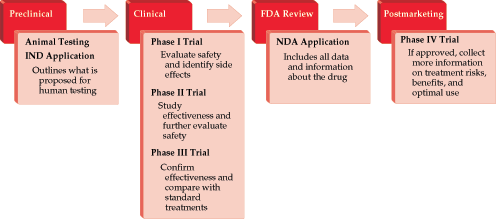
Clinical Trial Design and Statistics
- Because of the complex nature of clinical trial design, significant resources and infrastructure are invested in drug development. Many drugs fail to progress beyond the phase I/II stage, and many phase III trials take years to accrue and publish results, leading to a delay in Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval for diseases that desperately need better therapeutic options. The relatively recent FDA Safety and Innovation Act has allowed for the creation of priority and expedited review for drugs and biologics in serious conditions and where there is an unmet medical need. The designation of fast-track or breakthrough therapy may be granted when there is preclinical or clinical evidence to suggest that the intervention may result in a substantial improvement over currently available therapies.
- Prior to embarking on a clinical trial, data entry, editing (“cleaning”), and analysis should be anticipated. Planning for data management begins with developing rules for coding the variables for computer entry. The appropriate hardware and software programs should be selected and standardized across study sites.
- A type I error (false positive) occurs if an investigator rejects a null hypothesis that is true in the population. A type II error (false negative) occurs if the investigator fails to reject a null hypothesis that is false in the population. Neither of these errors can be avoided entirely.



.png)






