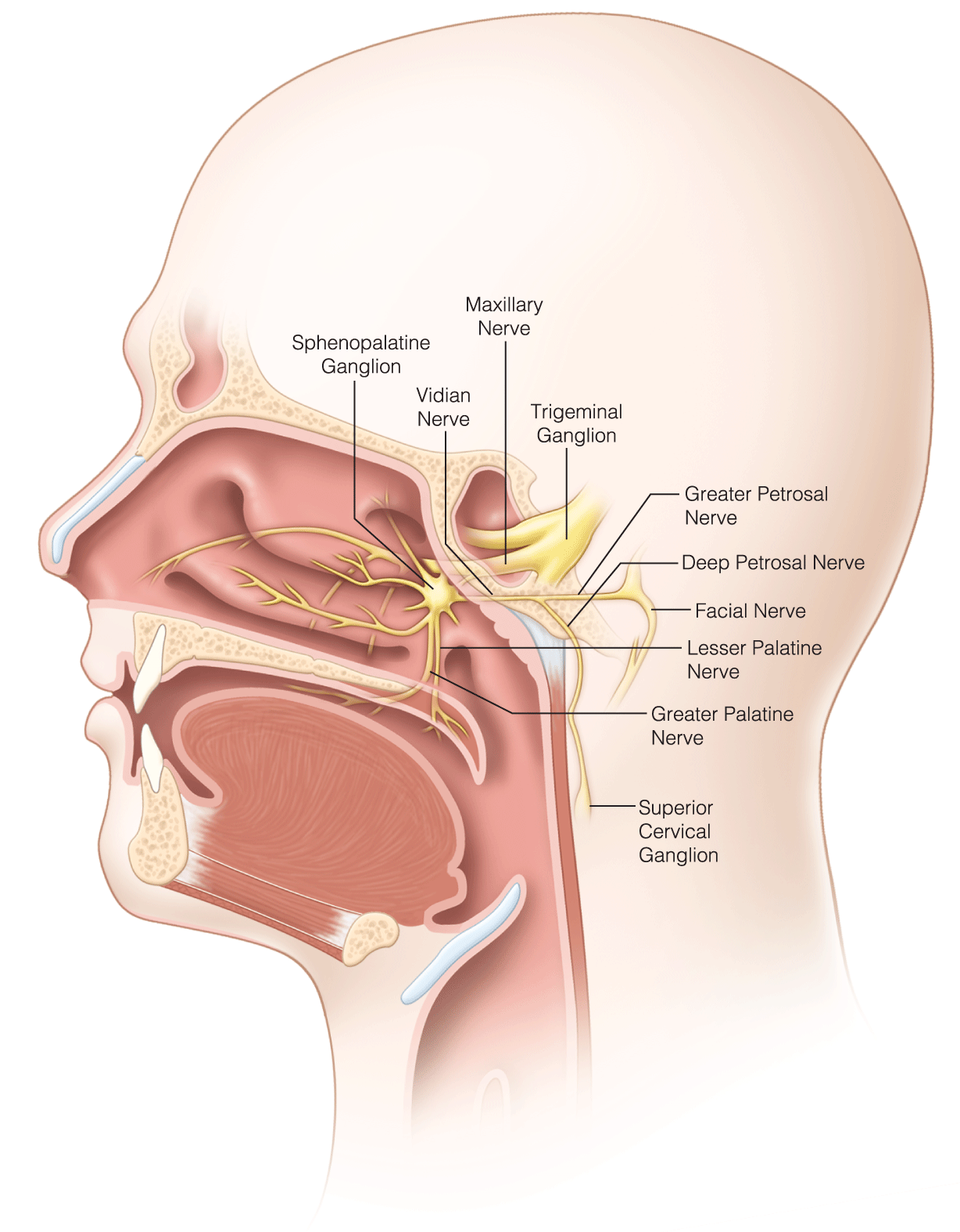
Nerve Blocks and Neurostimulation in the Treatment of Migraine
- Peripheral nerve and sphenopalatine ganglion blocks are a safe, effective treatment option for headache disorders, including migraine, although the evidence remains mixed for chronic migraine prophylaxis.
- Neurostimulation has emerged as an effective treatment modality for migraine, with both noninvasive and minimally invasive options available.
- Safe, effective, and noninvasive neurostimulation therapies available for migraine include transcutaneous supraorbital nerve stimulation for prophylaxis and single-pulse transcranial magnetic stimulation for the acute treatment of migraine with aura.
- Occipital nerve stimulation may be effective for some patients with intractable chronic migraine, although the evidence is mixed and procedure-related complications are common.
- Noninvasive vagus nerve stimulation and implanted sphenopalatine ganglion stimulation are emerging treatment options that may be useful for both acute and prophylactic treatment of episodic and chronic migraine.


Nerve Blocks and Neurostimulation in the Treatment of Migraine
- Peripheral nerve and sphenopalatine ganglion blocks are a safe, effective treatment option for headache disorders, including migraine, although the evidence remains mixed for chronic migraine prophylaxis.
- Neurostimulation has emerged as an effective treatment modality for migraine, with both noninvasive and minimally invasive options available.
- Safe, effective, and noninvasive neurostimulation therapies available for migraine include transcutaneous supraorbital nerve stimulation for prophylaxis and single-pulse transcranial magnetic stimulation for the acute treatment of migraine with aura.
- Occipital nerve stimulation may be effective for some patients with intractable chronic migraine, although the evidence is mixed and procedure-related complications are common.
- Noninvasive vagus nerve stimulation and implanted sphenopalatine ganglion stimulation are emerging treatment options that may be useful for both acute and prophylactic treatment of episodic and chronic migraine.


.png)






